Space Cloud Computing Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035
Space Cloud Computing Market Size
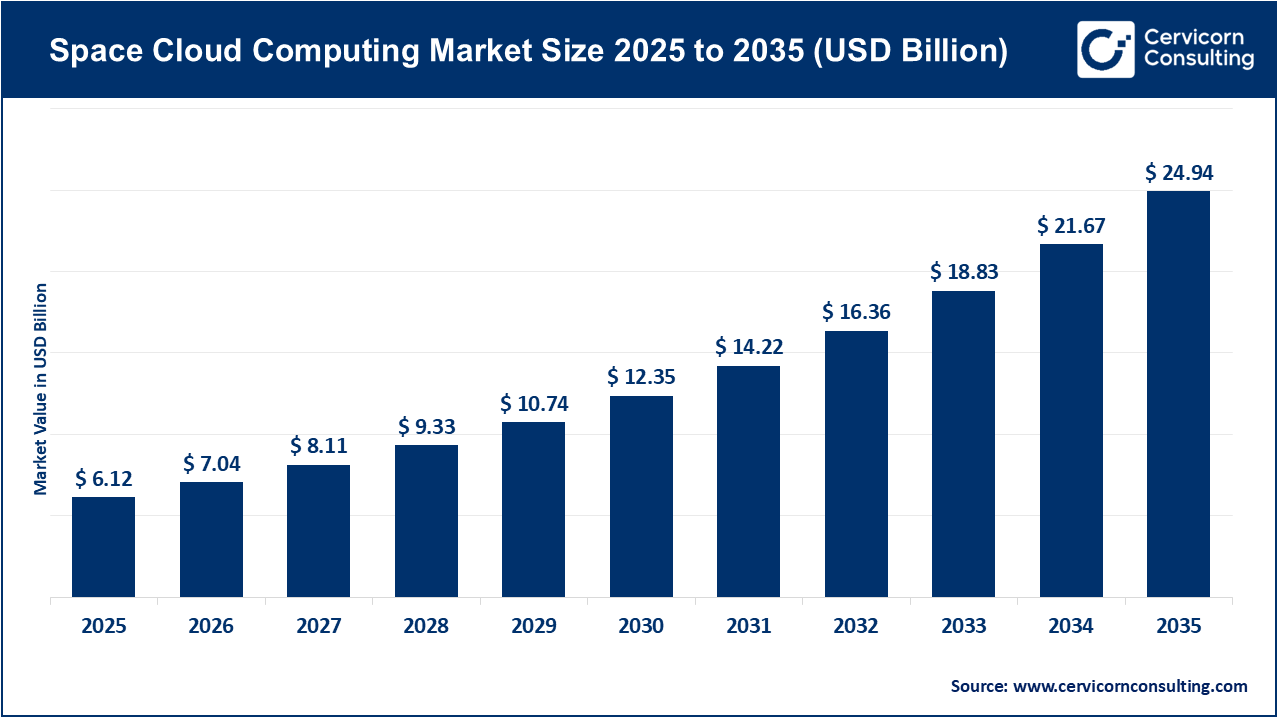
The global space cloud computing market size was worth USD 6.12 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 24.94 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.08% from 2026 to 2035.
What Is the Space Cloud Computing Market?
Space cloud computing refers to cloud-like services — compute, storage, networking, and application platforms — deployed in space rather than on Earth. These services run on Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, hosted payloads, modular data centers, or hybrid spacecraft capable of running high-performance hardware.
Typical space-cloud systems include:
- In-orbit compute nodes: satellites equipped with CPUs, GPUs, FPGAs, or radiation-hardened chips for data processing.
- Space-based storage: orbital “data vaults” for secure, sovereign data storage.
- On-orbit edge computing: compute near satellite sensors that process Earth observation (EO), radar, and scientific payloads before downlink.
- Space networking & relay systems: enabling persistent connectivity between terrestrial clouds, ground stations, and space assets.
