Chemical Decarbonization Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035
Chemical Decarbonization Market Size
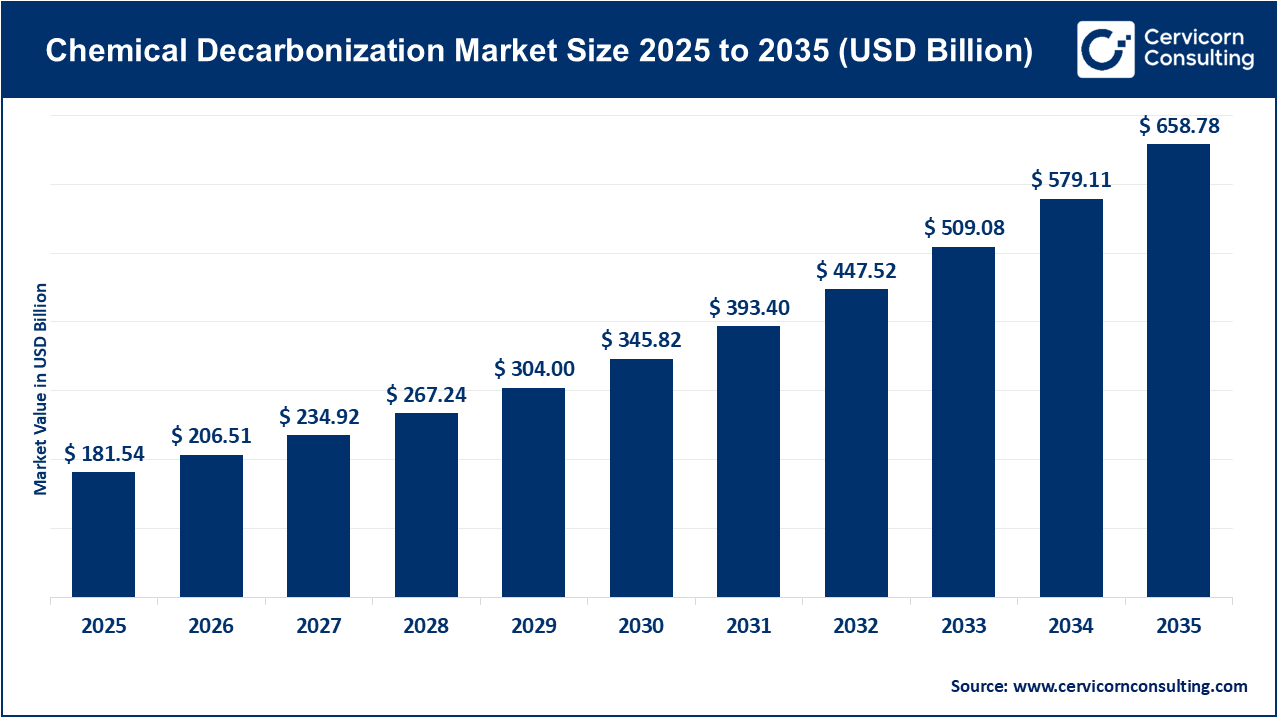
The global chemical decarbonization market size was worth USD 181.54 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 658.78 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.8% from 2026 to 2035.
Overview: What Is the Chemical Decarbonization Market?
The chemical decarbonization market encompasses technologies, solutions, and services designed to significantly reduce or eliminate carbon emissions from chemical production processes and chemical-dependent industries. It includes carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS); low-carbon and green hydrogen production; electrochemical and electrified manufacturing processes; bio-based and recycled feedstocks; sustainable fuels; advanced catalysts; membranes; and system integration services. This market serves some of the world’s most emission-intensive industries—such as chemicals, petrochemicals, cement, steel, refining, fertilizers, and fuels—helping them transition from fossil-based processes to low-emission or net-zero pathways while maintaining industrial competitiveness and output.
Chemical decarbonization goes beyond emission reduction at individual plants. It supports the development of circular carbon economies where captured carbon dioxide is reused as a feedstock for fuels, polymers, and specialty chemicals, creating new value chains and business models. The market includes technology developers, engineering firms, industrial manufacturers, utilities, governments, and financial institutions working together to scale solutions from pilot to commercial deployment.
Chemical Decarbonization Market Growth Factors
The growth of the chemical decarbonization market is driven by increasingly stringent climate regulations, national net-zero commitments, carbon pricing mechanisms, and rising corporate sustainability targets across heavy industries. Rapid cost declines in renewable electricity, growing availability of green hydrogen, advancements in electrochemical and catalytic technologies, and improved efficiency of carbon capture systems are accelerating adoption. Government incentives, tax credits, grants, and industrial transition programs are reducing financial risk for large-scale projects, while growing demand for low-carbon chemicals, fuels, and materials from sectors such as aviation, shipping, automotive, and consumer goods is creating strong market pull. In parallel, increased private equity, venture capital, and infrastructure investment are enabling faster commercialization, helping chemical decarbonization move from experimental projects to scalable industrial solutions.
Why Is Chemical Decarbonization Important?
Chemical decarbonization is essential because the chemical and process industries account for a substantial share of global greenhouse gas emissions, many of which are “hard to abate.” Unlike emissions from electricity generation, chemical-sector emissions often come from both energy use and inherent process chemistry, making simple electrification insufficient. Without decarbonizing chemical production, global climate targets cannot be achieved.
Beyond emissions reduction, chemical decarbonization is critical for energy security, industrial resilience, and economic competitiveness. Low-carbon chemicals such as green hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, and synthetic fuels act as key enablers for decarbonizing transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing. Countries and companies that invest early gain technological leadership, supply-chain control, and access to emerging premium markets for sustainable products. Additionally, chemical decarbonization supports circular economy principles by transforming waste carbon into valuable products, reducing reliance on virgin fossil resources.
