Long Duration Energy Storage Market Soars to USD 652.15 Bn by 2034
Long Duration Energy Storage Market Growth
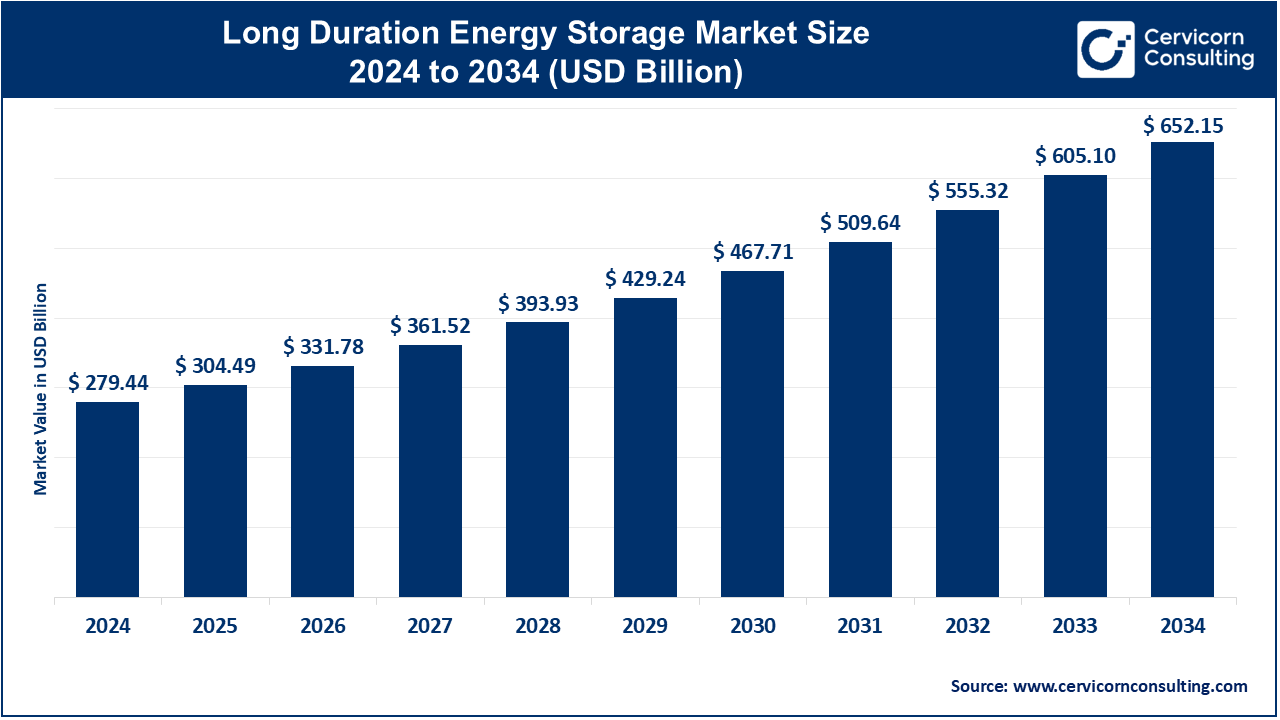
The long duration energy storage market is projected to grow substantially, it is estimated to reach USD 652.15 billion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.84% from its current valuation of USD 279.44 billion in 2024.
What are the emerging trends in the long duration energy storage market?
Technological Diversification
- Emerging Technologies: Companies are actively diversifying beyond traditional technologies like pumped hydro and lithium-ion batteries. Innovative solutions such as liquid air energy storage (LAES), gravity-based systems, and redox flow batteries are gaining momentum due to their unique advantages in scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
- GWh-Scale Deployments: There is increasing focus on deploying GWh-scale mechanical energy storage systems by 2030, with estimates suggesting that the global market for long-duration storage could exceed 1,000 GWh by that time. This shift underscores the growing demand for solutions capable of handling high-capacity energy requirements.
Cost Reduction Initiatives
- Government Support: Programs such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Earthshot aim to make long-duration energy storage (LDES) cost-competitive by 2030, targeting a 90% reduction in costs for systems that can store energy for 10 hours or more. This initiative is expected to catalyze market adoption and innovation.
- Falling Prices: Energy storage costs are dropping globally, with regions like China leading the charge. Recently, the cost of two-hour storage systems in China fell by 43%, reflecting economies of scale and technological advancements. Projections indicate a similar trend for LDES, where system costs could fall by an additional 30-40% by 2030 as production scales and technologies mature.’
