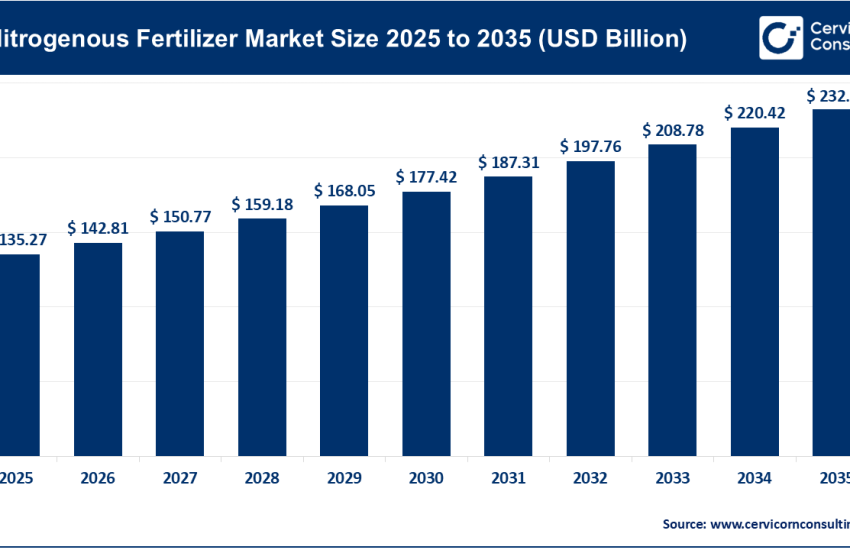
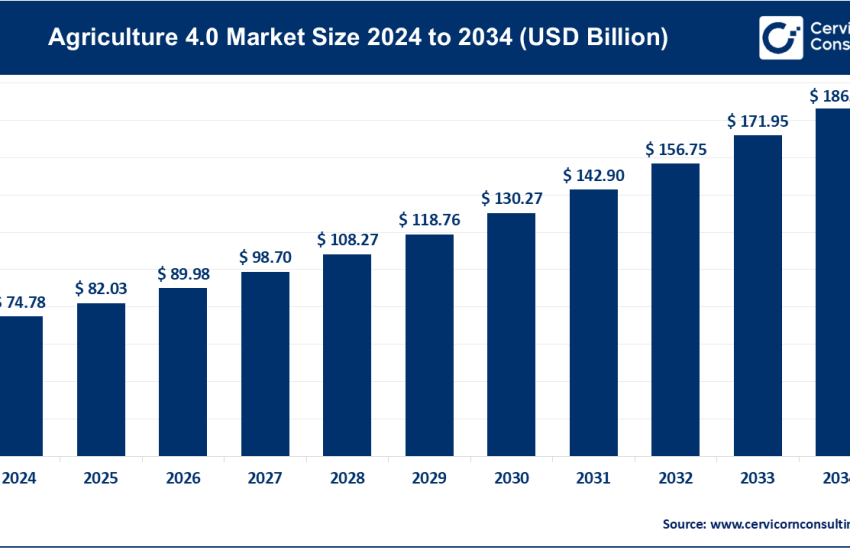
Farm Equipment Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035
Farm Equipment Market Size
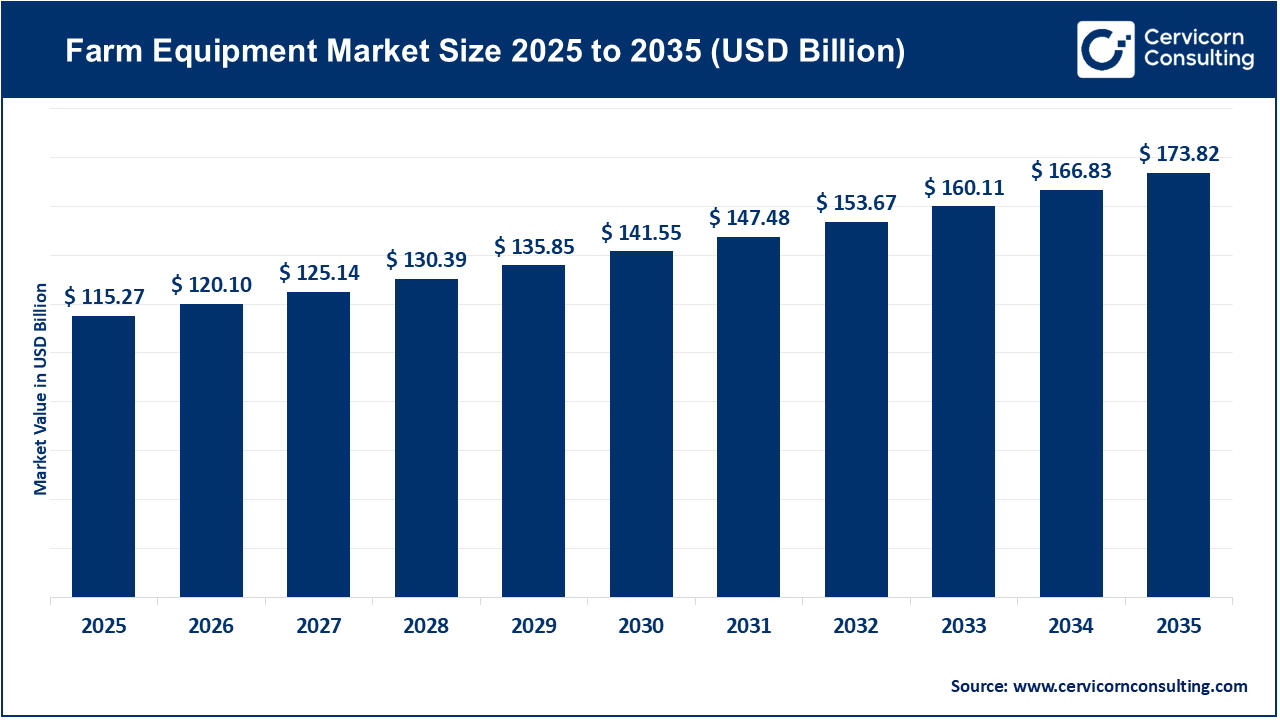
The global farm equipment market size was worth USD 115.27 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 173.82 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2026 to 2035.
Farm Equipment Market Growth Factors
The farm equipment market continues to grow steadily due to a combination of rising global food demand, shrinking agricultural labor availability, rapid advancements in precision agriculture, and government-led programs promoting farm mechanization. Increasing population pressure and higher consumption patterns are pushing farmers to adopt machinery that enhances productivity, reduces input waste, and performs tasks with greater speed. Labor shortages, especially in developed nations and emerging markets undergoing rural-to-urban migration, are further accelerating mechanization trends.
Additionally, subsidies, tax incentives, and rural credit schemes have made machinery more affordable, while advancements in GPS-guided tractors, telematics, sensors, remote monitoring systems, automation, and robotics are transforming operational efficiency. Rising farm incomes, better access to equipment financing, and the growing popularity of leasing models are enabling broader adoption. Tighter sustainability regulations are also influencing farmers to invest in fuel-efficient, low-emission, and precision-application machines. Altogether, these economic, technological, policy, and demographic drivers continue to expand the farm equipment market globally.
What is the Farm Equipment Market?
The farm equipment market refers to the global industry that designs, manufactures, distributes, and services agricultural machinery used throughout crop production, livestock management, land preparation, planting, irrigation, spraying, fertilizing, harvesting, post-harvest handling, and farm logistics. It includes tractors, combines, harvesters, seeders, planters, balers, sprayers, tillage tools, irrigation systems, implements, and increasingly advanced technologies such as agricultural drones, autonomous tractors, robotics, and precision-farming software platforms. The market spans new equipment sales, aftermarket parts, repair & maintenance services, financing, leasing, data solutions, subscription software, and fleet management tools. Essentially, it is the backbone of modern agricultural production, enabling farmers of all scales — from smallholders to industrial operations — to boost yields, reduce manual effort, save time, and increase operational consistency.
Why is the Farm Equipment Market Important?
Agricultural machinery is essential for ensuring food security, improving farm productivity, and addressing global challenges such as labor shortages, climate variability, and sustainable resource management. Mechanization enhances efficiency by minimizing manual labor, allowing timely planting and harvesting — two crucial determinants of yield outcomes. Precision equipment also helps farmers optimize water, fertilizer, pesticides, and energy use, reducing environmental impact while lowering cost-per-acre.