Rather than fully replacing terrestrial cloud systems, space cloud computing works as a hybrid model — Earth-based clouds handle the bulk of enterprise workloads, while orbit-based compute handles time-sensitive, high-volume, or security-critical tasks more efficiently in space.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2812
Why Space Cloud Computing Is Important
Space cloud computing is driven by transformational technical and economic advantages:
1. Processing data close to the source
Satellites generate petabytes of EO and sensor data, but downlinking it is expensive and slow. On-orbit compute enables:
- Real-time image analysis
- Event detection
- AI inference on raw data
Only processed or prioritized data needs to be sent to Earth.
2. Massive compute potential
Space offers virtually unlimited access to:
- Free solar power
- Passive radiative cooling
- Zero land constraints
This can reduce operating costs for high-performance compute compared to Earth.
3. Enhanced security and sovereignty
Orbital storage is naturally air-gapped, offering sovereign or highly secure data vaults for:
- Governments
- Defense agencies
- Critical industries
4. Global resilience and connectivity
Space-based cloud services enable compute or storage for remote regions, maritime industries, aviation, and disaster-prone areas without terrestrial infrastructure.
Together, these benefits make space cloud computing a strategic asset for governments, enterprises, and defense bodies.
Space Cloud Computing Market — Growth Factors
The space cloud computing market is expanding due to rapidly declining launch costs, increasing rideshare mission availability, and rising deployment of smallsat constellations requiring distributed edge compute. Growth is also driven by soaring Earth observation and remote-sensing data volumes that benefit from on-orbit processing; the global surge in AI/ML workloads needing low-latency inference close to spaceborne sensors; and strong investment from hyperscalers, venture capital, and national aerospace programs. Additional accelerators include demand for sovereign off-planet storage, advancements in radiation-tolerant processors, modular payload architectures, in-orbit servicing technologies, and geopolitical incentives that push countries to develop resilient, space-based digital infrastructure. Together, these forces are converting what was once a speculative idea into a viable and fast-growing commercial sector.
Top Companies in the Space Cloud Computing Market
Below is a detailed profile of the companies you requested, including their specialization, key focus areas, notable characteristics, available revenue notes, and global presence.
1. Axiom Space
Specialization
Commercial low-Earth orbit infrastructure, space station modules, and mission services.
Key Focus Areas
- Commercial LEO station modules
- Hosted payload services
- Platforms enabling research, manufacturing, and potential cloud/compute hosting in space
Notable Features
Axiom is building the first commercial space station modules to replace the ISS and support research, commercial services, and possibly hosted compute platforms.
2024 Revenue / Market Share
Axiom is private and does not publish detailed 2024 revenue. Available profiles indicate strong government and commercial contract-based revenues.
Global Presence
Based in the United States with international partnerships for research, manufacturing, and commercial operations.
2. Starcloud
Specialization
In-space GPU data centers and satellite-based high-performance computing for AI workloads.
Key Focus Areas
- GPU-equipped satellites
- On-orbit AI training and inference
- Always-on compute using solar power
Notable Features
Starcloud has announced satellites (e.g., Starcloud-2) equipped with GPU clusters, making it one of the first companies moving toward real commercial orbital data centers specifically for AI.
2024 Revenue / Market Share
Early-stage growth company; revenue details for 2024 are not publicly disclosed.
Global Presence
Headquartered in the U.S. with global customer targets focused on AI, defense, and satellite operators.
3. D-Orbit
Specialization
Space logistics, in-orbit transportation, payload hosting, and edge computing services.
Key Focus Areas
- ION orbital transfer vehicles
- Hosted payloads
- In-space compute and data relay
Notable Features
D-Orbit has strong flight heritage and offers commercial hosting services, making it one of the most operationally mature companies in this sector.
2024 Revenue / Market Share
D-Orbit generates recurring revenue from missions, contracts, and hosted services, though exact 2024 figures vary by source.
Global Presence
Based in Italy with an expanding international footprint across Europe, the U.S., and global space partners.
4. Cloud Constellation Corporation (SpaceBelt)
Specialization
Space-based secure data storage and global connectivity.
Key Focus Areas
- Orbital “data vault” storage
- Encrypted communication networks
- Data sovereignty solutions for regulated industries
Notable Features
The SpaceBelt constellation concept offers an air-gapped secure data environment hosted in LEO, attracting interest from defense and regulated sectors.
