Physical AI Market Growth Drivers, Key Players, Trends and Regional Insights by 2034
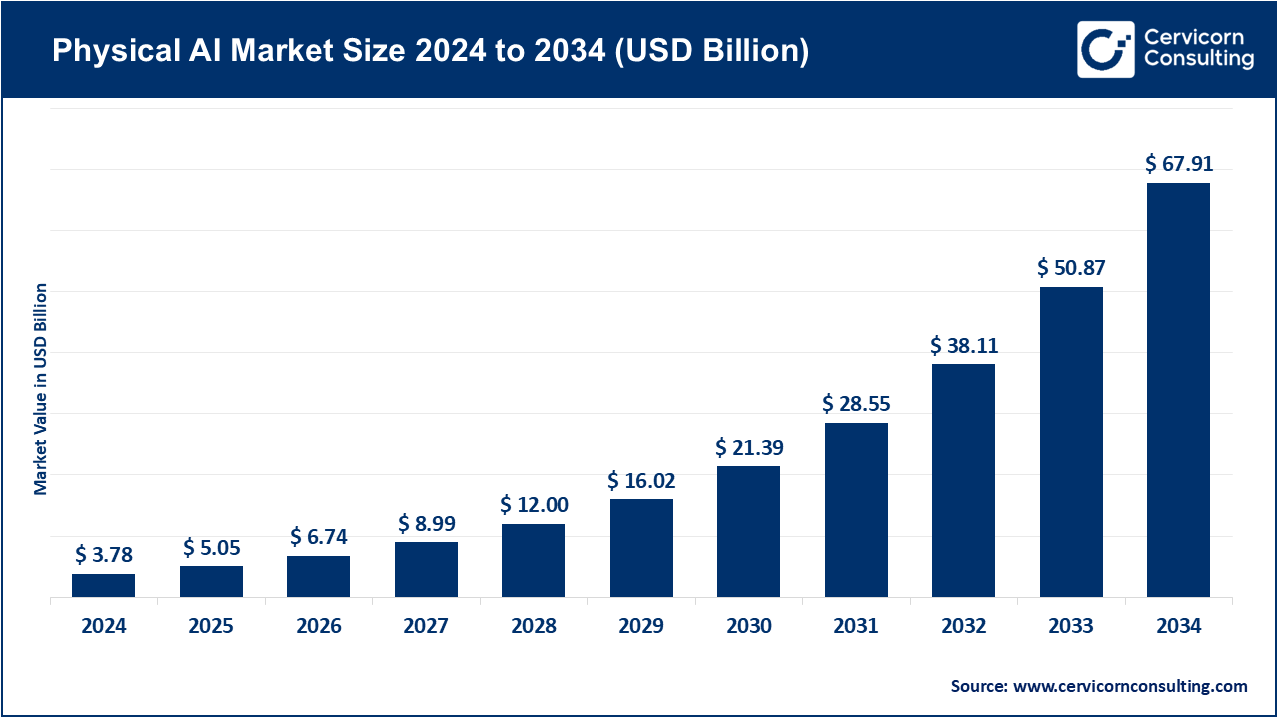
Physical AI Market Size
What is the Physical AI Market?
The Physical AI market is the collection of products, services, and systems that combine artificial intelligence (perception, reasoning, and learning) with robots, autonomous machines, and embedded devices that interact with the physical world. It includes industrial robot arms augmented with vision and adaptive control, mobile robots and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) for logistics, humanoid/service robots for customer assistance and care, robotic inspection systems for infrastructure, and hybrid cyber-physical systems that combine software-defined behavior with hardware platforms. The market also contains enabling components: perception stacks, edge AI compute, simulation platforms, digital twins, firmware, sensors, and system integrators that deploy and maintain the robots.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2741
Why Physical AI Matters
Physical AI matters because automation that can sense context, reason about unknowns, and adapt in real time unlocks productivity and capabilities unreachable by rigid automation. In manufacturing, it reduces changeover time, improves quality, and enables mass customization. In logistics, it speeds throughput and reduces human strain. In healthcare and elder care, it augments scarce professionals. In energy and infrastructure, it does dangerous inspection work. And in everyday environments, it creates new service experiences. Critically, Physical AI is not just software wins — it reshapes supply chains, labor economics, and the geography of production by making automation more flexible, safer, and economically viable outside the largest factories.
Growth Factors
Physical AI’s rapid expansion is propelled by five tightly linked forces: (1) advances in perception and generalization (vision transformers, multimodal models, and sim-to-real techniques) that let machines interpret noisy real-world inputs; (2) falling costs and improving performance of edge compute (AI accelerators and energy-efficient inference) enabling on-device decision making; (3) an urgent need to automate because of aging workforces, labor shortages, and rising wages in key manufacturing markets; (4) supply-chain reconfiguration and reshoring which pushes producers to automate flexibly at regional sites instead of relying on low-cost mass production; and (5) expanding non-industrial use cases — health, service, retail, and infrastructure inspection — where safe, adaptive autonomy creates entirely new product categories and service businesses.
Public and private investment (national robotics strategies, R&D programs, corporate investments) plus a growing ecosystem of system integrators and cloud/robotics platforms further accelerate adoption and lower deployment risk for end customers.
Leading Companies: Profiles, Specializations, and 2024 Context
SoftBank Robotics Group
-
Specialization: Humanoid and service robots (Pepper, NAO); software for human-robot interaction and cloud services; investments and partnerships across robotics startups.
