U.S. Energy Storage Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034
U.S. Energy Storage Market Size
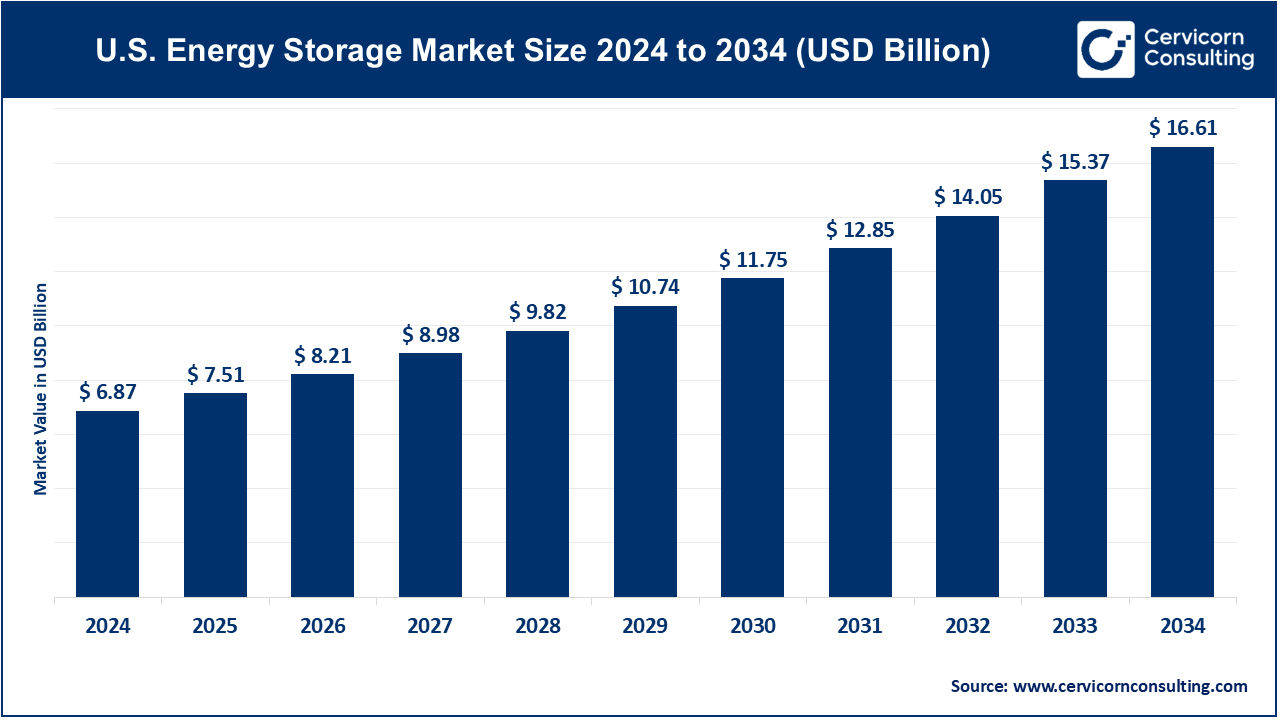
The U.S. energy storage market size was worth USD 6.87 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 16.61 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.23% from 2025 to 2034.
U.S. Energy Storage Market Growth Factors
The U.S. energy storage market is expanding due to a combination of accelerating renewable energy deployment, declining battery costs, increasing demand for grid reliability, rising electrification across industries, state-level storage mandates, and the introduction of strong federal incentives including tax credits for standalone storage. Additional drivers include growing corporate sustainability commitments, the need for peak-load management, advancements in battery technology that enable longer-duration storage, and widespread utility investment in grid modernization. These factors are reinforced by expanded domestic manufacturing of batteries, increasing residential adoption of solar-plus-storage systems, the proliferation of virtual power plants, and advanced energy management software—all of which collectively propel sustained year-over-year deployment growth.
What Is the U.S. Energy Storage Market?
The U.S. energy storage market comprises all technologies, systems, and services used to store electricity for later use. While multiple forms of storage exist, the market today is dominated by battery energy storage systems (BESS)—primarily lithium-ion batteries deployed at utility scale, commercial/industrial sites, and homes. Other storage technologies include pumped hydro, compressed air storage, flywheels, thermal storage, and emerging flow battery systems. Energy storage systems support a wide array of services including energy shifting, backup power, renewable integration, frequency regulation, peak shaving, and microgrid operation. As the grid becomes increasingly decentralized, digitalized, and reliant on intermittent renewable resources, energy storage has evolved into a central pillar of the U.S. power landscape.
