Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034
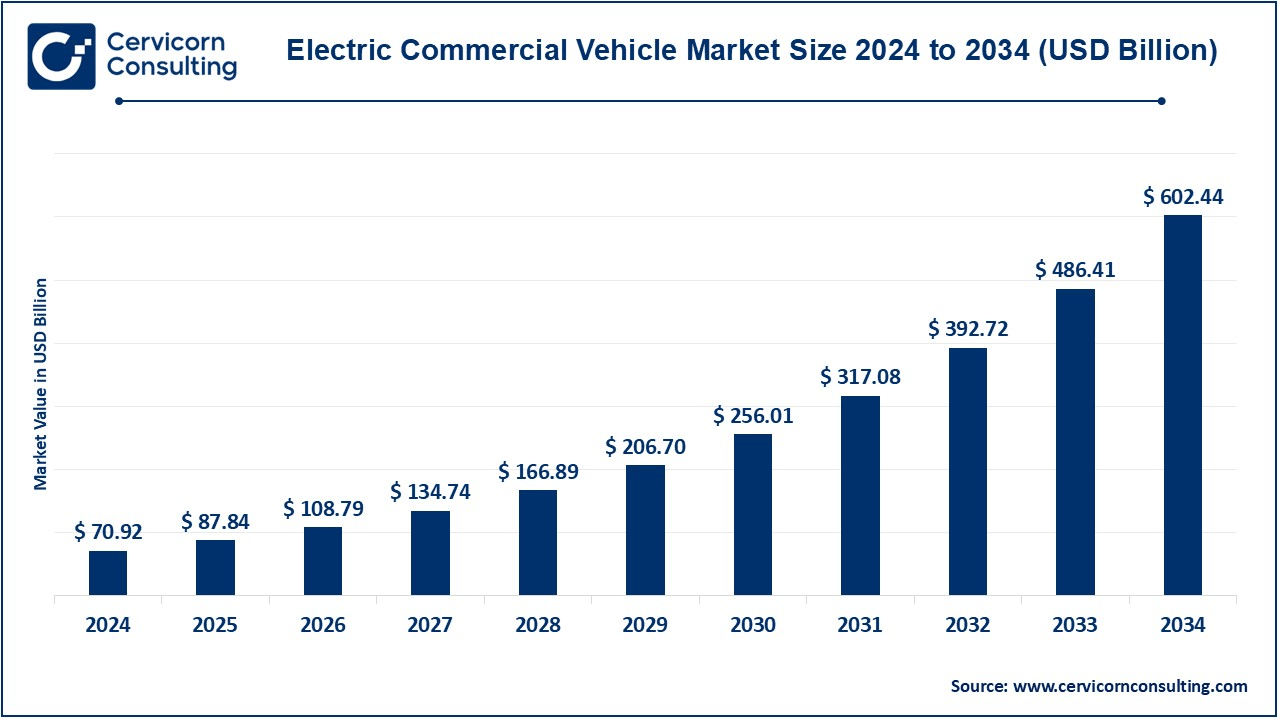
Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Size
Electric commercial vehicle market — Growth Factors
Growth in the electric commercial vehicle market is being driven by falling battery and fuel-cell costs, stricter urban and national emissions targets, generous fiscal incentives and procurement programs for zero-emission fleets, improving charging/refueling infrastructure, the rising economics of electrified total cost of ownership (especially in high-utilization fleets), rapid product launches by incumbent OEMs and new entrants, and growing corporate sustainability commitments from large shippers and municipal transit agencies; together these forces reduce purchase barriers for fleets, accelerate scale-up of energy and vehicle ecosystems, and create stronger demand signals for manufacturers and infrastructure providers.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2574
What is the electric commercial vehicle market?
The electric commercial vehicle market covers manufacturing, sales, services, and ecosystem products for electrically powered commercial vehicles: battery electrics (BEVs), plug-in hybrid commercial models (PHEVs), and hydrogen fuel-cell commercial vehicles (FCEVs). It includes OEMs that design and build chassis and complete vehicles, powertrain and battery suppliers, charging and hydrogen refueling infrastructure providers, telematics and fleet-management software providers, and aftermarket service networks. Use cases span urban buses, refuse trucks, last-mile delivery vans, medium-duty box trucks, regional distribution trucks and long-haul tractors (the latter currently more nascent). Market sizing depends on whether one counts just vehicle hardware, or also charging infrastructure and services; major analysts report mid-to-high-double digit CAGR expectations for the decade ahead.
