Electric Vehicle Charging (EV) Infrastructure Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035
Electric Vehicle Charging (EV) Infrastructure Market Size
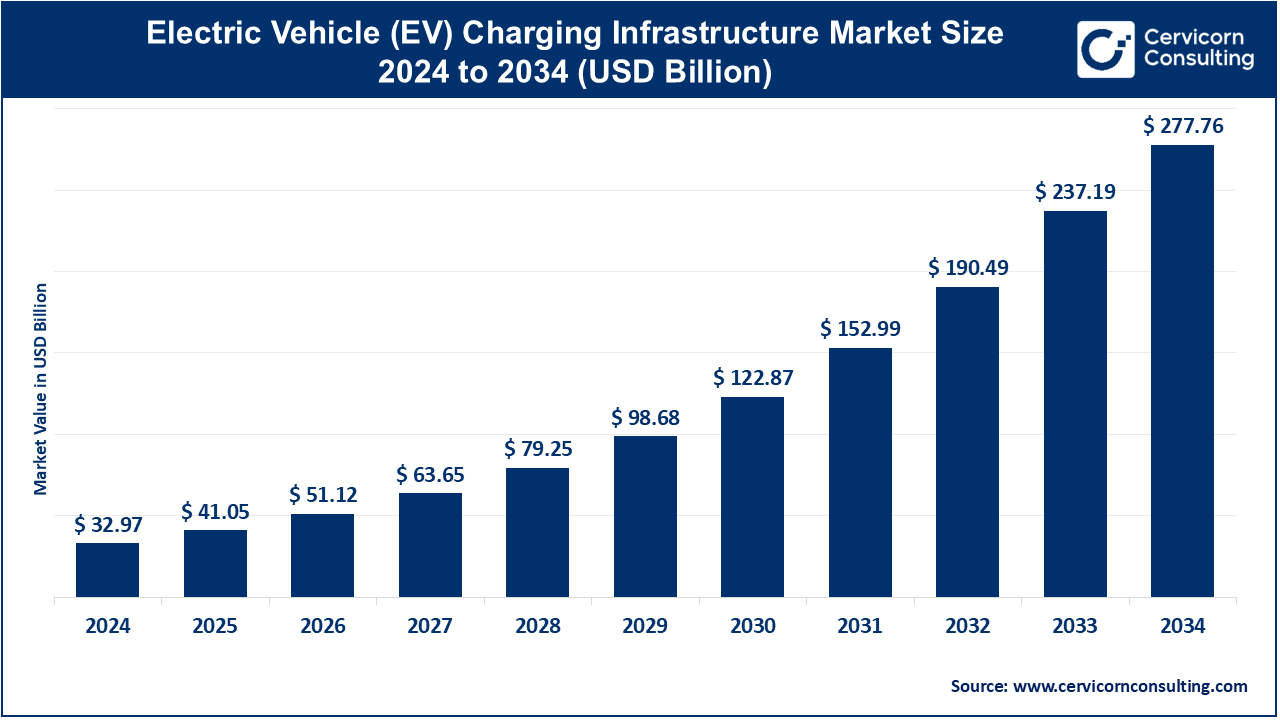
The global electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure market size was worth USD 32.97 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 277.76 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.75% from 2025 to 2034.
EV Charging Infrastructure Market Growth Factors
Growth in the electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure market is propelled by surging EV sales, strengthened government incentives, large-scale emissions-reduction commitments, and rapid technological advancement in fast-charging systems. Rising consumer preference for sustainable mobility, expanding fleet electrification, and the adoption of smart charging technologies further accelerate demand. Governments worldwide are providing subsidies, tax credits, and regulatory mandates for public and private charging deployment, while major energy, automotive, and tech companies invest heavily in building networks.
Improvements in battery technology, price drops in EV components, integration of renewable energy, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities, and advanced software platforms for charger management all contribute to the market’s rapid expansion. Collectively, these factors are creating a high-growth environment with a long-term, recurring revenue potential for hardware providers, network operators, utilities, and energy companies.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2374
What Is the EV Charging Infrastructure Market?
The EV charging infrastructure market encompasses the entire ecosystem of technologies, hardware, software, and services that enable electric vehicle charging. It includes charging stations (AC and DC), grid connections, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, charging management software, payment platforms, maintenance services, and energy-management tools. These elements work together to ensure that EV users—individual drivers, commercial fleets, and mobility service providers—can reliably charge their vehicles at home, at work, and on public networks.
