Resistant Starch Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2035
Resistant Starch Market Size
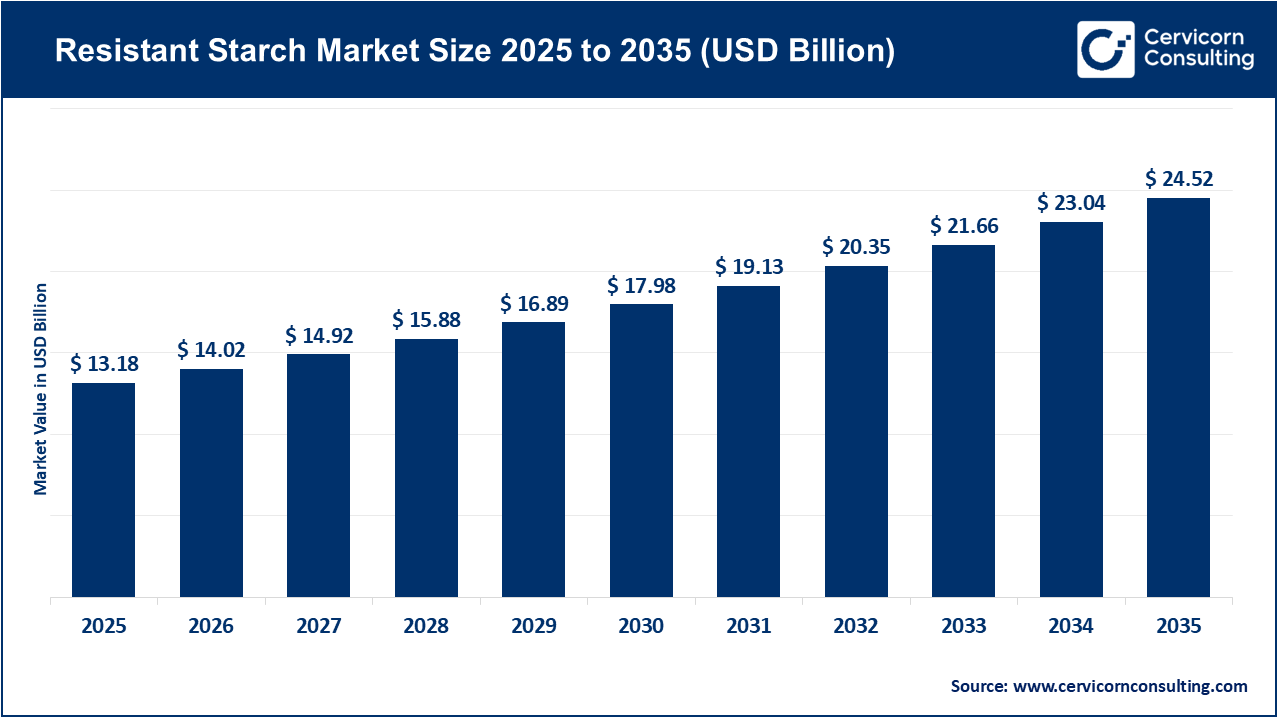
The global resistant starch market size was worth USD 13.18 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 24.52 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2026 to 2035.
Resistant Starch Market — Growth Factors
The resistant starch market is expanding rapidly due to rising global awareness of gut health, increasing demand for functional and fiber-rich foods, and growing interest in prebiotic ingredients that support metabolic wellness. Food manufacturers are incorporating resistant starch into bakery, beverages, dairy, cereals, snacks, and dietary supplements to enhance fiber levels without affecting taste or texture, which boosts adoption. New research linking resistant starch to benefits such as blood-glucose regulation, satiety, and improved gut microbiome health is shaping consumer preferences and product innovation.
Additionally, advances in enzymatic modification and retrogradation technologies are enabling the development of more stable and versatile resistant starch types (RS2, RS3, RS4, and RS5). Governments and regulatory bodies across major markets are increasingly recognizing resistant starch as a functional fiber, supporting labeling claims and fostering industry confidence. Finally, expanding production of green banana flour, cassava-based starches, and high-amylose maize starch in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and North America is strengthening supply chains and encouraging local manufacturing and export growth.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2835
What Is the Resistant Starch Market?
The resistant starch market encompasses the global production, processing, distribution, and commercialization of starches that resist digestion in the small intestine and function similarly to dietary fiber. These ingredients originate from high-amylose maize, potatoes, green bananas, cassava, pulses, wheat, and specially modified starches produced via heat, moisture, enzymatic treatment, or chemical modification. The market includes raw material suppliers, starch processors, specialty ingredient manufacturers, food and beverage producers, nutraceutical brands, and research organizations developing new resistant starch formulations.
