Industrial Software Market Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034
Industrial Software Market Size
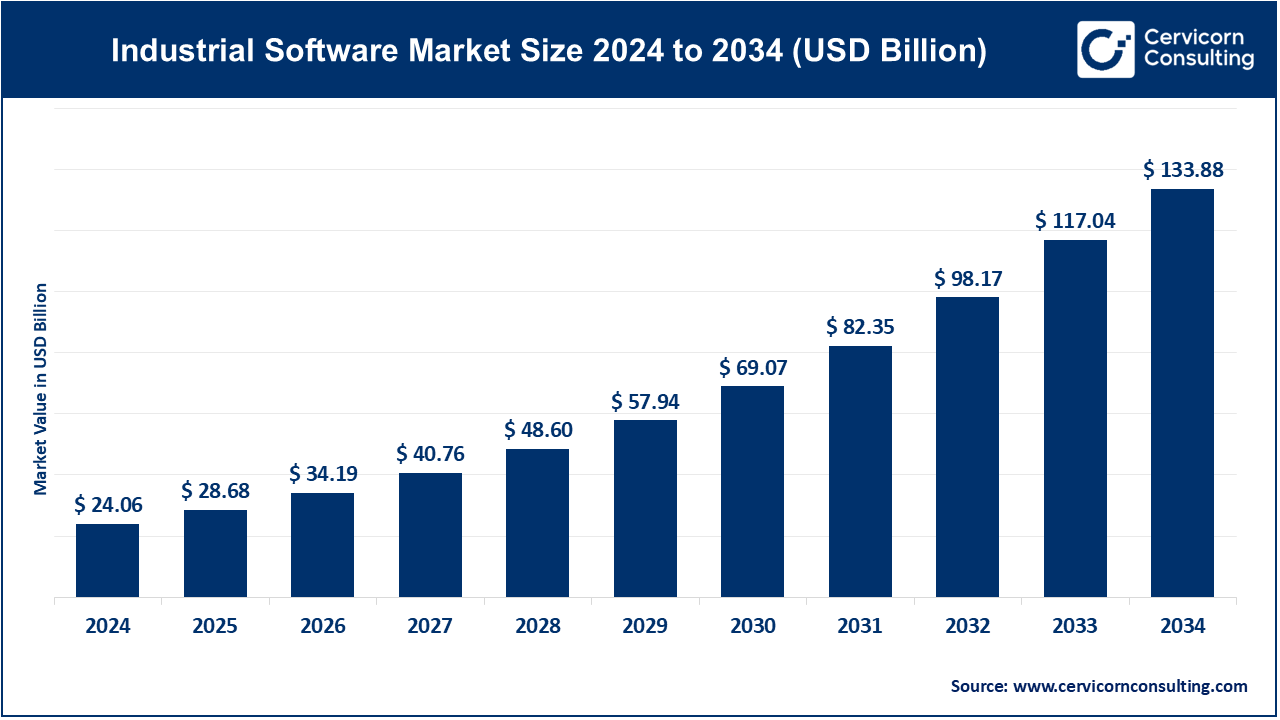
The global industrial software market size was worth USD 24.06 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 133.88 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.72% from 2025 to 2034.
Growth Factors
The industrial software market is experiencing strong growth due to a convergence of factors: the rapid digital transformation of manufacturing and process industries (Industry 4.0); widespread adoption of cloud, edge, and hybrid computing for scalable data analytics; increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for predictive maintenance and optimization; stricter regulatory and sustainability requirements demanding traceability and reporting; the growing need to integrate legacy operational technology (OT) with modern information technology (IT); heightened cybersecurity concerns; shorter product lifecycles demanding simulation and digital twin capabilities; and the expansion of connected ecosystems involving OEMs, system integrators, and software vendors. Together, these drivers are fueling double-digit growth and continuous innovation across the sector.
What Is the Industrial Software Market?
The industrial software market encompasses all software platforms designed specifically for industrial applications such as manufacturing, energy, utilities, chemicals, oil and gas, mining, and transportation. This includes systems like manufacturing execution systems (MES), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), product lifecycle management (PLM), distributed control systems (DCS), industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms, digital twin and simulation tools, and industrial cybersecurity and analytics software.
These solutions connect machines, sensors, and operators into a unified digital environment. They enable automation, monitoring, process optimization, and data-driven decision-making — bridging the gap between operational and enterprise systems. Essentially, industrial software transforms traditional plants and factories into smart, adaptive, and efficient ecosystems capable of real-time performance insights and rapid innovation.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2454
Why It Is Important
Industrial software is the cornerstone of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). It allows organizations to move from reactive operations to predictive and proactive management. By harnessing real-time data, industrial software reduces downtime, improves asset utilization, enhances quality control, and cuts operational costs. It also supports regulatory compliance and sustainability goals by enabling carbon tracking, resource optimization, and digital traceability. In an era of global competition and sustainability mandates, industrial software offers not only efficiency but also strategic advantage — turning physical assets into continuously improving, intelligent systems.