EV charging infrastructure typically includes:
- AC Chargers (Level 1 and Level 2): For residential, workplace, and low-power commercial applications.
- DC Fast Chargers (50 kW to 350+ kW): For public, highway corridor, and high-demand fleet use.
- Charging Management Software: Network monitoring, billing, diagnostics, energy optimization.
- Installation & Maintenance Services: Turnkey solutions, on-site evaluation, hardware deployment.
- Advanced Energy Systems: Load balancing, battery co-storage, renewable integration, and V2G capabilities.
This market is essential for supporting the EV ecosystem and ensuring smooth, efficient, and scalable electrification across transportation sectors.
Why Is It Important?
EV charging infrastructure is crucial because it directly determines the pace and scale of electric vehicle adoption. Without accessible and reliable charging, range anxiety persists, fleet electrification stalls, and the environmental benefits of EVs cannot be fully realized. Public charging networks enable long-distance travel, rapid turnover for delivery and logistics fleets, and increased convenience for drivers without access to home charging. Furthermore, advanced charging networks support grid resilience through smart charging and V2G programs, reduce carbon emissions by integrating renewables, and create economic opportunities in manufacturing, energy retail, software services, and infrastructure development.
Charging infrastructure also plays a central role in national energy strategies, urban planning, decarbonization goals, and large-scale shifts toward sustainable mobility.
Top Companies in the EV Charging Infrastructure Market
(Company, Specialization, Key Focus Areas, Notable Features, 2024 Revenue, Market Share, Global Presence)**
Below are detailed profiles of the leading companies shaping the EV charging infrastructure landscape.
1. Tesla, Inc.
Specialization:
Electric vehicles, energy systems, and one of the largest fast-charging networks in the world (Tesla Superchargers).
Key Focus Areas:
- Global expansion of the Supercharger network
- High-power DC fast charging
- Integration with vehicles, apps, navigation, and payments
- Increasing interoperability in select markets
Notable Features:
Tesla’s Supercharger network is known for exceptional reliability, high uptime, seamless user experience, and powerful charging speeds. It is fully integrated with Tesla vehicles, providing automatic routing and billing.
2024 Revenue:
Tesla generated approximately $97+ billion in total revenue in 2024, with charging-related revenue included under its services and energy segments.
Market Share:
One of the most influential EV charging network operators worldwide, especially in the U.S. and Europe.
Global Presence:
North America, Europe, China, Australia, and several other regions.
2. ChargePoint, Inc.
Specialization:
End-to-end EV charging hardware and software, with a strong emphasis on AC chargers and SaaS for businesses and fleets.
Key Focus Areas:
- Subscription-based charging management software
- Commercial charging for workplaces, fleets, and enterprises
- Robust AC charging network
- Cloud connectivity and advanced analytics
Notable Features:
ChargePoint operates one of the largest open charging networks globally, with a strong focus on software, recurring revenue, and enterprise fleet solutions.
2024 Revenue:
Generated around $506 million in FY2024.
Market Share:
Strong presence in North America and growing in Europe.
Global Presence:
United States, Canada, Europe, and strategic global partnerships.
3. Blink Charging Co.
Specialization:
Hardware manufacturing, network services, and turnkey charging station deployments.
Key Focus Areas:
- Site-host partnerships
- Product sales and charging services
- Public and private charging installations
- Growing operational and managed service models
Notable Features:
Blink supports both owner-operated and host-owned models, offering flexibility for landlords, businesses, and municipalities.
2024 Revenue:
Reported $126+ million in revenue for 2024.
Market Share:
Rapidly growing player with an expanding global footprint.
Global Presence:
United States, select markets in Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East.
4. ABB Ltd.
Specialization:
Global industrial manufacturer offering high-power DC fast chargers and integrated EV charging systems.
Key Focus Areas:
- Ultra-fast charging (150–350 kW+)
- Fleet depot and highway corridor solutions
- Grid-connected charging
- Industrial reliability and scalability
Notable Features:
ABB is a major supplier of high-power DC fast chargers used by governments, utilities, and private charging operators worldwide.
2024 Revenue:
Recorded over $32 billion in total revenue in 2024.
Market Share:
Dominant in DC fast charging manufacturing, particularly across Europe and Asia.
Global Presence:
Over 100 countries, with strong infrastructure support networks.
5. BP Chargemaster (BP Pulse)
Specialization:
Fast-charging networks powered by the energy giant BP.