Why It Is Important
Energy storage delivers essential flexibility to the grid, enabling the large-scale adoption of solar and wind power while maintaining reliability. It ensures clean energy generated during periods of low demand can be used later during peak hours, reducing curtailment and maximizing renewable utilization. Storage also supports grid stability through fast-response services like frequency regulation and voltage control. For residential and commercial consumers, batteries provide backup power during outages—critical as extreme weather and grid failures become more frequent. Energy storage also reduces consumer electricity bills by optimizing usage during low-cost periods and minimizing demand charges. At an economic level, storage reduces the need for expensive transmission upgrades, enhances national energy security, and accelerates the transition away from fossil fuels.
Market Landscape and Deployment Growth
The U.S. energy storage market has experienced record-breaking deployment over the last several years, with utility-scale batteries leading the surge. States like California, Texas, and Arizona have become hotspots for gigawatt-scale installations. Simultaneously, residential storage adoption—often paired with rooftop solar—is rising rapidly due to falling costs, improved installer networks, and increasing concerns about power reliability. Commercial and industrial customers are also investing heavily in storage for resilience and energy cost management. Analysts estimate the market valuation in 2024 to be in the low hundreds of billions of dollars, with projections suggesting a massive expansion through the mid-2030s as policy support and manufacturing capacity grow.
Top Companies in the U.S. Energy Storage Market
Below are detailed profiles of the major companies shaping the U.S. energy storage landscape, including their specialization, key focus areas, notable features, and publicly available information on 2024 revenue or market position.
1. Tesla, Inc.
Specialization:
Tesla is a major designer and manufacturer of stationary storage products, including the Powerwall for homes and the Megapack for utility-scale deployments. It also develops energy management and trading software such as Autobidder.
Key Focus Areas:
- Rapid deployment of utility-scale Megapack projects
- Integration of solar, storage, and EV systems
- Expansion of its vertically integrated battery supply chain
- Software-driven optimization of storage assets
Notable Features:
Tesla is recognized for the largest deployment volumes among energy storage system providers, high energy density battery systems, and modular, plug-and-play architecture that shortens project timelines.
2024 Revenue & Market Share Context:
Tesla’s Energy Generation and Storage division recorded multi-billion-dollar revenue in 2024, driven by record energy storage deployments exceeding 30 GWh. The company remains one of the top leaders in U.S. residential and utility-scale BESS deployments.
2. Fluence
Specialization:
Fluence provides integrated utility-scale storage systems, project development, and energy analytics platforms.
Key Focus Areas:
- Grid-scale storage systems
- Digital optimization tools for battery fleets
- EPC and long-term services
- Expansion of global BESS deployments
Notable Features:
Fluence is widely considered one of the largest independent integrators of utility-scale storage globally, with advanced software that enables multi-market revenue stacking.
2024 Revenue & Market Share Context:
Fluence posted record revenue of around $2.7 billion for 2024 across its global operations, driven by strong order backlogs and U.S. utility-scale projects.
3. NextEra Energy Resources
Specialization:
A leading renewable energy developer in the U.S., NextEra focuses heavily on solar-plus-storage and wind-plus-storage hybrid systems.
Key Focus Areas:
- Co-locating storage with large-scale renewables
- Building contracted utility-scale storage projects
- Energy shifting for solar-dominant grids
- Integrated renewable resource planning
Notable Features:
NextEra is well known for its large renewable portfolio and for systematically adding storage to its wind and solar projects to improve dispatchability.
2024 Revenue & Market Share Context:
NextEra Energy Resources reported owning thousands of MW of battery capacity by the end of 2024, positioning it as one of the largest U.S. storage operators by net ownership and project pipeline.
4. LG Energy Solution
Specialization:
A global battery manufacturer that supplies lithium-ion cells for EVs and stationary storage applications.
Key Focus Areas:
- Expanding North American manufacturing
- Scaling production of high-energy-density cells
- Supply partnerships with energy storage integrators
- Development of next-generation chemistries
Notable Features:
LG Energy Solution plays a critical role in supplying the batteries used by integrators across the market. Its large manufacturing scale directly influences storage system costs.
2024 Revenue & Market Share Context:
LG Energy Solution recorded multi-trillion-KRW revenue in 2024, with a significant share coming from global battery supply. While not a system integrator, it remains one of the most influential companies in the U.S. storage supply chain.
5. AES Corporation
Specialization:
AES develops and operates utility-scale energy storage projects, integrated renewable solutions, and energy-as-a-service offerings for utilities.
