Generative AI in Insurance Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034
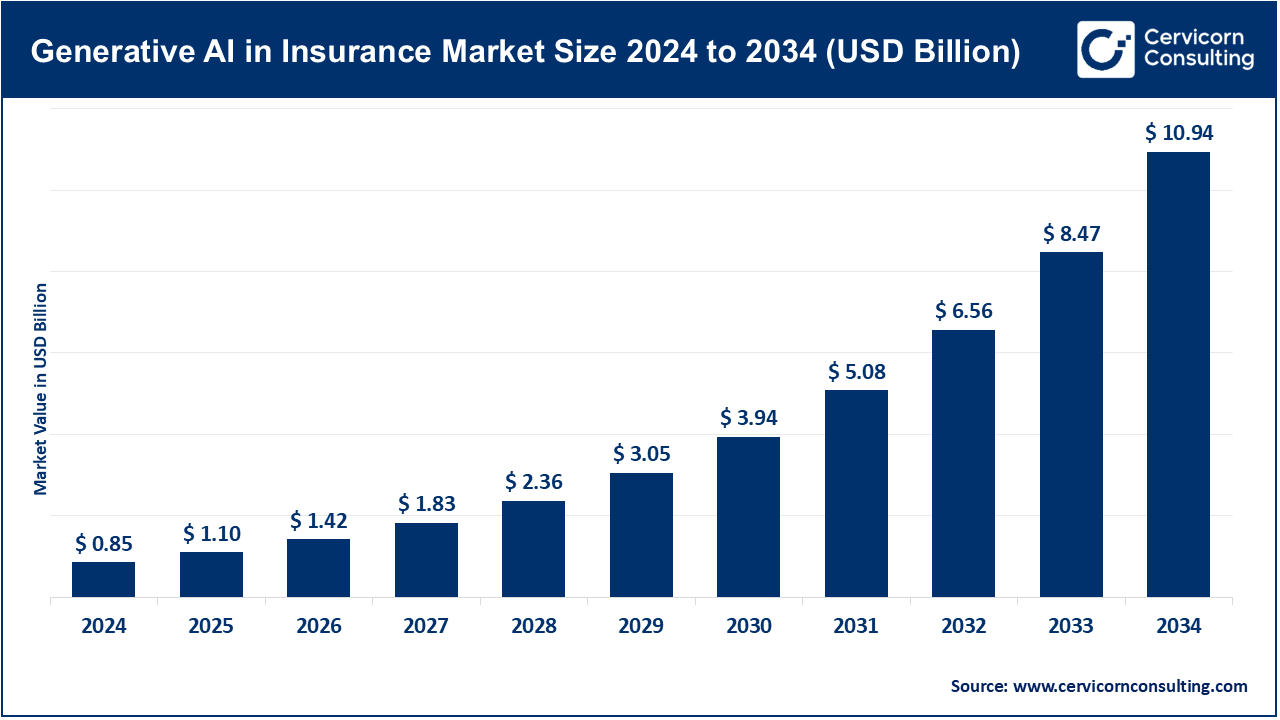
Generative AI in Insurance Market Size
Growth factors
The generative AI in insurance market is being driven by exploding volumes of structured and unstructured insurance data (claims notes, images, satellite/IoT feeds), rising pressure to reduce costs and cycle times in claims and underwriting, demand for hyper-personalized products and real-time customer servicing, improvements in foundation models, APIs and cloud infrastructure that make enterprise-grade generative AI feasible, regulatory and governance toolkits that are maturing to enable safer rollouts, and insurer partnerships with hyperscalers and niche AI vendors that speed deployment and deliver domain-specific models and data integrations. These factors together create a steep adoption curve and high investor interest as the market matures.
What is generative AI in the insurance market?
In the insurance context, generative AI refers to models (large language models, multimodal models, and related tools) that can generate human-readable outputs — policy summaries, claims narratives, decision explanations, synthetic training data, or structured risk features — from raw inputs such as documents, photos, and sensor streams. Instead of purely predictive scoring, generative AI synthesizes and composes new content and justifications. For example, it can draft a claim denial letter supported by evidence or create an automated underwriting memo that explains why a property is considered high risk. When combined with retrieval and domain constraints, these models become productivity assistants for underwriters, claims managers, customer service agents, and risk modelers.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2757
Why is generative AI important for insurance?
Insurance is a data-heavy, knowledge-work industry: decisions hinge on reading large volumes of documentation (policies, contracts, inspection reports, photos), contextualizing prior claims, and producing regulatory-compliant outputs. Generative AI helps scale that expertise by drafting structured outputs, surfacing reasoning traces, enabling faster and more consistent decisions, and improving customer experience through conversational interfaces. Because insurers operate on thin margins and within strict regulatory frameworks, the productivity gains and improved risk selection offered by generative AI can materially affect loss ratios, operational cost structures, and time-to-service, while also enabling new personalized pricing and product innovations.
Generative AI in Insurance — Top Companies
Microsoft Corporation
- Specialization: Cloud and AI platform including Azure, Azure OpenAI Service, industry accelerators, and Copilot-style integrations for enterprise workflows.
- Key Focus Areas for Insurance: Cognitive automation for claims and underwriting, enterprise-grade compliance and model governance, low-latency inference on Azure, prebuilt insurance accelerators for document ingestion and policy summarization.
- Notable Features: Tight integrations of OpenAI-powered models with Azure’s data and governance stack, measurable productivity gains shown in enterprise deployments, strong partner ecosystem with insurers and system integrators.
- 2024 Revenue (company level): Approximately USD 245 billion.
- Market Share: Not disclosed specifically for insurance, but Microsoft is a leading provider for enterprises through Azure and OpenAI integrations.
