India Insurance Market Growth Drivers, Key Players, Trends and Regional Insights by 2034
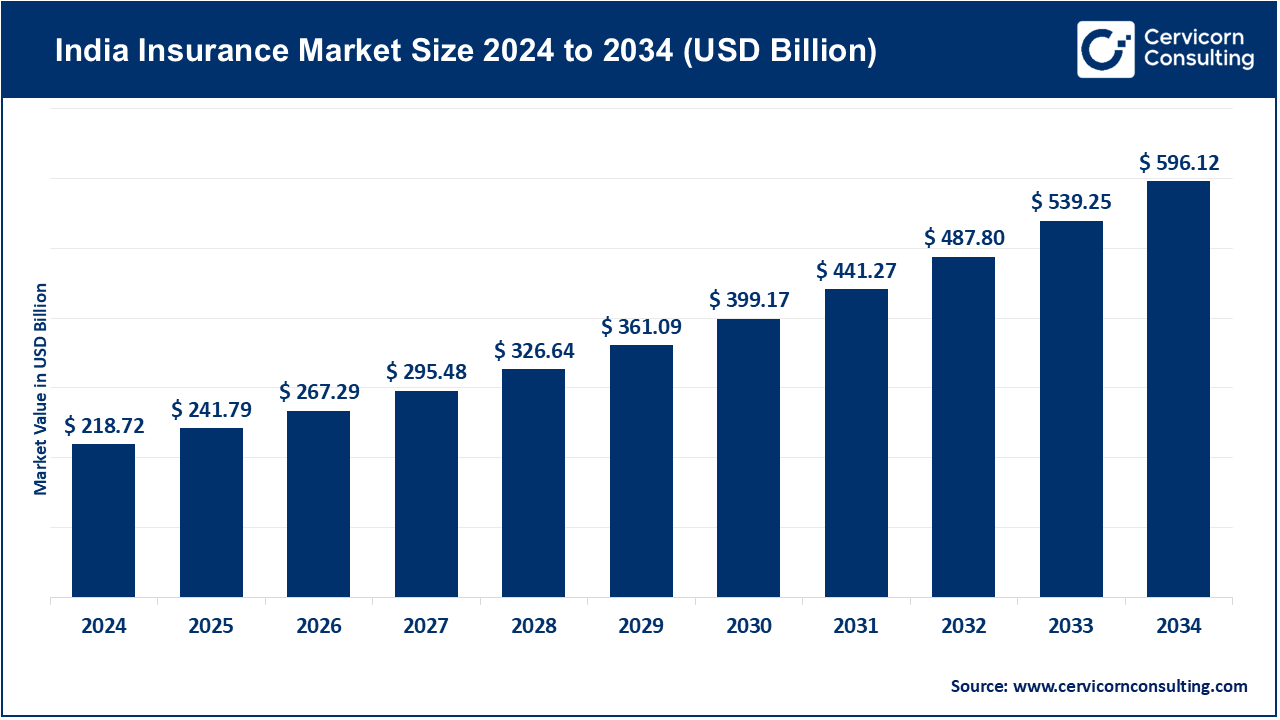
India insurance market size
India insurance market Growth Factors
A combination of macro and micro forces is driving the India insurance market: rising disposable incomes and a growing middle class that want protection and savings; urbanization and salaried employment that increase demand for group and retail solutions; changing demographics (longer life expectancy, aging cohorts in urban pockets) that boost life and health products; increasing healthcare costs that push retail health insurance uptake; government-led financial inclusion initiatives and state-sponsored schemes that broaden the addressable market; technology diffusion — specifically mobile penetration, digital KYC, and API-driven distribution — lowering distribution costs and reaching remote customers; product innovation (hybrid savings-insurance products, microinsurance, telemedicine-linked health policies); regulatory reforms that strengthen solvency, disclosure and consumer protections.
Growing investor interest which supplies capital for scale, partnerships and insurtech experimentation. These forces combine to expand premium volumes, but they also push insurers to focus on unit economics, persistency, and shifting product mixes (for example toward low-margin ULIPs during buoyant equity markets), which influence profitability and product strategy.
What is the India insurance market? Why is it important?
The India insurance market consists of two principal segments: life insurance (protection, savings and investment-linked life products) and non-life (general) insurance (motor, health, property, liability, crop, travel, etc.). Historically, life insurance accounts for the majority of premium volumes in India — significantly higher than many countries where non-life share is larger — although non-life has been growing strongly in recent years (notably health and motor).
The market comprises public sector behemoths, large private players, specialized insurers (health, crop, reinsurance), and a vibrant distribution ecosystem of bancassurance, agency networks, brokers, digital aggregators, and direct channels. Its importance stems from multiple channels: insurance protects households and businesses against idiosyncratic shocks (health, death, liability, property loss), fosters savings and long-term capital formation (insurer investments support bond and equity markets), supports credit markets (through collateralization and credit-life products), and is a critical social stabilizer in the face of healthcare inflation and climate risk. A deeper, accessible insurance market also helps the broader economy become more resilient — reducing systemic vulnerability from health or disaster shocks and enabling entrepreneurs and households to take productive risks.
