Nuclear Power Market Analysis & Forecast to 2034
Nuclear Power Market Size
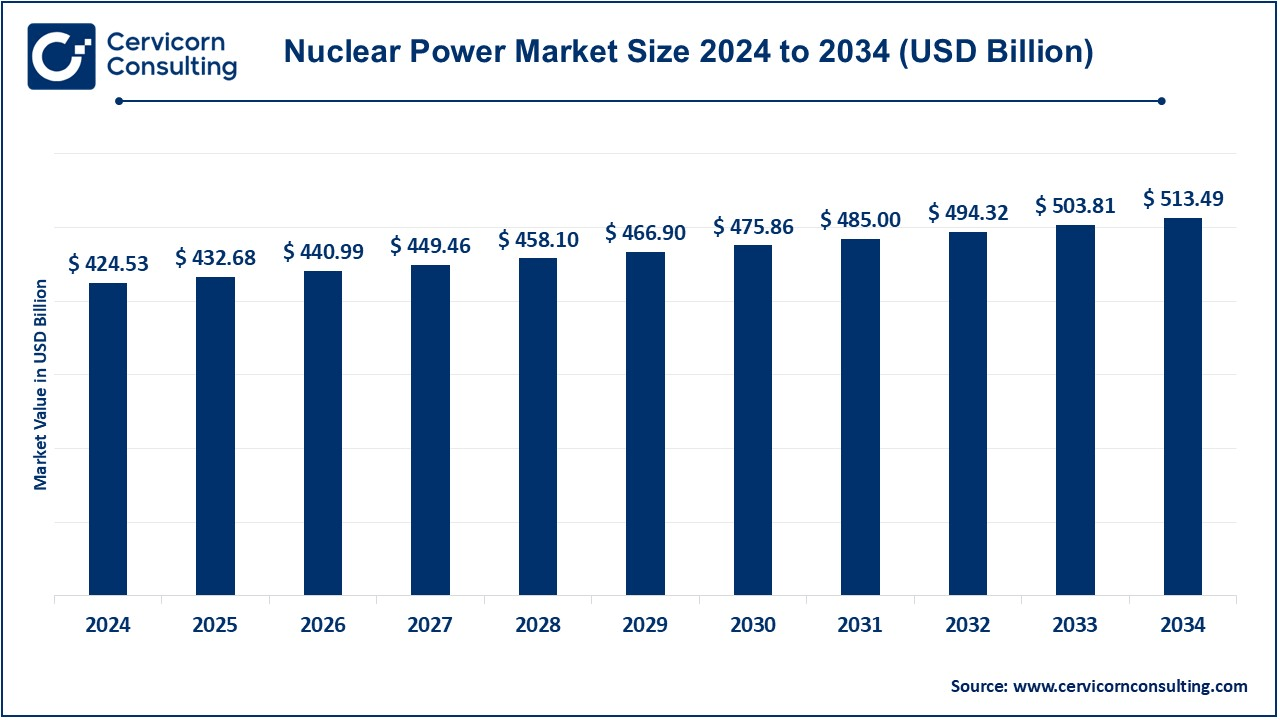
The global nuclear power market size was worth USD 424.53 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 513.49 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.92% from 2025 to 2034.
What is the Nuclear Power Market?
The nuclear power market encompasses the entire value chain involved in generating electricity from nuclear energy. This includes uranium mining and processing, fuel fabrication, nuclear reactor design and construction, plant operations, maintenance, decommissioning, and nuclear waste management. The market also incorporates research and development in next-generation nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), advanced reactors, and nuclear fusion.
This market consists of utilities, technology providers, equipment manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and support service companies. It includes various reactor types—pressurized water reactors (PWRs), boiling water reactors (BWRs), fast breeder reactors, and innovative designs such as thorium reactors or molten salt reactors. These systems provide clean baseload electricity that complements intermittent renewable sources like wind and solar.
As the world moves toward decarbonization, energy security, and electrification, nuclear power has regained relevance for its ability to deliver continuous, low-emissions energy.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2584
Growth Factors
The global nuclear power market is witnessing a resurgence, driven by several interrelated factors. First, the rising global energy demand, especially in emerging markets and energy-intensive sectors like AI and digital infrastructure, necessitates stable, large-scale energy sources. Nuclear fills this gap by offering carbon-free baseload capacity. Second, national governments are increasingly integrating nuclear into their long-term energy transition plans to meet net-zero emission targets.
Third, technological innovations—especially in SMRs and advanced reactors—are reducing capital and construction risks, opening doors for private investments and decentralized applications. Fourth, geopolitical instability and supply chain vulnerabilities have reignited interest in nuclear as a means of ensuring energy independence. Finally, regulatory reforms and public funding initiatives in countries such as the U.S., China, and India are accelerating project pipelines and modernizing existing fleets.
Why is Nuclear Power Important?
Clean Baseload Energy
Nuclear energy produces consistent electricity with virtually no carbon emissions. Unlike renewables, which are intermittent, nuclear can run continuously for 18–24 months without refueling, making it essential for stabilizing grids.
Emissions Reduction
Each year, nuclear power helps avoid billions of tonnes of CO₂ emissions that would otherwise be generated by fossil fuels. This is essential to meeting climate goals and avoiding the most severe effects of global warming.
Energy Security
Countries with limited domestic fossil fuel reserves or high import dependence are turning to nuclear for long-term, sovereign energy supply. It diversifies energy portfolios and reduces geopolitical risk.
Grid Reliability
Nuclear supports the stability of increasingly renewable-powered grids by offering a steady output that balances the variability of wind and solar.
Industrial & Heat Applications
Beyond electricity, nuclear reactors—especially advanced designs—can be used for industrial heating, hydrogen production, and even water desalination.
