Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Market Trends, Growth Drivers, and Industry Forecast by 2034
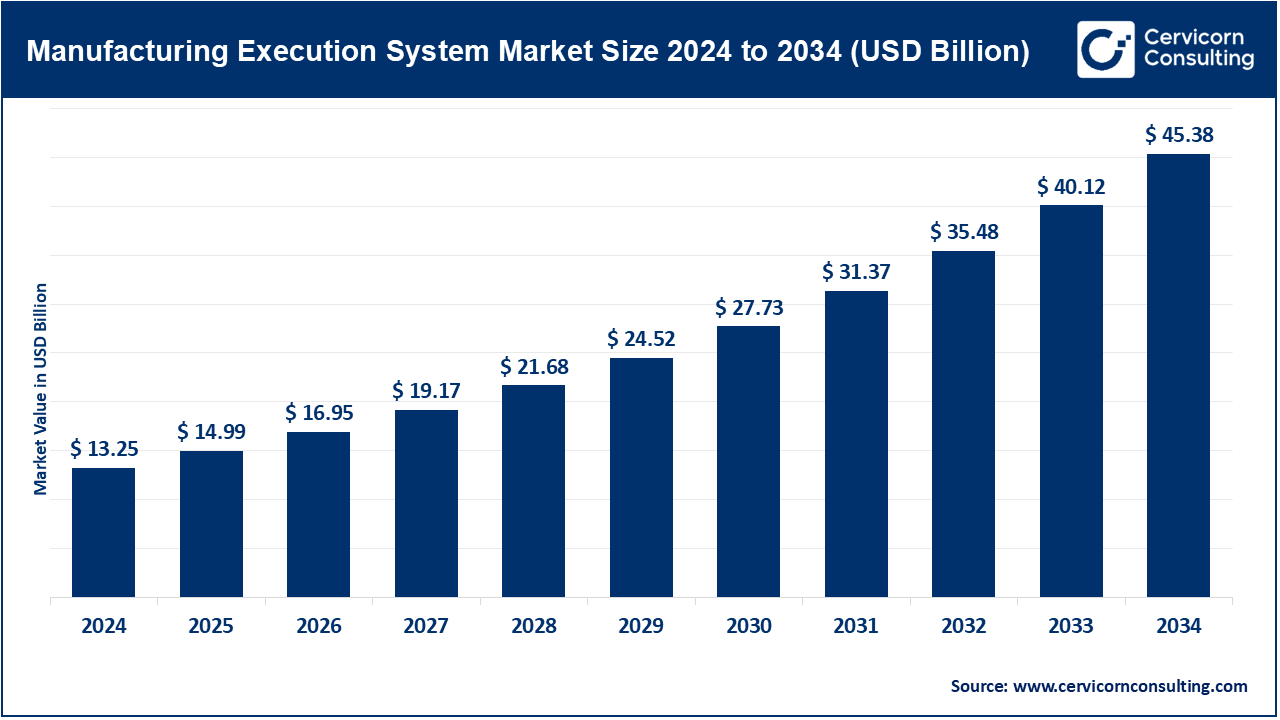
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Market Size & Projections
What is the Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Market?
The MES market is the business ecosystem for software and services that provide shop-floor execution capabilities: work order execution, resource and material tracking, batch and recipe management, electronic batch/device history records, quality management, operator guidance, OEE and downtime capture, traceability, and regulatory reporting. MES products may be sold as stand-alone systems, as modules inside broader Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) suites, or as capabilities embedded inside process control and ERP/cloud manufacturing products. MES sits between control/PLC systems and enterprise systems (ERP/PLM/QMS) and has become a critical element of digitized manufacturing stacks. Siemens Opcenter, Emerson’s DeltaV/Syncade offerings, ABB Ability MOM, Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing (MES capabilities), and GE’s digital solutions are among the best-known offerings.
Why is MES Important?
MES is important for three tightly connected reasons:
- Operational control & speed — MES turns plans into actions and enforces process steps (operator instructions, set points, recipes) so production runs predictably and safely.
- Quality & compliance — electronic batch records, traceability, automated quality checks, and audit trails reduce recalls and speed regulatory approvals (especially critical in pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and medical devices).
- Data-driven improvement — MES is the canonical source of real-time production data (OEE, yields, scrap, cycle times). When combined with analytics/AI it enables predictive maintenance, bottleneck elimination, and faster new-product ramp-ups.
These capabilities deliver measurable KPIs: higher throughput, lower scrap, faster changeovers, improved on-time delivery, and auditable compliance.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2695
Growth Factors
Demand for MES is being driven by manufacturers’ push to digitalize operations (Industry 4.0/Smart Factory programs), the growth of mixed-mode and high-mix manufacturing (which increases the need for flexible execution and traceability), stricter regulatory and sustainability reporting requirements (which push companies to capture electronic records and emissions/energy data), the proliferation of IIoT sensors and edge devices (which make shop-floor data cheap and actionable), and rising adoption of cloud, SaaS, and subscription models that lower entry costs for MES (enabling SMEs to adopt capabilities previously only available to large enterprises). Add to this supplier consolidation and M&A (which expands vendor portfolios), increasing demand for integrated quality and operations (closed-loop quality), and the application of AI/advanced analytics to shop-floor data — together these create a multi-year, compound growth runway for MES vendors and integrators across process and discrete industries. Market research estimates and vendor roadmaps show continued double-digit CAGR in many forecasts.