Key Focus Areas:
- Long-duration storage and grid resilience
- Large renewable-plus-storage deployments
- Modernization of utility infrastructure
- Contracted storage services
Notable Features:
AES is recognized for pioneering early grid-scale storage projects and continues to lead in building highly reliable, contracted storage assets.
2024 Revenue & Market Share Context:
AES expanded its investment in energy storage and grid modernization in 2024, maintaining its position among the top developers of utility-scale storage capacity in the U.S.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Standalone Storage Tax Credits
With federal legislation granting full investment tax credits to standalone storage, the economics of battery projects improved dramatically. This unlocked merchant storage, grid services projects, and standalone deployments not tied to solar or wind.
Impact: A surge in utility-scale storage development pipelines and increased investor interest.
2. Declining Battery Costs & Manufacturing Expansion
Battery prices continue to fall as U.S. and global manufacturers scale production. Domestic manufacturing incentives are accelerating this trend.
Impact: Lower system costs and increased adoption across all segments—utility, commercial, and residential.
3. Advanced Software & Grid Integration
Modern BESS platforms use AI and machine learning to optimize battery dispatch, trade energy, and extend asset life.
Impact: Higher revenue potential for storage developers and better grid stability.
4. Long-Duration Storage (LDS) Momentum
Growing solar and wind penetration is creating demand for storage that can last beyond 4–8 hours.
Impact: Increased funding for technologies such as flow batteries, thermal storage, and iron-air batteries.
5. Resilience-Driven Distributed Storage
From hospitals to data centers to communities, distributed storage systems are being installed to provide backup during outages.
Impact: Growth in microgrid projects and new business models—resilience-as-a-service.
6. Virtual Power Plants (VPPs)
Residential batteries are increasingly aggregated to participate in grid services markets.
Impact: Consumers are becoming active grid participants, reducing peak loads and operational costs.
Successful Examples of U.S. Energy Storage Deployment
1. Tesla Megapack Utility Projects
Large-scale deployments such as those in California showcase how modular batteries can be rapidly deployed to deliver massive capacity, frequency regulation, and renewable firming. These installations have influenced storage procurement strategies worldwide.
2. Solar-Plus-Storage in California
Hybrid solar and storage facilities support the grid during evening peaks and mitigate the “duck-curve” challenge. This model has been replicated globally in solar-heavy regions, including the Middle East, Australia, and parts of Southern Europe.
3. Merchant Storage Participation in Wholesale Markets
Battery systems operating in markets such as ERCOT and PJM demonstrate the profitability of participating in frequency response, arbitrage, and ancillary services. This framework has inspired reforms in other countries seeking to enable storage participation in competitive markets.
4. Residential Solar-Plus-Storage Virtual Power Plants
Programs in states like California, Hawaii, and Vermont aggregate thousands of home batteries to create dispatchable capacity. Similar programs are being adopted in Germany, Australia, Japan, and the U.K.
Government Initiatives & Policies Shaping the Market
1. Federal Incentives: Investment Tax Credit for Standalone Storage
Under recent legislation, standalone storage qualifies for the full investment tax credit. This policy dramatically improves project financing and accelerates the adoption of large-scale storage.
2. State-Level Energy Storage Mandates
Numerous states—including California, New York, Massachusetts, and New Jersey—have introduced multi-GW energy storage targets and procurement mandates.
Impact: Guaranteed regional demand that accelerates market maturity.
3. FERC Regulations Supporting Market Access
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission rules require regional grid operators to allow storage to participate in wholesale markets, opening the door to revenue stacking.
Impact: Market competition increases, and storage becomes more financially viable.
4. DOE Funding for Grid Modernization & Long-Duration Storage
The U.S. Department of Energy has invested heavily in pilot projects for long-duration storage and microgrid resilience, as well as grants for domestic battery supply chain development.
Impact: Faster commercialization of emerging technologies and reduced dependence on foreign battery sourcing.
5. Local and Municipal Initiatives
Cities and counties are integrating storage into resilience hubs, public infrastructure, and community microgrids.
Impact: Storage becomes essential for local-level preparedness and climate resilience.
Market Challenges
Although the U.S. energy storage market is expanding rapidly, it faces several challenges such as grid interconnection delays, supply-chain constraints for battery materials, inflationary pressures on EPC costs, and evolving market rules that sometimes lag technological capability. Nonetheless, strong policy momentum and manufacturing expansion provide a clear roadmap for overcoming these barriers.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Insulation Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034