-
Key Focus Areas: Social/service robots for retail and customer engagement, developer ecosystems for conversational/gesture interfaces, and partnerships to commercialize robotics as a service.
-
Notable Features: Early commercial humanoids (Pepper), large brand recognition in service/retail deployments, close ties to SoftBank’s investment and AI strategy.
-
2024 Revenue / Market Share: SoftBank Robotics Group’s standalone 2024 revenue is not disclosed separately; however, it remains a globally recognized player in service/humanoid robotics.
-
Global Presence: Headquartered in Japan with deployments across Europe, North America, Middle East, and Asia.
ABB (Robotics)
-
Specialization: Industrial robot arms, collaborative robots, controllers, and software for manufacturing automation; systems integrator services.
-
Key Focus Areas: Automotive, electronics, food & beverage, logistics automation, and digital services.
-
Notable Features: Deep installed base in industrial customers, strong service network, and investments in training and local manufacturing. ABB is preparing to spin out its robotics division to sharpen focus.
-
2024 Revenue / Market Share: ABB’s Robotics division generated about $2.3 billion in revenues in 2024, making it a top global player in industrial robotics.
-
Global Presence: Strong manufacturing and service footprint across Europe, North America, China, and other manufacturing hubs.
Toyota Motor Corporation (Robotics & Mobility Divisions)
-
Specialization: Mobility robotics (autonomous and assisted driving), factory automation, logistics robots, and human-assistance robots via Toyota Research Institute.
-
Key Focus Areas: Autonomous mobility, manufacturing automation, robotics for home/elder care, and logistics.
-
Notable Features: Massive R&D resources, deep expertise in manufacturing, and long-horizon investments in robotics and autonomy.
-
2024 Revenue / Market Share: Toyota’s consolidated revenue for FY2024 was about $311 billion; robotics revenue is embedded within its broader automotive and mobility reporting.
-
Global Presence: Major R&D and production in Japan, North America, Europe, and Asia with growing robotics research labs.
FANUC
-
Specialization: Industrial automation, CNC controllers, and a broad portfolio of industrial robots.
-
Key Focus Areas: Factory automation, electronics, machine tools, and digitalization for next-gen operators.
-
Notable Features: Large installed base worldwide, reputation for reliability, and product innovation in heavy-payload robots.
-
2024 Revenue / Market Share: FANUC’s 2024 annual revenue was approximately $5.5 billion, making it one of the largest industrial robot vendors globally.
-
Global Presence: Japan-based with strong global networks across Asia, North America, and Europe.
Siemens (Digital Industries / Automation)
-
Specialization: Industrial automation, motion control, digital twin, and software for robotic and automated systems.
-
Key Focus Areas: Industrial digitalization (Siemens X), additive manufacturing automation, and software ecosystems for orchestration.
-
Notable Features: Strong digital twin portfolio, cross-industry reach, and systems integration expertise.
-
2024 Revenue / Market Share: Siemens reported €75.9 billion in revenue for fiscal 2024; robotics revenue sits within its industrial automation segments.
-
Global Presence: Extensive footprint across Europe, Asia, and the Americas, with strong partnerships across industrial ecosystems.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
-
Embodied foundation models & multimodal learning — Robots are gaining the ability to generalize across tasks, lowering engineering costs and enabling higher autonomy.
-
Edge AI and accelerators — On-device AI lowers latency, improves safety, and enables deployment in environments without reliable connectivity.
-
Robotics as a Service (RaaS) — Subscription-based robotics adoption is lowering upfront costs, enabling SMEs to scale automation quickly.
-
Human-robot collaboration (cobots) — Certified cobots allow safe side-by-side work with humans, boosting factory flexibility.
-
Regional supply chain reshaping — National strategies and subsidies are influencing where robots are built, tested, and deployed, creating localized supply ecosystems.
Successful Examples Around the World
-
ABB’s U.S. Robotics Expansion (Auburn Hills) — Increasing capacity and training to serve North American customers.
-
China’s Service Robot Investments — Large municipal programs and subsidies scaling service and humanoid robot deployments.
-
FANUC & Toyota in Automotive Factories — Longstanding examples of high-throughput, AI-enabled automation in vehicle production.
-
Humanoid Startups (e.g., Figure) — Attracting large funding rounds, showing investor confidence in general-purpose physical AI.
Global Regional Analysis — Demand, Government Initiatives and Policies
Asia (China, Japan, South Korea)
-
Demand Drivers: Factory automation, logistics modernization, and service robot pilots.
-
Policy: National robotics strategies, subsidies, and municipal funding accelerate adoption.
North America (U.S., Canada)
-
Demand Drivers: Logistics automation, reshoring, healthcare, and defense.
-
Policy: CHIPS and Science Act and robotics-focused R&D funding support domestic ecosystems.
Europe
-
Demand Drivers: High-value manufacturing, healthcare robotics, and strong focus on safety.
-
Policy: EU AI Act, robotics standardization, and dedicated robotics programs.
Middle East, Latin America, Africa
-
Demand Drivers: Pilots in logistics, mining, and public services, with varying adoption speeds.
-
Policy: Gulf states investing in robotics diversification, while others rely on foreign partnerships.
How Policy is Shaping Vendor Strategy
Government strategies are pushing vendors to localize manufacturing, comply with evolving safety standards, and adopt Robotics-as-a-Service models to expand adoption. Funding programs and national robotics roadmaps are accelerating R&D, while procurement policies in Asia, the U.S., and the EU are reshaping vendor go-to-market strategies.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Whey Protein Market Growth Trends, Top Companies, Global Insights and Adoption