Resistant starch is classified into multiple types—RS1 (physically inaccessible), RS2 (native granular), RS3 (retrograded), RS4 (chemically modified), and RS5 (amylose-lipid complexes)—each offering different functional and nutritional attributes that determine their use across food, health, and industrial applications. The global market has grown to a multibillion-dollar industry as manufacturers adopt resistant starch to create healthier, fiber-enriched, low-glycemic, and digestive wellness products.
Why Is Resistant Starch Important?
Resistant starch plays a pivotal role in modern nutrition, public health initiatives, and food technology. It behaves like dietary fiber, bypassing digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract and fermenting in the colon, producing beneficial short-chain fatty acids such as butyrate. This fermentation supports microbiome diversity, colon health, inflammation reduction, and improved metabolic function. For food manufacturers, resistant starch is a high-value functional ingredient enabling reformulation of everyday foods—bread, pasta, snacks, milk alternatives, yogurts, infant foods—without compromising taste or texture. It allows brands to meet rising consumer expectations for clean-label, high-fiber, and gut-friendly products.
For governments and regulators, resistant starch aligns with programs aimed at improving fiber intake, combating obesity, supporting diabetic populations, and enhancing public nutrition. It also has a sustainability dimension, as resistant starch production often uses underutilized crops such as green bananas, cassava, and pulses, supporting rural economies and reducing agricultural waste.
Top Companies in the Resistant Starch Market
Below are detailed profiles of the leading companies, including specialization, focus areas, notable features, revenue insights, and global presence.
1. Cargill
Specialization:
A leading global agribusiness and food-ingredients corporation supplying starches, sweeteners, plant-based ingredients, and agricultural commodities.
Key Focus Areas:
Starch innovation, functional food ingredients, sustainable sourcing, crop-based industrial ingredients, and large-scale supply chain solutions for global food manufacturers.
Notable Features:
Cargill operates one of the largest ingredient production networks in the world, giving it a significant advantage in supplying high-quality maize-based and modified starch products that serve as platforms for resistant starch development. It partners with major consumer brands to deliver functional ingredients tailored for fiber enhancement and clean-label reformulation.
2024 Revenue / Market Share:
Cargill reported approximately USD 160 billion in total revenue in 2024. Although the company does not disclose resistant starch–specific revenue, its specialty starch division contributes a growing share to the functional ingredient market.
Global Presence:
A truly global footprint with operations in North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, supported by extensive R&D centers, processing plants, distribution hubs, and supplier networks.
2. Xian Kono Chem (Kono Chemical)
Specialization:
A Chinese manufacturer specializing in chemicals, nutraceutical ingredients, plant extracts, and specialty starches, including resistant starch products such as RS3.
Key Focus Areas:
Bulk ingredient manufacturing, modified starch production, export-oriented supply chains, and custom formulation for global B2B buyers.
Notable Features:
The company offers a range of chemically modified and physically treated starches suited for functional food applications. It is known for producing RS3 resistant starch using retrogradation and other processing methods.
2024 Revenue / Market Share:
As a privately held Chinese exporter, the company does not publicly disclose audited revenue figures. Resistant starch is one of several product categories it supplies to international clients.
Global Presence:
Exports to North America, Europe, Southeast Asia, and South America. Operates primarily from Xi’an with a strong online and distributor-based international sales model.
3. Sheekharr Starch Private Limited (India)
Specialization:
An Indian starch and derivatives supplier focused on maize, potato, tapioca, and modified starches for food and industrial applications.
Key Focus Areas:
Native starches, modified starches, functional ingredients for snack manufacturing, bakery, textile processing, paper industry, and food processing.
Notable Features:
Sheekharr Starch is part of India’s rapidly expanding starch-processing ecosystem. The company manufactures both native starch and higher-value derivatives that can be developed into resistant starch ingredients for domestic and regional customers.
2024 Revenue / Market Share:
The company’s revenue is modest relative to multinational competitors. It does not publicly publish resistant-starch-specific revenue figures; available corporate filings indicate steady operations in the Indian starch sector.
Global Presence:
Serves the Indian market with some exports to nearby regions. Most operations and partnerships are domestic, supporting local food and industrial manufacturers.
4. SunOpta
Specialization:
A North American plant-based food and ingredient company producing oat beverages, plant-based extracts, fruit ingredients, and nutritional solutions.
Key Focus Areas:
Plant-based beverages, sustainable ingredient sourcing, organic fruit-based ingredients, and functional food components that can integrate resistant starch for fiber enhancement.