India Insurance Market — Top Companies (profiles)
Below are profiles of the most prominent life insurers you asked to include. For each I summarize specialization, focus areas and notable features; for 2024 revenue/premium context and market share I use regulator/annual report indicators and company disclosures where available.
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC)
- Company: Life Insurance Corporation of India (state majority / listed arm after IPO).
- Specialization: Mass-market life protection and savings; large public-sector retail presence; significant group business.
- Key focus areas: Retail protection, traditional endowment and pension products, large agency distribution, increasing digital servicing, and strategic investments in financial services.
- Notable features: Dominant distribution footprint (millions of agents and a presence in rural and urban India), extremely large asset base (LIC is by far the largest institutional investor among Indian insurers), government ownership linkages which influence scale and public trust.
- 2024 revenue / premium: LIC’s published accounts show very large premium inflows and a sizeable revenue and investment income base. LIC continues to report the largest share of life premiums in India given its scale.
- Market share: LIC remains the market leader in life insurance by new business volumes and overall AUM/premiums, though its share has been declining gradually as private players expand.
- Global presence: LIC’s operations are predominantly India-centric; its international footprint is limited compared with global life insurers, although it has been expanding certain cross-border offerings for NRIs and exploring strategic investments and reinsurance partnerships.
HDFC Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: HDFC Life (one of India’s leading private life insurers).
- Specialization: Retail protection and savings products, ULIPs (unit-linked plans), pension plans, group policies.
- Key focus areas: Technology-enabled distribution (agency + bancassurance), digital onboarding, product innovation (pension & retirement solutions), and improving persistency and VNB (value of new business) margins.
- Notable features: Strong bancassurance ties (initially with HDFC Bank), broad retail footprint, emphasis on AUM growth through wealth-linked products and renewal income.
- 2024 revenue / premium: HDFC Life’s FY2024 consolidated filings report continued premium and AUM growth; the company publishes detailed integrated annual reports.
- Market share: Among the top private life insurers by new business APE and overall weighted premium; market share has trended upward in retail segments.
- Global presence: Focused largely on India, with targeted international products (for NRIs) and reinsurance relationships abroad.
ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: ICICI Prudential Life (large private sector life insurer).
- Specialization: Broad retail and group life products; significant presence in ULIPs and protection products.
- Key focus areas: Strengthening agency and bancassurance channels, product segmentation to balance ULIP vs protection margins, and distribution efficiency.
- Notable features: One of the pioneers among private life insurers in combining bancassurance with agency networks; strong brand recognition and retail reach.
- 2024 revenue / premium: ICICI Prudential reported APE and premium growth in FY24 but also disclosed a contraction in VNB and VNB margin linked to product mix shifts.
- Market share: Typically among the top two or three private life insurers by APE and volumes.
- Global presence: Operations are India-focused; reinsurance and product partnerships with global reinsurers.
SBI Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: SBI Life (joint venture between State Bank of India and a private partner).
- Specialization: Retail life, group, and pension products; strong bancassurance via SBI.
- Key focus areas: Leveraging SBI’s vast branch network and customer base, diversifying product mix, and improving VNB through higher-margin products.
- Notable features: Deep bancassurance advantage (access to SBI’s customer ecosystem), competitive product pricing and distribution strength.
- 2024 revenue / premium: SBI Life’s FY24 integrated annual report documents premium growth and financial metrics; the company reported strong renewal and new business premium trends.
- Market share: Among the leading private life insurers — often ranking in the top three by new business APE and overall premium income.
- Global presence: India-centric with limited overseas operations; some NRI-facing products.
Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: Bajaj Allianz Life (private sector life insurer, JV between Bajaj Finserv and Allianz).
- Specialization: Protection, savings, ULIPs, term and health riders.
- Key focus areas: Agency and corporate agency distribution, digital sales, product bundling with lending and consumer finance (Bajaj Finserv ecosystem).
- Notable features: Synergies with Bajaj Finserv for cross-sell; Allianz’s global expertise in risk management and product design.
- 2024 revenue / premium & market share: A major private player; continues to grow APE and retail flows, contributing to the private sector’s rising share.
Reliance Nippon Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: Reliance Nippon Life (rebranded variations exist after restructuring).
- Specialization & focus areas: Broad life product mix with emphasis on retail protection and mass distribution.
- Notable features: Tends to leverage Reliance’s consumer reach and distribution; corporate structure has evolved through strategic transactions.
- 2024 revenue / premium & market share: Part of the competitive private cohort — figures shift with corporate reorganizations; consult company filings for exact FY24 numbers.
Tata AIA Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: Tata AIA Life (JV between Tata Group and AIA Group).
- Specialization: Retail protection, savings and health riders; strong emphasis on customer service and digital propositions.
- Key focus areas: Omnichannel distribution, affinity partnerships, product innovation aimed at working professionals and affluent segments.
- Notable features: Benefits from Tata’s brand trust and AIA’s Asiawide life insurance expertise and product playbook.