Advanced machines like GPS-guided tractors and autonomous systems allow highly accurate operations in large fields, supporting high-output commercial agriculture. Modern equipment also strengthens rural economies by creating employment opportunities in sales, servicing, and manufacturing sectors. In a world that must feed nearly 10 billion people by 2050, the farm equipment market plays an indispensable role in ensuring scalable, resilient, and resource-efficient agricultural production.
Farm Equipment Market — Top Companies
Below are detailed profiles of the world’s leading agricultural machinery manufacturers, including their specialization, key focus areas, notable features, 2024 revenue overview, approximate market position, and global presence.
1. Deere & Company (John Deere)
Company: Deere & Company
Specialization: Full-range agricultural equipment, precision farming technologies, construction & forestry machines.
Key Focus Areas: Autonomous tractors, data-driven farming (Operations Center), telematics, electrification, sustainable equipment platforms, dealer-driven after-sales ecosystem.
Notable Features: One of the world’s most recognized machinery brands, strong global dealer network, leading precision agriculture software ecosystem, high R&D commitment.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 51–52 billion in total sales.
Market Share: Often ranked as the largest global agricultural equipment manufacturer with a significant share across tractors, combines, and precision farming solutions.
Global Presence: Strong in North America, Europe, Brazil, Australia, and expanding presence in Asia-Pacific, including India and China.
2. CNH Industrial (Case IH & New Holland)
Company: CNH Industrial
Specialization: Tractors, combines, balers, harvesters, utility equipment, and construction machinery.
Key Focus Areas: Precision farming integration, electric equipment development, connected machinery, digital aftermarket services.
Notable Features: Operates two globally recognized agricultural brands — Case IH for high-power machines and New Holland for mid-range & versatile offerings.
2024 Revenue: Around USD 19–20 billion in consolidated revenues.
Market Share: Consistently among the top 3 global OEMs with strong footholds in high-horsepower tractors and harvesting machines.
Global Presence: Strong distribution across North America, Europe, India, Brazil, and emerging markets.
3. AGCO Corporation (Fendt, Massey Ferguson, Valtra)
Company: AGCO Corporation
Specialization: Tractors, combines, sprayers, hay & forage equipment, smart farming technologies.
Key Focus Areas: High-end machinery (Fendt), precision ag systems (FendtONE, Fuse), aftermarket services, and global dealer partnerships.
Notable Features: The world’s largest pure-play agricultural equipment manufacturer; diverse brand portfolio serving multiple farm sizes.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 11–12 billion.
Market Share: Strong competitive position globally, particularly in Europe and North America with leadership in premium tractor segments.
Global Presence: Active in over 140 countries with strong manufacturing bases in the U.S., Germany, Brazil, and Finland.
4. Kubota Corporation
Company: Kubota Corporation
Specialization: Compact & mid-sized tractors, agricultural implements, rice & vegetable harvesters, engines, and construction machinery.
Key Focus Areas: Compact tractor innovation, small-field mechanization, fuel-efficient engines, electrification for smaller tractors.
Notable Features: Known for reliability and suitability in markets with small, fragmented land holdings.
2024 Revenue: Roughly USD 19–20 billion.
Market Share: Leading brand in compact tractor categories globally; strong market presence in Asia, North America, and Europe.
Global Presence: Deep distribution across Japan, Southeast Asia, India, the U.S., Europe, and expanding into Africa.
5. CLAAS Group
Company: CLAAS
Specialization: Combine harvesters, forage harvesters, balers, tractors (select ranges), and precision harvesting technologies.
Key Focus Areas: High-performance harvesting machinery, automation, forage systems, digital farm services.
Notable Features: One of Europe’s most respected harvesting machine manufacturers with cutting-edge engineering.
2024 Revenue: Approximately EUR 5 billion.
Market Share: Global leader in combine and forage harvester segments; strong in Europe, Russia, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
Global Presence: Manufacturing and distribution networks across Europe, North America, South America, and Asia.
Leading Trends in the Farm Equipment Market & Their Impact
1. Precision Agriculture and Data-Driven Farming
Precision agriculture technologies — GPS guidance, auto-steer, yield mapping, soil sensors, drones, variable-rate systems, and telematics — are transforming farm operations. These tools improve input efficiency, crop health management, and real-time decision-making. The shift from mechanical equipment to integrated digital machinery creates recurring revenue opportunities through software subscriptions and analytics services.
2. Autonomy and Robotics
Self-driving tractors, robotic harvesters, and automated spraying systems are gradually entering mainstream use. Automation addresses labor shortages and extends working hours. This trend benefits large-scale farms first but is gradually trickling down to smaller farmers through rental and shared models.