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2455
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
- Support for VRE Penetration: LDES technologies are increasingly critical for integrating variable renewable energy (VRE) sources like solar and wind into power grids. Analysts project that VRE penetration in global energy grids could reach 60-70% by 2050, further driving the need for LDES to ensure grid stability and reliability.
- Energy Arbitrage Opportunities: By enabling energy storage when prices are low and discharging during peak demand periods, LDES systems optimize both grid operations and economic returns. In 2023, energy arbitrage contributed to a 15% increase in revenue for early LDES adopters in markets with high renewable penetration.
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks
- Incentives for Adoption: Governments worldwide are implementing incentives and regulatory measures to accelerate LDES adoption. For instance, the European Union’s Green Deal includes provisions for funding LDES projects, with an estimated €50 billion earmarked for energy storage investments by 2030.
- Focus on Grid Modernization: Efforts to modernize electrical grids include integrating advanced LDES systems to enhance reliability and flexibility. North America alone plans to invest over $100 billion in grid modernization by 2035, which includes significant allocations for energy storage solutions.
Hybrid Energy Storage Systems
- Combining Technologies: Hybrid energy storage systems, which pair short-duration technologies like lithium-ion batteries with long-duration solutions, are gaining traction. These systems address diverse energy demands, from handling short-term fluctuations to providing multi-day backup. By 2030, hybrid systems are projected to account for over 25% of global LDES installations, driven by their superior efficiency and adaptability.
What strategies are leading companies in the long duration energy storage market using to expand their operations?
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
- Hydrostor’s Acquisition
- Details: Hydrostor’s acquisition of the remaining 50% interest in the Silver City Energy Storage Centre demonstrates its commitment to consolidating its project portfolio. This move allows Hydrostor to have complete operational and strategic control, enhancing its ability to efficiently manage and implement the project’s capabilities.
- Significance: Such acquisitions help streamline decision-making, reduce risks associated with joint ventures, and enable better alignment with long-term business goals in the LDES sector.
- Collaborative Ventures
- Details: Partnerships, like those between Fluence Energy and Energy Vault, showcase a collaborative approach where companies pool their unique expertise. Fluence brings its experience in battery-based storage systems, while Energy Vault focuses on gravity-based solutions.
- Significance: These collaborations enable innovation through shared resources, access to diverse technologies, and the creation of more robust and scalable energy storage systems, meeting a wide array of market demands.
Technological Innovation and R&D Investment
- Investment in New Technologies
- Details: Form Energy is leading the way with its iron-air battery technology, which promises extended storage durations at a fraction of the cost compared to lithium-ion batteries. The technology supports a more consistent energy supply from renewable sources, addressing variability issues.
- Significance: By investing in groundbreaking technologies, companies ensure they stay ahead in the competitive LDES market and contribute to the overall reduction of energy costs.
- Exploration of Diverse Technologies
- Details: Companies are not limiting themselves to one type of storage technology. Innovations include gravity storage systems that use potential energy, CO2 batteries that utilize carbon dioxide as a working fluid, and advanced compressed air systems for energy storage.
- Significance: Exploring diverse technologies allows companies to cater to different geographic and market-specific energy needs, while also mitigating risks associated with over-reliance on a single technology.
Market Development Initiatives
- Pilot Projects
- Details: Pilot projects by companies like NTPC are critical for testing the feasibility and performance of LDES technologies under real-world conditions. These projects allow companies to gather data, refine technologies, and build confidence among stakeholders.
- Significance: Successful pilot projects serve as proof-of-concept and pave the way for scaling up operations, thereby accelerating the commercialization of innovative storage solutions.
- Government Engagement
- Details: Companies are actively engaging with governments to advocate for supportive policies and incentives. For example, Arizona’s initiatives for longer-duration storage technologies help attract investments and encourage broader adoption.
- Significance: Policy support ensures a favorable environment for deploying LDES systems, enabling companies to overcome financial and regulatory barriers.
Focus on Sustainability and Decarbonization
- Aligning with Environmental Goals
- Details: LDES is being marketed as a solution to integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the power grid, addressing their intermittent nature. This aligns with global decarbonization targets set by organizations and governments worldwide.
- Significance: Positioning LDES as a sustainability enabler attracts environmentally conscious investors and establishes companies as leaders in the transition to clean energy.
- Targeting Emerging Markets
- Details: Regions such as the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries, with high solar and wind energy potential, are emerging as key markets for LDES technologies. Deploying these systems here ensures a reliable energy supply while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Significance: Expanding into emerging markets allows companies to tap into new revenue streams while contributing to global renewable energy adoption.