- 2024 revenue / premium & market share: A leading private insurer with steady growth in premium and new business metrics.
Max Life Insurance Company Ltd.
- Company: Max Life (large private life insurer; Max Financial Services listed parent).
- Specialization: Protection, savings, term plans, retirement products, group solutions.
- Key focus areas: Agency network strength, digital sales and advice models, and enhancing persistency through customer engagement.
- Notable features: Solid retail orientation, focus on higher-margin protection products and bancassurance partnerships.
- 2024 revenue / premium & market share: Among top private insurers; FY24 figures and investor materials provide exact numbers for APE and premium.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
- Digital distribution and insurtech: Mobile onboarding, e-sign/KYC, robo-advice and API distribution lower acquisition costs and enable micro-insurance and on-demand offerings. Impact: faster reach into semi-urban and rural markets, better unit economics for small premium products, and higher competition from digital natives.
- Shift toward health insurance and top-ups: Rising healthcare costs and post-COVID risk awareness have accelerated retail health adoption and group health renewals. Impact: General insurers see double-digit premium growth in health; life insurers add health riders and bancassurance bundles.
- ULIP vs Protection product dynamics: Buoyant equity markets push customers toward unit-linked plans (ULIPs), improving top-line premium growth but compressing VNB margins. Impact: Insurers must rebalance product mix to protect profits by selling more pure protection and higher-margin term plans.
- Regulatory changes (IRDAI): New persistency rules, surrender value guidelines, and product standardization aim to protect consumers. Impact: Short-term churn in product offerings, direct effects on surrender costs and profitability; long-term gains in consumer confidence.
- Data, analytics and pricing sophistication: Telematics for motor, wearables for life/health underwriting, and AI for fraud detection. Impact: Better risk segmentation, personalized pricing, and potential reduced loss ratios — but also privacy and data governance challenges.
- Climate and catastrophe risk modeling: For non-life (property, crop), climate volatility pushes reinsurers and insurers to price risk more accurately. Impact: Need for catastrophe capital, parametric products (especially for agriculture), and increased government-private collaboration for affordability.
- Bancassurance and ecosystems: Banks, fintechs and retail conglomerates embed insurance into lending and payment flows. Impact: Distribution scale benefits incumbents, but digital aggregators and marketplaces intensify competition.
- Talent and operating model shifts: Insurers invest in agile teams, cloud migration and partnerships with fintechs. Impact: Faster product rollout and improved customer journeys, but legacy firms face transformation costs.
Successful Examples of India Insurance Models Replicated Globally
- Bancassurance scale model: Large bank-insurer tie-ups (e.g., SBI Life with SBI) demonstrate how leveraging retail bank branches and customer data can drive efficient distribution — a model copied by banks and insurers in Southeast Asia and Africa.
- Microinsurance & mobile first distribution: Indian microinsurance pilots that combine low premiums with mobile premium collection inspired similar offerings in parts of Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Agency plus tech hybrid: Large Indian insurers combine extensive agency networks with digital tools (lead generation, mobile apps, analytics) — a blended approach that emerging markets emulate.
- Parametric crop and hybrid health products: India’s development of agriculture insurance and government-linked crop schemes has informed parametric designs elsewhere where fast payouts are needed after weather events.
Global Regional Analysis — Government Initiatives and Policies
India (national)
- IRDAI oversight & reforms: The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) sets solvency, product approval and disclosure standards. Recent focus has been on enhancing consumer protection, improving product standardization, tightening surrender rules and promoting digital KYC and e-sign.
- Government insurance schemes: Large, government-sponsored schemes such as Ayushman Bharat (PM-JAY), crop insurance programs, and subsidized life/accident covers expand coverage and create distribution opportunities for private insurers.
- Financial inclusion & Jan Dhan / digital ID: Aadhaar and Jan Dhan accounts plus digital payments make it easier to underwrite, collect premiums and deliver claims, lowering costs for last-mile distribution.
Asia (regional context)
- ASEAN & South Asia: Many neighboring countries with under-penetrated markets look to India’s mix of private competition, public schemes, and digital adoption as a model; cross-border reinsurance and product innovation flows are evident between India, Singapore, and Middle Eastern hubs.
- Reinsurance & capital flows: Global reinsurers and private equity are active in the region; India’s growing premium pool attracts capacity but also higher scrutiny on pricing for catastrophe and health risks.
Developed markets (EU, USA)
- Regulatory differences & product sophistication: Developed markets show higher penetration and different product mixes (greater non-life share), but Indian insurers increasingly adopt their underwriting, analytics and governance frameworks (Solvency practices, IFRS/IND AS accounting, risk management).
Global initiatives affecting India
- Climate and disaster finance initiatives: International climate funds and insurance-linked securities (ILS) platforms encourage parametric solutions for agriculture and disasters in India.
- Bilateral regulatory collaboration: Cross-border cooperation on reinsurance, standard setting and data sharing helps domestic insurers access global capital and technical expertise.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Warehousing Market Growth Drivers, Key Players, Trends & Regional Insights by 2034