Technology Leadership
Investments in advanced reactors, SMRs, and eventually nuclear fusion can place countries at the forefront of a trillion-dollar future energy economy.
Top Nuclear Power Companies: Profiles
Below is a snapshot of key players involved in the nuclear energy value chain, including mining, plant operations, and infrastructure support:
| Company | Specialization | Key Focus Areas | Notable Features | 2024 Revenue | Est. Market Share | Global Presence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHP Billiton | Uranium mining & production | Sustainable uranium supply | One of the largest uranium suppliers | ~$65 billion | ~20% uranium market | Australia, North America, Europe |
| Paladin Energy | Uranium mining/exploration | High-grade uranium production | Low-cost operations in Africa and Australia | ~$1.5 billion | ~5% uranium market | Namibia, Australia |
| Bulgarian Energy Holding | Nuclear & thermal energy generation | Power plant operations, distribution | Bulgaria’s major energy entity | ~$4 billion | ~12% national market | Europe (Bulgaria) |
| Electrabel | Nuclear power generation (subsidiary of Engie) | Reactor operation and maintenance | Runs multiple Belgian nuclear reactors | ~$8 billion | ~15% national market | Europe (Belgium) |
| Electronuclear | Nuclear plant operations | Fleet maintenance and grid integration | Plays a vital role in South American markets | ~$5 billion | ~10% market share | Europe, South America |
Leading Trends & Their Impact
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
SMRs are compact nuclear reactors with output capacities typically below 300 MW. They are factory-built, transportable, and suitable for deployment in remote or constrained sites. Their smaller footprint and modular construction can reduce both costs and timelines, making them ideal for industrial clusters, islanded grids, and emerging markets.
Advanced Reactor Designs
New generations of reactors, such as liquid metal-cooled, high-temperature gas-cooled, and molten salt reactors, offer greater safety, fuel efficiency, and waste reduction. Some designs even allow for passive safety mechanisms and can be used for industrial heat or hydrogen production.
Reactor Life Extensions
Rather than building new facilities, many countries are extending the operational lives of existing reactors by 20 to 40 years. This involves safety upgrades, digitalization, and core component replacements, which are more cost-effective than new builds.
Supportive Government Policies
Countries are increasingly passing legislation to accelerate nuclear innovation. Examples include fast-track permitting, public-private partnership frameworks, and investment tax credits for SMR deployment.
Hybrid Power Systems
Nuclear is being coupled with renewables and storage systems to form hybrid grids. These offer resilience, especially during peak loads or renewable intermittency, and improve decarbonization outcomes.
Geopolitical Diversification
In response to geopolitical tensions and reliance on Russian nuclear technology, many nations are seeking supply chain alternatives through Western reactor vendors and independent uranium enrichment capabilities.
Successful Examples of Nuclear Power Deployment
France
With over 70% of electricity coming from nuclear, France has long been a model for nuclear-centric grids. Its government plans to extend the lifespan of its existing fleet and build at least six new EPR reactors in the next decade.
United States
The U.S. has the world’s largest fleet of nuclear reactors, generating about 20% of its electricity. Recent projects like Vogtle Units 3 and 4, as well as extensive investment in SMR developers such as NuScale and TerraPower, underscore continued leadership.
China
China has 58 operating nuclear reactors and another 27 under construction, making it one of the fastest-growing nuclear markets. It is developing indigenous reactor designs and exporting its technology to other countries in Asia and Africa.
Russia
Through its state-owned company, Russia leads in reactor exports, especially to developing nations. Its VVER designs are being built in countries like Turkey, Egypt, and India, strengthening its global influence.
United Arab Emirates
The Barakah Nuclear Power Plant, built with South Korean technology, has four operational reactors and now provides over 25% of the country’s electricity. It showcases how new entrants can rapidly integrate nuclear into their grids.
Regional Analysis: Government Initiatives & Policies
North America
- United States: Nuclear policy has shifted toward revitalization. The ADVANCE Act and the Inflation Reduction Act both provide support for SMRs and advanced reactors through tax credits and R&D funding.
- Canada: Canada has partnered with provinces like Ontario and Saskatchewan to develop SMRs for off-grid and industrial applications. Its CANDU reactor technology also plays a key role in global partnerships.
Europe
- France and UK: Both nations are planning or building new reactors to replace aging fleets. France focuses on EPR reactors, while the UK is developing Rolls-Royce SMRs.
- Belgium and Netherlands: Life extension plans are underway, and new build strategies are being reconsidered post energy crisis.
- Germany and Switzerland: While some countries have phased out nuclear, they are reassessing policies in light of energy shortages and decarbonization needs.
- Eastern Europe: Countries like Poland, Czech Republic, and Slovakia are expanding their nuclear programs to reduce coal reliance.
Asia-Pacific
- China: Ambitious plans to install over 200 GW of nuclear capacity by 2045. Indigenous reactor designs like Hualong One are central to this expansion.
- India: With plans to reach 100 GW of nuclear capacity by 2047, India is reforming its legal structure to allow private participation and is focusing on domestic reactor designs like the PHWR.
- Japan and South Korea: Japan is restarting reactors with upgraded safety standards post-Fukushima. South Korea is positioning itself as a global exporter of nuclear technology.
Middle East and Africa
- UAE: A regional pioneer, the UAE has completed its first nuclear plant and is training local expertise for long-term sustainability.
- Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Turkey: These nations have formal nuclear ambitions and are in various stages of reactor planning, licensing, or construction.
- South Africa: The Koeberg Nuclear Power Station continues to operate, and the country has plans to expand its nuclear fleet to address load shedding and power shortages.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Floating Power Plant Market Size, Share & Industry Growth Analysis by 2034