Notable Features:
SunOpta leverages advanced processing facilities and strong relationships with major foodservice chains and retail brands. Its ingredient platforms support the inclusion of resistant starch in plant-based and better-for-you product lines.
2024 Revenue / Market Share:
The company reported USD 193.9 million in revenue for Q4 2024, with full-year revenue reflecting mixed performance in plant-based beverages and fruit-based ingredients. Resistant starch is not reported as a separate revenue line.
Global Presence:
Primary operations in the United States and Canada, with supplier relationships and export capabilities connecting the company to global markets.
5. Natural Stacks
Specialization:
A U.S.-based nutritional supplement brand focused on nootropics and gut-health support products, including resistant-starch-based prebiotics.
Key Focus Areas:
Consumer health supplements, prebiotic blends, gut-brain health formulas, and natural ingredient-based wellness products.
Notable Features:
Known for transparent labeling, clean-label formulas, and direct-to-consumer marketing. Produces resistant starch prebiotic capsules and powders aimed at improving digestion, microbiome health, and metabolic function.
2024 Revenue / Market Share:
Estimated annual revenue for 2024 is approximately USD 4.2 million, according to business intelligence reports. Resistant starch supplements form part of its core product offerings.
Global Presence:
Primarily focused on the U.S. market with international online sales and online reseller networks.
Leading Trends in the Resistant Starch Market and Their Impact
1. Rising Focus on Gut Health and Microbiome Science
Growing consumer awareness about the gut microbiome is driving demand for prebiotic fibers like resistant starch. Brands are highlighting digestive health, IBS relief, metabolic wellness, and immunity benefits. This trend is accelerating product launches in the functional foods and dietary supplements categories.
2. Innovation in Processing Technologies
Advancements in enzymatic modification, heat-moisture treatment, and retrogradation processes allow manufacturers to create more stable RS2 and RS3 starches. These technologies improve solubility, heat resistance, and sensory properties, enabling resistant starch to be incorporated into mainstream products.
3. Alternative Feedstocks and Sustainability
Farmers and ingredient companies are increasingly using green bananas, pulses, and cassava to produce resistant starch. These crop sources support sustainability, reduce food waste, and promote agricultural diversification.
4. Clean-Label and High-Fiber Reformulation
Food manufacturers are replacing synthetic additives with natural functional fibers. Resistant starch helps companies meet clean-label demands while improving nutritional profiles—raising fiber content, reducing net carbs, and lowering glycemic index.
5. Regulatory Support for Dietary Fiber Labeling
In several regions, specific types of resistant starch qualify as dietary fiber. This allows manufacturers to make legally compliant fiber-boost claims, increasing its commercial attractiveness.
Successful Examples of Resistant Starch Use Worldwide
1. Green Banana Flour in Latin America and Africa
Producers have commercialized green banana flour (naturally rich in RS2), using it in bakery mixes, gluten-free foods, and nutritional supplements. This has empowered local farmers and created export-oriented value chains.
2. High-Amylose Maize Starch in the U.S. and Europe
Large food manufacturers use high-amylose maize–derived resistant starch to develop low-carb breads, cereals, and snack bars, achieving better texture and fiber levels without compromising product quality.
3. Cassava-Based Resistant Starch in Southeast Asia
Cassava processors are producing modified starches that retrograde into RS3, fueling exports of high-value starch derivatives and expanding regional manufacturing capacity.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Policies Shaping the Market
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific leads the global market due to abundant raw materials such as cassava, rice, maize, and bananas. Countries like India, Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia have government programs supporting value-added starch processing, export incentives, and agricultural R&D. Public institutions are funding research into RS3 and RS4 technology, positioning the region as both a major consumer and supplier.
North America
North America is a major hub for functional foods, clinical nutrition, and nutraceutical innovation. Strong R&D infrastructure and clear dietary fiber regulations support resistant starch growth. The U.S. market has high demand for gut-health products, diabetic-friendly foods, and low-carb formulations, directly benefiting RS suppliers.
Europe
Europe emphasizes clean-label, organic, and sustainability-driven nutrition trends. Resistant starch adoption is rising in bakery, gluten-free foods, and plant-based categories. EU regulations around fiber claims, labeling, and health messaging significantly influence formulation decisions.
Latin America
Countries like Brazil, Colombia, and Peru are increasing investments in banana and cassava processing. Governments promote rural development and crop diversification, creating opportunities for resistant starch producers using locally available resources.
Middle East & Africa
Growing urbanization and rising lifestyle-related disease rates are increasing interest in fiber-enriched foods. Africa, with its large production of plantains, sorghum, and cassava, has strong potential for local resistant starch industries, supported by agricultural development programs.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Organic Starch Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035