Industrial Software Market — Top Companies
Below is an overview of the leading companies shaping the industrial software landscape, focusing on their specialization, key focus areas, notable features, 2024 revenues, estimated market share, and global presence.
| Company | Specialization | Key Focus Areas | Notable Features | 2024 Revenue | Market Share (Industrial Software) | Global Presence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rockwell Automation | Industrial automation and control software (FactoryTalk, analytics, MES) | Automation systems, analytics, MES, industrial AI | Deep integration with PLC hardware, strong ecosystem with OEMs, and edge computing capabilities | USD 8.26 billion (FY 2024) | Leading position in North America for control systems and MES solutions | Global presence with strong base in the Americas, EMEA, and APAC |
| Schneider Electric | Energy management and industrial automation software (EcoStruxure platform) | Energy efficiency, digital twin for operations, sustainability software | Unified platform combining power management and automation; strong ESG-focused portfolio | EUR 38.15 billion (FY 2024) | Significant share in energy, buildings, and process automation software | Headquartered in France; strong global operations across Europe, Asia, and North America |
| Autodesk | Design and engineering software (CAD/CAM/PLM) | 3D design, generative design, PLM integrations | Leader in CAD and generative design with cloud-based collaboration | USD 5.5 billion (FY 2024) | Dominant in design software; growing in industrial digital twin applications | Global SaaS presence across construction, manufacturing, and design sectors |
| Honeywell | Process automation and control software | Process industries, industrial cybersecurity, analytics | End-to-end integration from sensors to enterprise systems; strong presence in chemicals and oil & gas | USD 38.5 billion (FY 2024) | Key player in process automation software | Global operations across industrial, building, and aerospace markets |
| Siemens AG | Comprehensive industrial software suite (Xcelerator, MindSphere, PLM) | PLM, simulation, digital twin, IIoT platforms, AI | End-to-end digital transformation solutions; leading PLM and digital twin ecosystem | EUR 75.9 billion (FY 2024) | Market leader in industrial software by breadth and scale | Headquartered in Germany; strong global footprint in manufacturing and energy |
Note: The revenue figures represent total company revenues; actual industrial software revenue forms a subset. Market shares vary across subsegments like PLM, MES, IIoT, and control systems.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The integration of IIoT platforms allows manufacturers to connect machines, sensors, and enterprise systems through cloud or hybrid networks. This connectivity improves asset visibility, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization. The impact is clear — improved uptime, reduced costs, and enhanced decision-making.
2. Cloud and Edge Computing
Industrial operations increasingly rely on hybrid environments, where edge computing provides real-time local control and cloud computing handles large-scale data analytics. This dual approach ensures both speed and scalability, particularly in sectors like energy and manufacturing.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-driven analytics help identify process inefficiencies and predict equipment failures. Machine learning models continuously refine performance, improving operational accuracy and production quality. In design, generative AI accelerates innovation by creating optimized component geometries.
4. Digital Twins and Simulation
Digital twins — virtual representations of physical assets — have become essential tools for simulation, design, and performance optimization. Manufacturers use them to test production changes in a virtual environment before implementation, reducing downtime and cost.
5. Cybersecurity and IT/OT Convergence
As operational technology connects to enterprise networks, cybersecurity becomes crucial. Vendors now integrate secure architectures, intrusion detection, and real-time monitoring into their software ecosystems to safeguard critical infrastructure.
6. Sustainability and ESG Compliance
Governments and corporations are prioritizing decarbonization. Software solutions for energy management, emissions tracking, and resource optimization are now key components of industrial strategies. These solutions help companies meet ESG goals and enhance brand value.
7. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Subscription Models
The shift from perpetual licenses to SaaS-based delivery allows manufacturers to access the latest features with lower upfront costs. It also enables vendors to maintain continuous customer relationships and recurring revenue streams.
8. Mergers, Acquisitions, and Ecosystem Expansion
Large players are acquiring niche software companies to expand capabilities in AI, simulation, and cybersecurity. This consolidation is reshaping the competitive landscape and creating integrated end-to-end platforms that cover the full industrial lifecycle.
Successful Examples of Industrial Software Adoption
Siemens Digital Twin in Automotive Manufacturing
Siemens’ Xcelerator and PLM software enable automotive manufacturers to build full digital twins of vehicle production systems. This allows virtual testing, reducing physical prototyping costs and accelerating time-to-market by months.