Top Companies — Profiles
Below are concise, practical profiles of five leading vendors (Emerson, General Electric, Oracle, Siemens, ABB). Each profile includes specialization, key focus areas, notable product features, company-level 2024 revenue, and global presence notes.
Emerson Electric Co.
Specialization: Process automation, life sciences MES, and plant operations (DeltaV, Syncade).
Key focus areas: Life sciences/batch manufacturing, electronic batch records, operator guidance, equipment management, and lifecycle services; integration of MES with DeltaV control systems.
Notable features: Deep integration with Emerson control systems and strong offerings for batch/continuous process industries.
2024 revenue (company-level): ~USD 17.49 billion.
General Electric (GE)
Specialization: Industrial software historically embedded in GE Digital, now distributed across GE Aerospace, GE Vernova, and GE Healthcare post-restructuring.
Key focus areas: Asset performance management, industrial analytics, and sector-specific manufacturing support (aerospace MRO, energy equipment manufacturing).
2024 revenue (company-level): GE Aerospace: $38.7B; GE Vernova: ~$34.9B; GE Healthcare: ~$5.3B.
Oracle Corporation
Specialization: Cloud manufacturing and ERP-native MES capabilities (Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing).
Key focus areas: Cloud-native manufacturing execution, unified ERP+MES stack, closed-loop quality, traceability, SaaS delivery.
2024 revenue (company-level): $53.0 billion.
Siemens AG
Specialization: Broad discrete and process MES (Opcenter portfolio), MOM, PLM, and automation integration.
Key focus areas: Semiconductor, electronics, medical devices, automotive, CPG, and pharma.
2024 revenue (company-level): €75.9 billion.
ABB Ltd.
Specialization: ABB Ability™ MOM and MES capabilities; strong in electrification, robotics, and automation.
Key focus areas: Connected worker apps, production orchestration, integration with ABB automation and robotics.
2024 revenue (company-level): $32.9 billion.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
- Cloud & SaaS MES: Speeds deployment, lowers cost, enables multi-site rollout.
- Edge-to-Cloud & IIoT: Richer data, better OEE, faster anomaly detection.
- Embedded AI & Analytics: From descriptive to prescriptive MES; reduces scrap, improves yield.
- Industry-Specific Templates: Reduces customization, speeds ROI.
- Digital Thread Integration: Seamless flow from design to execution; faster new product introductions.
- Connected Worker Solutions: Mobile guidance, AR, and SOP digitization; reduces errors.
- Sustainability Integration: Tracks energy, water, and emissions; supports compliance.
Successful MES Examples Around the World
- Siemens Opcenter in Semiconductor/Electronics: Reduced lead times, lowered WIP, improved first-pass yield.
- Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing: Consolidated MES and ERP in the cloud for faster analytics and integration.
- Emerson Syncade in Life Sciences: Automated batch records, improved compliance, and accelerated product release.
- ABB Ability MOM in Pulp & Paper: Optimized throughput and decision-making in continuous manufacturing.
- Cloud MES Providers: Rapid ROI, improved OEE, and accelerated multi-site rollout.
Global Regional Analysis — Government Initiatives & Policies
Europe (Germany/EU): Industry 4.0 programmes and EU digital transition strategies promote MES adoption with funding, standards, and public-private cooperation.
China: National industrial upgrade policies drive heavy investment in smart manufacturing and MES, supporting large-scale adoption.
India: Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes and Make-in-India initiatives encourage MES adoption in electronics, pharma, and automotive sectors.
United States: Manufacturing USA programmes, semiconductor onshoring support, and tax incentives promote MES in high-value manufacturing.
Rest of APAC: Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia push MES through industry-led digitalisation and smart factory pilots.
Latin America & Middle East/Africa: Adoption grows alongside high-value manufacturing projects, supported by vendor–integrator partnerships.
Vendor Selection Checklist (Practical Notes)
- Prefer vendors with industry-specific templates for your vertical (pharma, semiconductor, food, discrete assembly).
- Validate PLC/SCADA integration and data-model compatibility before piloting.
- Start with a phased rollout: focus on high-impact lines, measure OEE and defect-rate improvements, then scale.
- Clarify cloud vs on-prem deployment, data residency and validation (especially for regulated industries).
- Plan for change management: MES projects succeed or fail largely on process discipline and operator adoption.
- Consider vendors’ services ecosystem and local integrator partners for faster go-live and sustained support.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Active Electronic Components Market to Hit USD 639.52 Bn by 2034