2024 Revenue / Market Share
Still in development and pre-commercial stages; no official 2024 revenue publicly reported.
Global Presence
U.S. headquarters with a global target market, especially for governments and enterprises needing extreme data security.
5. Blue Origin
Specialization
Launch vehicles, spacecraft platforms, and advanced in-space infrastructure.
Key Focus Areas
- New Glenn heavy-lift rocket
- Blue Ring spacecraft platform (potential compute host)
- Cloud integration concepts in partnership with tech companies
Notable Features
The Blue Ring platform can maneuver and host payloads in various orbits, making it suitable for space cloud hosting, networking, and logistics.
2024 Revenue / Market Share
As a private company, Blue Origin’s exact revenue is not disclosed, though it has multi-billion-dollar programs and contracts.
Global Presence
Global presence through customers, partnerships, and launch service agreements.
Leading Trends in the Space Cloud Computing Market and Their Impact
1. Rise of In-Orbit AI and GPU Hosting
Space-based GPU clusters enable direct AI inference on EO data, reducing downlink costs and enabling real-time applications like disaster detection, maritime surveillance, and defense analytics.
2. Growth of Hosted Payload and In-Space Edge Services
Payload hosting platforms allow startups and enterprises to test or deploy compute workloads in space without building their own satellites — lowering barriers to entry.
3. Secure Orbital Data Storage for Sovereign Cloud
Data residency rules and cybersecurity concerns encourage governments to explore orbital data centers for air-gapped resilience.
4. Hyperscaler Partnerships
Cloud giants increasingly collaborate with space companies, integrating space-data pipelines and exploring hybrid cloud architectures that use orbital compute nodes.
5. Falling Launch Costs
More affordable access to orbit enables frequent testing, iterative development, and deployment of dedicated compute hardware in space.
Successful Examples of Space Cloud Computing
Starcloud’s GPU Satellites
Demonstrates early operational steps toward AI compute platforms in orbit.
D-Orbit’s ION Platforms
A fully operational example of in-space logistics and hosted payload compute environments.
Cloud Constellation’s SpaceBelt Concept
A strong example of the demand for sovereign off-planet data storage.
Blue Origin’s Blue Ring
Represents a scalable, modular platform for hosting next-generation compute or networking payloads.
These examples collectively show that multiple aspects of space cloud computing — compute, storage, networking, and logistics — are being commercially validated.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Influence
North America (U.S. & Canada)
The U.S. leads the global market due to:
- Strong NASA commercialization programs
- Department of Defense budgets supporting resilient satellite compute
- A robust private launch ecosystem
- Space-friendly regulatory frameworks
Canada’s space programs and data sovereignty rules also support regional growth.
Europe
Europe is accelerating adoption through:
- EU space and defense programs
- Investments in downstream analytics and dual-use technologies
- Strong emphasis on sovereign cloud initiatives
- Funding mechanisms that support companies like D-Orbit
These policies position Europe as a major adopter and supplier of space cloud technologies.
Asia Pacific
Countries like India, Japan, China, and South Korea are heavily investing in:
- Satellite constellations
- Earth observation infrastructure
- AI-driven downstream applications
Japan and India, in particular, are strengthening their commercial space ecosystems, creating new markets for orbital compute and storage.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East is rapidly emerging as a major investor in space, data centers, and sovereign cloud strategies. Initiatives in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar focus on:
- Smart city monitoring
- Secure data storage
- Climate and environmental analytics
Africa, with growing interest in EO data services, stands to benefit from regional cloud and data resilience through space-based services.
Government Initiatives Shaping the Market
Across regions, several common policy drivers are accelerating space cloud computing:
1. Sovereign Cloud & Data Residency
Governments are pushing for greater control over national data, making orbital data storage a compelling option.
2. Defense Modernization
Defense agencies require low-latency processing of surveillance data, making space-based compute essential.
3. Public–Private Partnerships
Agencies like NASA are actively fostering commercial LEO markets, enabling compute-hosting platforms.
4. Supportive Regulatory Frameworks
Progressive satellite licensing, spectrum allocations, and launch regulations support rapid deployment of space cloud infrastructure.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Solar Tracker Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034