Rockwell Automation’s AI-Driven Factories
Rockwell’s FactoryTalk Analytics and partnerships with AI firms have helped electronics and packaging manufacturers achieve double-digit improvements in yield and reduced downtime through automated root-cause analysis.
Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure for Energy Optimization
Schneider’s EcoStruxure has been deployed across industrial facilities, enabling real-time energy monitoring and control. This has helped companies lower energy costs, reduce emissions, and improve grid reliability.
Autodesk Generative Design in Aerospace
Autodesk’s generative design software has been used by aerospace companies to create lighter, stronger components, cutting material usage and improving fuel efficiency — a tangible example of digital design driving sustainability.
Honeywell Process Optimization in Refineries
Honeywell’s process control and analytics solutions are used in large-scale refineries to optimize throughput, maintain safety compliance, and ensure continuous production with minimal operator intervention.
These success stories demonstrate that industrial software not only boosts efficiency but also creates measurable business value across diverse industries.
Global and Regional Analysis: Policies and Government Initiatives
Europe
Europe leads in digital manufacturing initiatives, largely driven by Germany’s Industry 4.0 program. This government-backed framework promotes the integration of cyber-physical systems, digital twins, and smart factories. The European Union further supports digitization through funding programs under Horizon Europe and green transition policies encouraging energy-efficient operations. These initiatives have accelerated adoption of industrial software solutions for sustainability and competitiveness.
North America
The United States focuses on industrial modernization through initiatives like Manufacturing USA and MxD (Manufacturing x Digital), which aim to strengthen domestic supply chains, enhance cybersecurity, and train a digital-ready workforce. Federal policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) incentivize software-driven energy optimization, while private industry investment in AI and automation continues to expand. Canada similarly supports Industry 4.0 adoption through grants and tax credits for industrial digital transformation.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for industrial software. China’s Made in China 2025 plan emphasizes industrial self-reliance, advanced manufacturing, and automation — propelling domestic demand for digital twins, CAD, and IIoT platforms. Japan’s Society 5.0 initiative promotes the integration of digital technologies across all industries, while India’s Digital Manufacturing and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes encourage smart factory adoption among manufacturers. Southeast Asia, especially Singapore and Malaysia, is emerging as a regional hub for industrial innovation.
Middle East and Africa
Countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are incorporating industrial software into their diversification agendas (Vision 2030) to modernize oil, gas, and energy sectors. Smart city and smart grid projects are major adopters of automation and SCADA systems. In Africa, emerging industrial corridors in South Africa and Egypt are exploring automation solutions to increase production efficiency.
Latin America
Latin America’s adoption is driven by the modernization of mining, automotive, and energy industries. Governments in Brazil and Mexico are supporting digitalization through industrial cluster programs and partnerships with European and American software providers. While adoption levels are lower than in developed regions, investment momentum is rising sharply.
How Government Policies Shape the Market
- Incentives for Innovation and R&D: Many countries provide tax breaks or grants for companies investing in industrial digitalization, which lowers the barriers for adopting industrial software.
- Standards and Interoperability Frameworks: Initiatives like OPC UA and RAMI 4.0 in Europe ensure interoperability between different vendors’ systems, encouraging software ecosystem growth.
- Cybersecurity Regulations: Governments are setting stricter cybersecurity requirements for industrial control systems, driving adoption of integrated and certified software platforms.
- Sustainability Mandates: Energy efficiency and emission-reduction targets are accelerating demand for software that can monitor, report, and optimize energy use.
- Workforce Development Programs: Training initiatives help upskill the industrial workforce to operate and maintain advanced software tools, reducing resistance to digital adoption.
- Local Content Requirements: Some regions (like China and parts of the Middle East) encourage the use of domestic industrial software, prompting the rise of regional players and joint ventures.
Key Takeaways for Industry Stakeholders
- Integration is critical: The success of industrial software hinges on seamless integration between IT and OT environments. Companies must prioritize interoperability and data architecture planning early in deployment.
- Cybersecurity cannot be optional: With increasing connectivity comes higher vulnerability. Embedded security features must be part of every deployment.
- ROI should drive adoption: Successful digital transformations begin with measurable objectives like OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), energy savings, and reduced downtime.
- Vendor ecosystems matter: Selecting vendors with open APIs, strong partner networks, and consistent upgrade paths ensures long-term scalability.
- Sustainability and compliance will define the next phase: Environmental performance tracking will soon be as important as productivity metrics, positioning industrial software as a central enabler of ESG reporting.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Food Packaging Market Growth Drivers, Key Players, Trends, and Regional Insights by 2034