Why it matters
Commercial vehicles punch above their weight in emissions and urban impacts: fleets operate high mileage, so switching to zero-emission drivetrains can deliver outsized reductions in CO₂ and air pollutants per vehicle. Electrification lowers operating noise, reduces fuel costs (especially when electricity/hydrogen prices are favorable), and simplifies maintenance by removing many moving parts found in ICE drivetrains. For cities and corporates pursuing climate and air-quality targets, electrifying buses and delivery fleets is a fast, visible lever with measurable benefits. Finally, electrification reshapes logistics economics, energy demand profiles and opportunities for vehicle-to-grid services, generating new business models for fleet operators, utilities and mobility providers.
Top companies — profiles, focus areas and 2024 figures
Volvo Group (AB Volvo)
- Specialization: Heavy trucks, buses, construction equipment; strong focus on electrified heavy-duty platforms and integrated fleet services.
- Key focus areas: Battery electric trucks and buses, hybrid drivetrains for city buses, telematics and service contracts, charging ecosystem partnerships.
- Notable features: Legacy OEM with global dealer and service network, recent multi-model BEV bus/truck launches, and a strong emphasis on lifecycle services.
- 2024 revenue / performance: Volvo Group reported currency-adjusted net sales of roughly SEK 526.8–527 billion in 2024. The company continues to ramp BEV production while balancing cyclical demand for conventional vehicles.
Daimler Truck (formerly part of Daimler AG)
- Specialization: Heavy and medium-duty trucks, buses (Mercedes-Benz Trucks; Freightliner in North America).
- Key focus areas: Battery-electric trucks for regional and urban applications, fuel-cell systems for longer range, integration of digital fleet solutions.
- Notable features: Large scale production capability, strong dealer footprints (especially NA and Europe), and a public commitment to broad BEV model ranges.
- 2024 revenue / performance: Daimler Truck Group reported group revenue ≈ €54.1 billion for 2024; unit sales of battery-electric trucks and buses rose significantly year-on-year (units of BEV trucks/buses increased by double digits).
Traton Group (Volkswagen family + MAN, Scania)
- Specialization: Heavy-duty and medium-duty trucks, buses — Scania and MAN under the Traton umbrella.
- Key focus areas: Electrification of core truck lines (BEV and e-axle tech), modular vehicle platforms, and commercial services via financial and fleet solutions.
- Notable features: Strong European and Latin American presence via established brands; focus on scalable e-platforms for varied transport tasks.
- 2024 revenue / performance: Traton Group recorded sales revenue of about €47.5 billion in 2024. The group continued to expand e-truck and e-bus offerings across regions.
BYD (Build Your Dreams)
- Specialization: Broad manufacturer: passenger EVs, electric buses, trucks, and power electronics; vertical integration across batteries and drivetrains.
- Key focus areas: Mass market electric buses and commercial vehicles, integrated battery manufacturing, and rapid overseas expansion.
- Notable features: One of the world’s highest volume EV manufacturers; strong position in electric buses and growing presence in commercial trucks/van segments.
- 2024 revenue / performance: BYD reported revenue of ~777.1 billion yuan in 2024 and sold roughly 4.27 million vehicles worldwide, reflecting rapid scale and profitability improvements. BYD’s export footprint grew in 2024 as it expanded into Europe and other markets.
Nikola Corporation
- Specialization: Hydrogen fuel-cell and battery electric heavy-duty trucks for long haul and regional freight, and hydrogen refueling ecosystem development partnerships.
- Key focus areas: Commercial hydrogen fuel-cell trucks (FCEVs), BEV tractors, and building dealer and service capabilities for fleet customers.
- Notable features: Early mover in hydrogen tractor commercialization with pilot fleet deployments; smaller scale revenue but accelerating deliveries of FCEVs in 2024.
- 2024 revenue / performance: Nikola’s 2024 reported quarters show modest revenues relative to incumbents; Q2 2024 revenue was reported at ~$31.3M with increasing wholesale deliveries of hydrogen FCEVs through 2024 (dozens to low hundreds of units across quarters). Nikola is still ramping commercial production.
Notes on “market share”: because the electric commercial vehicle market is fragmented by vehicle class (buses vs light commercial vans vs medium/heavy trucks) and by geography, deriving a single global market share per company is misleading. Incumbent truck OEMs (Volvo, Daimler, Traton) dominate heavy-duty markets in Europe and North America by legacy footprint, BYD dominates high-volume electric bus and light commercial segments globally (especially China), while Nikola occupies a small but strategic niche in hydrogen FCEVs in North America. Market share figures therefore should be read per segment and region.