- Global Presence: Worldwide; strong presence in North America, Europe, and APAC with Azure regions and a broad partner network.
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS)
- Specialization: Cloud infrastructure and foundation model hosting through Amazon Bedrock and SageMaker, managed AI services, and vertical reference solutions for insurance.
- Key Focus Areas for Insurance: Claims automation, underwriting assistance, ingestion and vector retrieval for documents and images, custom model deployment, and insurtech partnerships.
- Notable Features: Bedrock managed foundation model service, diverse model catalog, and geospatial and data services essential for property risk analysis.
- 2024 Revenue (segment level): Around USD 107.6 billion.
- Market Share: Not published specifically for insurance, but AWS is widely used by insurers and insurtechs.
- Global Presence: Extensive data center footprint and deep partner network worldwide.
IBM Corporation
- Specialization: Enterprise AI and consulting with Watsonx platform, hybrid cloud, and governance frameworks for regulated industries.
- Key Focus Areas for Insurance: Safe model deployment in regulated environments, claims and document automation, domain-specific model development, and customer experience improvements.
- Notable Features: Watsonx as an enterprise foundation for generative AI, consulting expertise for integration into legacy systems, and strong emphasis on governance, explainability, and compliance.
- 2024 Revenue (company level): Around USD 62.8 billion.
- Market Share: Not disclosed specifically for insurance but recognized as a leader in governance-heavy deployments.
- Global Presence: Operations and clients globally with strong presence in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Avaamo Inc.
- Specialization: Conversational and generative AI platforms for enterprise with vertical templates in banking, insurance, and healthcare.
- Key Focus Areas for Insurance: Customer service automation, virtual assistants for claims and policies, data handling, and vertical-specific prebuilt models.
- Notable Features: Low-code deployment, insurance-focused templates, multilingual support, and contact center integrations.
- 2024 Revenue: Estimated USD 20–25 million.
- Market Share: Niche vendor specializing in conversational automation and enterprise-grade generative AI.
- Global Presence: Headquartered in the U.S. with global deployments across insurance and other industries.
Cape Analytics LLC
- Specialization: Geospatial and computer vision analytics for property risk assessment.
- Key Focus Areas for Insurance: Automated property risk intelligence, underwriting support, pre-fill inspection attributes, and climate resilience overlays.
- Notable Features: High-resolution property features, portfolio-scale analytics, and integration with underwriting systems. Recently acquired by Moody’s to enhance geospatial risk intelligence.
- 2024 Revenue: Not publicly disclosed.
- Market Share: Leading niche provider in property analytics.
- Global Presence: Strong North American presence with growing international interest.
Leading trends and their impact
- From pilot to embedded workflows: Early pilots were chatbot-focused, but the next wave embeds generative AI into core underwriting and claims orchestration. This results in shorter cycle times, reduced manual effort, and significant cost savings.
- Multimodal models and geospatial fusion: Combining text, imagery, and sensor feeds enables more accurate property risk assessments and automated underwriting narratives.
- Responsible AI as a differentiator: With customer trust and regulatory scrutiny at stake, vendors emphasizing transparency and governance are gaining traction.
- Cloud ecosystems driving adoption: Hyperscalers like Microsoft and AWS are reducing barriers by offering managed generative AI services. This accelerates innovation but concentrates reliance on large providers.
- Domain-specific models and synthetic data: Fine-tuned models trained on industry data and synthetic datasets improve reliability in rare event scenarios, such as catastrophic losses.
Successful examples of generative AI in insurance
- Claims drafting and triage: Large P&C insurers have deployed assistants that extract facts from claims forms, propose coverage pathways, and draft investigator notes — reducing triage time from days to minutes.
- Underwriting narratives from imagery: Firms like Cape Analytics produce automated property risk summaries and recommended actions from satellite and street-level imagery, now a mainstream underwriting tool.
- Conversational customer service: Platforms like Avaamo provide multilingual, generative AI-powered assistants to handle policy queries, claims initiation, and routine service tasks.
- Compliance and reporting: Carriers in Europe and North America use generative AI to draft regulatory reports, policy amendments, and audit trails, improving accuracy and cutting documentation time.
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives and policies
North America (U.S. & Canada):
This region leads the market with insurers quickly adopting generative AI, often through partnerships with Microsoft, AWS, and other cloud providers. U.S. regulators, including state insurance commissioners and the NAIC, are emphasizing fairness, transparency, and explainability in AI models. Canada is also active in developing AI oversight while supporting innovation.
Europe (EU & UK):
The European market is shaped heavily by regulation, especially the EU AI Act, which classifies insurance applications as “high-risk.” This slows reckless adoption but ensures robust governance. Insurers here focus on transparency, data provenance, and human-in-the-loop approaches.
Asia-Pacific:
The region is expected to see the fastest growth. Countries like Japan, Singapore, India, and Australia are implementing generative AI in claims handling, chatbots, and distribution channels. Regulators encourage innovation via sandboxes while stressing ethical AI use.
Latin America and Middle East/Africa:
Adoption is at an earlier stage but growing steadily, often via partnerships with global providers. Sandboxes and pilot programs are being used to explore how generative AI can improve access, affordability, and efficiency in insurance.
Practical considerations for insurers
- Hallucinations and trust: Generative AI can produce plausible but incorrect outputs. Fact-checking layers and human validation are critical.
- Data privacy: Strict governance around customer data is essential to comply with GDPR, HIPAA, and other privacy regulations.
- Model governance: Insurers must maintain decision logs, model versioning, and audit trails to meet regulatory standards.
- Consumer transparency: Explaining how AI-assisted decisions are made is vital for customer acceptance and regulator approval.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Recyclable Packaging Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034