Key Focus Areas:
- Public rapid charging at fuel stations
- Destination charging expansion
- Integration with BP’s retail energy network
- Growth of energy-as-a-service charging models
Notable Features:
BP Pulse leverages BP’s existing retail footprint (fuel stations) to deploy ultra-fast charging hubs in high-demand areas.
2024 Revenue:
BP does not report the charging segment separately, but the division continues to see significant growth in energy delivered and charger installations.
Market Share:
A leading operator in the UK and expanding across Europe.
Global Presence:
UK, Europe, and select international markets.
Leading Trends and Their Market Impact
1. Shift Toward Ultra-Fast DC Charging
Charger power levels continue to rise (150–350 kW+), enabling long-distance travel and supporting commercial fleet electrification. This dramatically increases the demand for grid partnerships, energy storage, and high-power components.
2. Growth of Software, IoT, and Managed Services
Charging networks now rely heavily on software platforms that offer:
- Remote diagnostics
- Billing and roaming
- Demand management
- Predictive maintenance
This shift boosts profitability via subscription-based models.
3. Integration of Renewable Energy & Energy Storage
On-site energy storage helps reduce demand charges and allows renewable-powered charging hubs. This trend supports grid stability and lowers operating costs.
4. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Adoption
Bi-directional charging allows EVs to act as mobile energy storage systems. Fleets and utilities are exploring V2G to offset energy costs and improve resilience.
5. Automaker-Energy Company Collaborations
Car manufacturers, utilities, and oil companies are investing directly in charging networks. This accelerates deployment speed and expands brand-controlled ecosystems.
6. Standardization & Interoperability
Interoperable charging standards enhance user experience and reduce fragmentation. Universal connectors and roaming agreements are gaining traction.
Successful EV Charging Infrastructure Examples Around the World
1. Tesla Supercharger Network (Global)
Recognized for convenience, high uptime, and seamless integration into Tesla vehicles, the Supercharger network remains one of the world’s most successful fast-charging systems.
2. China’s Nationwide Public Charging Expansion
China has built the largest EV charging network globally, with millions of chargers across residential complexes, commercial areas, and major highways. This mass deployment helped the country achieve one of the highest EV adoption rates in the world.
3. BP Pulse Charging Hubs (UK & Europe)
By converting fuel stations into charging hubs, BP Pulse provides accessible, high-speed charging for both commuters and long-distance travelers.
4. ChargePoint’s Enterprise Charging Programs (U.S. & Europe)
ChargePoint’s workplace and fleet solutions demonstrate how businesses can adopt EV infrastructure to reduce transportation emissions and improve fleet efficiency.
5. Government-Backed Corridor Charging Projects (EU & UK)
Large-scale, public-private programs have expanded coverage across key transport corridors, balancing urban and rural access.
Global Regional Analysis & Government Initiatives
North America (United States & Canada)
Government Initiatives:
- Federal tax credits for chargers
- Grants for rural and highway corridor charging
- State utility rebate programs
- Fleet electrification mandates
Impact:
These policies are accelerating public fast-charging installations and incentivizing workplaces, apartments, and fleets to adopt smart chargers.
Europe & United Kingdom
Government Initiatives:
- Binding charging infrastructure targets
- Funding for rapid charging corridors
- Incentives for residential and commercial chargers
- Strong environmental policies driving EV adoption
Impact:
Europe remains one of the most EV-friendly regions, with dense charging networks, strict emissions targets, and rapid buildout of ultra-fast chargers.
China
Government Initiatives:
- Subsidies for charging stations
- Urban planning policies mandating charger-to-parking ratios
- Support for battery-swapping networks
- Strong domestic manufacturing push
Impact:
China leads the world in EV charging density, affordability, and scale.
India & Southeast Asia
Government Initiatives:
- FAME II subsidies
- Tax reductions for EV charging equipment
- State-level incentives
- Support for electrification of public transport and fleets
Impact:
Growth is accelerating, but infrastructure gaps remain in rural and semi-urban areas. Fleet charging (buses, e-scooters) drives early adoption.
Latin America, Middle East, and Africa
Government Initiatives:
- Early-stage incentive programs
- Pilot corridor charging projects
- Urban sustainability initiatives
Impact:
EV charging is in the early growth phase, with significant long-term potential due to rising EV imports and sustainability mandates.
Final Note
The EV charging infrastructure market continues to expand rapidly due to technology innovation, supportive policies, rising EV adoption, and strong industry participation. Hardware, software, and energy services are converging into a unified ecosystem, transforming how people and businesses access clean mobility.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Industrial Distribution Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035