Leading trends and their impact
- Electrified total cost of ownership (TCO) economics: High-mileage fleets (delivery, transit, waste collection) see faster payback from fuel and maintenance savings — this pushes EV adoption where utilization is high. Impact: Accelerated electrification of last-mile and transit fleets first; long-haul remains harder without hydrogen or ultra-fast charging scale.
- Policy and procurement programs: Governments are using procurement rules, grants and tax credits to force or incentivize fleet electrification (urban zero-emission zones, bus replacement grants, tax credits for clean commercial vehicles). Impact: Predictable demand pipelines for OEMs and financing support for fleet purchasers.
- Diverse powertrain strategies (battery + hydrogen): BEVs are accelerating in urban/regional routes; hydrogen FCEVs are being trialed for long-range heavy trucking. Impact: OEMs and fleets are hedging with both technologies while infrastructure builds out.
- Vertical integration and battery manufacturing: BYD’s control of battery and cell production shortens supply chains and reduces costs. Impact: Cost advantage and faster scale for companies with integrated battery capabilities, pressuring others to secure cell supply or partnerships.
- Digitalization and fleet telematics: Software for route optimization, charge scheduling and energy management improves uptime and TCO. Impact: New recurring-revenue business models (software + services) for OEMs and outsourcers.
Successful examples around the world
- China — BYD buses & delivery vans: Large-scale municipal bus electrification and massive volume production of e-buses and light commercial vehicles made China the leading global market for electric buses and light e-CVs. BYD has supplied thousands of buses and is exporting at scale.
- Europe — City bus electrification & zero-emission zones: Multiple European cities have replaced diesel bus fleets with BEVs or hybrids and implemented low-emission zones that accelerate municipal adoption. OEMs such as Volvo and Traton brands (Scania, MAN) are supplying e-buses and e-trucks.
- North America — Fleet pilots and procurement programs: Large parcel and grocery fleets are piloting electric delivery vans and trucks; federal and state incentives (plus programs like NEVI) support charging infrastructure needed for commercial fleets. Daimler Truck and Nikola have been active with product launches and pilot deployments.
- Public transit success stories: Cities replacing entire bus depots with electric fleets (often with government grant co-funding) show the environmental, acoustic and operational benefits in everyday operations. These projects are often bundled with depot charging installations and grid coordination.
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives and policies shaping the market
North America
The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and associated tax credits for clean vehicles and infrastructure support commercial electrification; federal programs (NEVI and discretionary grants) fund charging corridors and depot charging. States and municipalities add further incentives and procurement programs. This creates strong financial incentives and infrastructure grants that spur fleet electrification pilots and larger procurements in transit and last-mile sectors. OEMs scale product availability for NA markets.
Europe
EU directives and national incentives (plus city-level low-emission zones and public procurement rules) encourage zero-emission buses and urban delivery trucks. ACEA and member states publish guidance and tax benefit maps for ZEV acquisition and charging investment. Europe sees rapid electrification of buses, increasing launches of e-truck models tailored to regional regulations and city operations, and greater collaboration between utilities and municipalities on depot charging.
China & Asia Pacific
China offers direct subsidies (phased over time), strong industrial policy support for EV production, mandated fleet electrification targets at municipal levels, and an abundant manufacturing ecosystem for batteries and components. As a result, China leads in scale for electric buses and light commercial BEVs; Chinese OEMs like BYD deploy globally. Battery and component cost reductions originating in China reduce global BEV costs.
Latin America, Middle East & Africa
Policy support is less uniform — some early adopters (major cities and transit authorities) receive international finance for bus fleet upgrades; incentives are emerging, often supported by multilateral funding for low-carbon public transport. Adoption is incremental and often dependent on donor financing or municipal budgets; pilots commonly target buses and municipal fleets. International OEMs supply turnkey depot + vehicle packages for early projects.
How policy + market dynamics interplay
The market is policy-sensitive: direct purchase incentives, tax credits, public procurement and infrastructure funding create the “pull” fleets need to adopt e-CVs. At the same time, sustained cost declines in batteries and increased model availability from established OEMs (Volvo, Daimler, Traton) and high-volume specialists (BYD) create the “push” from the supply side. Smaller, specialized players (e.g., Nikola in hydrogen FCEVs) target niches where batteries are less practical today, while software and charging service providers build the operational tools fleets need to realize TCO advantages.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Pharmaceutical Packaging Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034