Company Profiles in the Chemical Decarbonization Market
Carbon Clean
- Specialization: Modular carbon capture technology for industrial emissions
- Key Focus Areas: Post-combustion carbon capture, steel and cement decarbonization, proprietary solvent systems, modular plant retrofits
- Notable Features: Known for compact, scalable carbon capture systems designed to reduce capital costs and installation timelines; strong presence in industrial pilot and commercial projects
- 2024 Revenue: Privately held; absolute revenue figures not publicly disclosed
- Market Share: Not publicly reported; recognized as a fast-growing specialist in industrial carbon capture
- Global Presence: Operations and projects across the UK, India, Europe, and other industrial regions
Aker Carbon Capture
- Specialization: Large-scale carbon capture solutions and project delivery
- Key Focus Areas: Engineering and construction of capture facilities, industrial retrofits, mobile testing units, integrated CCUS solutions
- Notable Features: Strong project backlog and extensive experience in industrial-scale carbon capture; strategic consolidation with global energy services players enhances execution capabilities
- 2024 Revenue: Reported strong revenue growth during 2024; full-year audited revenue available in corporate financial disclosures
- Market Share: Considered one of the leading established players in large-scale industrial carbon capture
- Global Presence: Strong footprint in Europe with expansion into North America and other international markets
LanzaTech
- Specialization: Biological carbon recycling using gas fermentation
- Key Focus Areas: Converting industrial waste gases into ethanol and chemicals, licensing fermentation technology, industrial partnerships
- Notable Features: Unique microbial technology that captures and converts carbon emissions into usable products; publicly listed company offering higher transparency
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 49.6 million
- Market Share: Leading pure-play provider in biological carbon utilization, particularly in gas fermentation
- Global Presence: Operations and commercial projects across the United States, India, and other international markets
Twelve
- Specialization: Electrochemical conversion of carbon dioxide into fuels and chemicals
- Key Focus Areas: Power-to-fuels technology, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), electrochemical reactor scale-up
- Notable Features: Secured significant project financing to develop commercial e-fuel facilities; strong airline and industrial offtake partnerships
- 2024 Revenue: Privately held; revenue figures not publicly disclosed, with emphasis on large-scale project funding
- Market Share: Emerging leader in electrochemical CO₂ conversion and e-fuels
- Global Presence: Based in the United States with global commercial partnerships
Dioxide Materials
- Specialization: Advanced materials for electrochemical CO₂ conversion
- Key Focus Areas: Anion exchange membranes, ionomers, CO₂ electrolyzer materials, catalyst-support systems
- Notable Features: Focuses on enabling technologies critical for durability and cost reduction in electrochemical decarbonization systems
- 2024 Revenue: Privately held; revenue not publicly disclosed
- Market Share: Niche but strategically important supplier to the electrochemical decarbonization ecosystem
- Global Presence: U.S.-based with international research and industrial customers
Leading Trends and Their Impact
One of the most significant trends in chemical decarbonization is the shift toward electrification and electrochemical manufacturing pathways. These processes use renewable electricity to replace fossil-fuel-driven thermal reactions, enabling near-zero-emission production of fuels and chemicals. Carbon capture and utilization is another major trend, transforming captured CO₂ into valuableusable products such as methanol, ethanol, synthetic fuels, and polymers, which improves project economics and encourages wider deployment of capture systems.
Modular carbon capture technologies are gaining traction, as they lower installation costs and allow faster retrofitting of existing plants. Policy-driven demand for low-carbon fuels—particularly in aviation and maritime sectors—is accelerating investment in e-fuels and sustainable chemicals. At the same time, vertical integration and long-term offtake agreements between technology developers and end users are reducing risk and accelerating commercial scale-up.
Successful Examples of Chemical Decarbonization Around the World
Several industrial-scale projects demonstrate the commercial viability of chemical decarbonization. In the steel sector, modular carbon capture systems have been successfully deployed to capture emissions from blast furnaces and reuse the CO₂ in downstream chemical processes. Biological carbon recycling plants have converted industrial waste gases into ethanol for fuel blending and chemical manufacturing, proving the scalability of fermentation-based solutions.
Electrochemical fuel production facilities, particularly those targeting sustainable aviation fuel, have secured significant financing and long-term purchase agreements, validating the market for low-carbon synthetic fuels. These examples show how technology innovation, policy support, and industrial collaboration can successfully reduce emissions while maintaining economic performance.
Global Regional Analysis: Government Initiatives and Policies Shaping the Market
North America
North America, particularly the United States, has emerged as a major hub for chemical decarbonization due to strong fiscal incentives, tax credits, and federal funding programs. These policies have significantly improved project economics for carbon capture, hydrogen production, and low-carbon fuels, encouraging large-scale industrial investment and accelerating commercialization.
Europe
The European Union is actively shaping the chemical decarbonization market through industrial climate policies, carbon pricing mechanisms, and strategic manufacturing initiatives. Regulations aimed at reducing industrial emissions, combined with financial support for clean technology deployment, are driving widespread adoption across chemicals, cement, and steel sectors.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific countries are rapidly expanding chemical decarbonization initiatives, driven by industrial growth and climate commitments. China is scaling carbon capture and utilization projects alongside emissions trading mechanisms, while India is investing in pilot projects and industrial collaborations focused on steel, chemicals, and power generation.
Emerging Markets
In emerging economies, chemical decarbonization is increasingly supported through public-private partnerships, international climate finance, and multilateral development programs. These regions represent significant long-term growth opportunities due to large industrial bases and rising demand for sustainable development solutions.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Nitrogenous Fertilizer Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035