3. Electrification & Alternative Power Systems
Battery-powered compact tractors, hybrid machines, and hydrogen-fueled prototypes are emerging in response to emissions regulations and sustainability goals. Electrification reduces noise, emissions, and maintenance costs but requires new charging infrastructure and battery solutions.
4. Integrated Digital Ecosystems
Equipment manufacturers are building connected-farm ecosystems offering remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and OTA (over-the-air) updates. This reduces downtime, extends machinery life, and enhances equipment ROI for farmers.
5. Value Shift Toward Aftermarket Services
Aftermarket parts, machine servicing, predictive maintenance, and equipment financing are becoming major revenue drivers. OEMs are focusing on recurring-service models to offset cyclical new equipment sales.
6. Sustainable Farming & Regulatory Compliance
Governments are mandating reduced carbon emissions, efficient fertilizer use, and low-drift spraying, which is pushing modernization of farm equipment. Machines with precision input application and cleaner engines help farmers meet compliance requirements.
Successful Examples of Farm Equipment Adoption Around the World
United States (Precision Agriculture Leadership)
Large-scale U.S. farms have adopted GPS-guided tractors, automated steering, variable-rate application technologies, and telematics systems. These innovations save labor, reduce fuel use, and boost yield consistency across large acreage.
Western Europe (High-Performance Harvesting)
Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. utilize high-powered combines, forage harvesters, and balers to optimize harvest windows. CLAAS, Fendt, and other European brands dominate large farm segments due to engineering and automation excellence.
India & South Asia (Compact Machinery Success)
India’s agricultural landscape, dominated by small and medium farms, has embraced compact tractors and implements. Affordable pricing, government subsidies, and financing support have made tractors more accessible, resulting in one of the world’s highest tractor sales volumes.
Brazil & Latin America (Large-Scale Mechanization)
Brazilian soybean and corn farms rely heavily on high-horsepower tractors, planters, and combines. Localized manufacturing and credit programs have encouraged broad adoption, making Brazil a fast-growing agricultural equipment market.
Japan (Agricultural Robotics)
Japan leads in agricultural robotics due to aging farm populations and labor constraints. Robotic transplanters, autonomous mini-tractors, and smart-irrigation systems are common in high-value crop farming.
Global Regional Analysis — Including Government Initiatives and Policies
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents the largest agricultural equipment market by volume. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asian nations are aggressively promoting mechanization.
Key enablers include:
- Subsidies on tractors and harvesters
- Low-interest credit for machinery
- Smart farming pilot programs
- Government-backed machinery leasing centers
- Incentives for electric/low-emission farm equipment
India’s Farm Mechanization Program and China’s Agricultural Machinery Subsidy Program have significantly boosted tractor and harvester adoption.
North America
The U.S. and Canada have mature agricultural markets with high technology penetration. Policies emphasize conservation farming, sustainable practices, and adoption of precision agriculture.
Supporting elements include:
- USDA grants
- Research programs for automation
- Crop insurance incentives linked to modern practices
- Tax depreciation benefits for equipment purchases
Large growers routinely invest in high-horsepower tractors, combines, and precision systems.
Europe
European Union policies strongly emphasize sustainability and emissions reductions. The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) supports rural development, modern equipment adoption, and climate-smart farming.
Policies support:
- Low-emission machinery
- Smart farming grants
- Robotics and digital innovation funding
- Organic farming initiatives
European OEMs such as CLAAS and AGCO (Fendt) benefit from high demand for advanced harvesting and precision machines.
Latin America
Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico are major markets for high-horsepower tractors, sugarcane harvesters, planters, and sprayers. Adoption is heavily tied to commodity price cycles.
Government support includes:
- Rural credit programs
- Export competitiveness policies
- Local manufacturing incentives
Brazil has become a manufacturing hub for global OEMs due to high domestic demand.
Middle East & Africa
Mechanization levels vary greatly, but many regions are experiencing rapid growth due to food-security initiatives, irrigation development, and government-backed equipment programs.
Key drivers include:
- Subsidized tractor procurement
- Public–private mechanization centers
- Donor-funded development programs
- Strong investment in irrigation machinery
African nations are increasingly adopting compact and utility tractors to improve productivity on smallholder farms.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Diabetes Drugs Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2035