Combined Heat and Power Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034
Combined Heat and Power Market Size
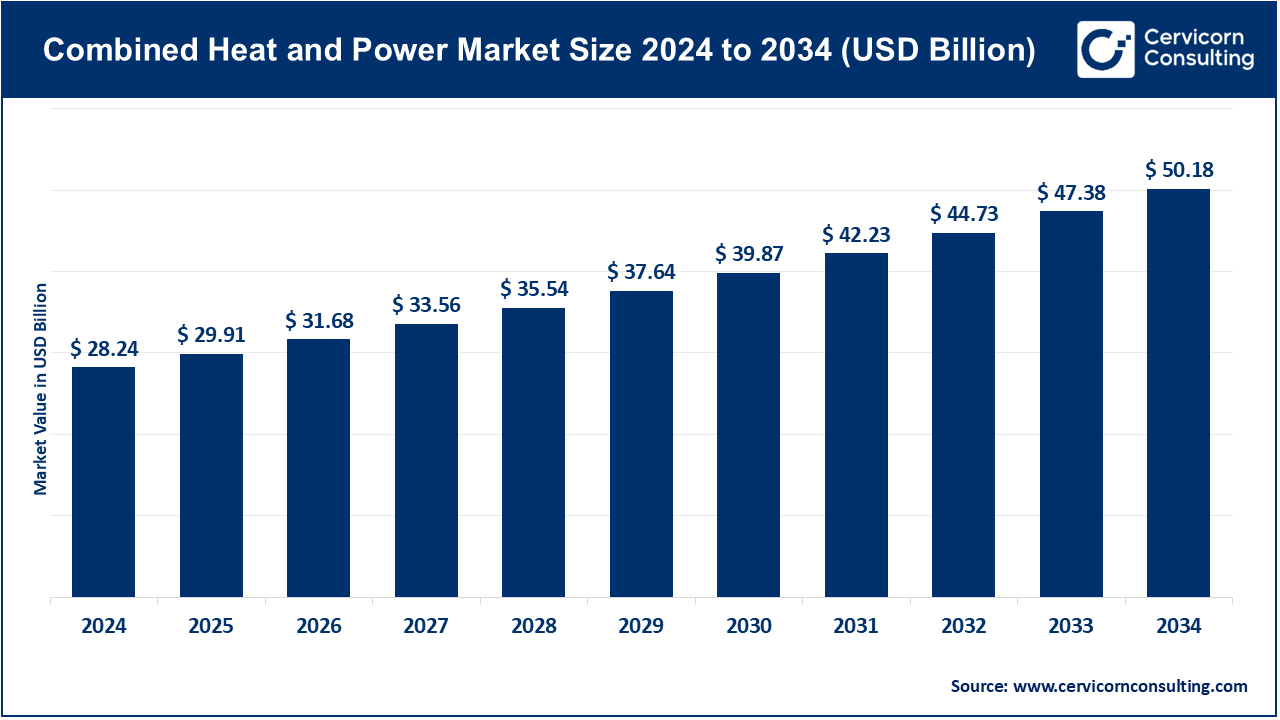
The global combined heat and power market size was worth USD 28.24 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 50.18 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.92% from 2025 to 2034.
Combined Heat and Power Market Growth Factors
Growth in the combined heat and power (CHP) market is being driven by a convergence of technological, economic, and policy factors. Rising energy prices and the need for cost stability are pushing industries and institutions toward onsite energy generation. The growing emphasis on decarbonization and energy efficiency underpins global efforts to adopt low-carbon solutions like CHP. Advances in gas engines, turbines, and fuel-flexible technologies, including biogas and hydrogen-based systems, are expanding CHP’s applicability across industries.
Additionally, aging grid infrastructure and increasing focus on resilience for critical facilities such as hospitals and data centers are creating new demand for localized power systems. Supportive government regulations, tax incentives, and grants further enhance adoption. Moreover, the integration of CHP into microgrids, smart control systems, and combined cooling, heating, and power (CCHP) setups offers additional economic and operational advantages, making CHP a central feature in the future of distributed energy systems.
What Is the Combined Heat and Power Market?
The combined heat and power market encompasses technologies and services that produce electricity and useful thermal energy simultaneously. Unlike conventional power generation, which wastes much of the fuel energy as heat, CHP systems capture and reuse this heat for heating, cooling, or industrial processes. These systems achieve overall efficiencies of 65%–90%, compared to 40% for separate heat and power generation. The market includes a variety of systems—ranging from small residential micro-CHP units below 50 kW to industrial-scale systems exceeding several megawatts—using technologies such as reciprocating engines, gas turbines, steam turbines, and fuel cells. CHP systems are utilized across industrial, commercial, and institutional sectors, with solutions spanning equipment manufacturing, engineering, installation, maintenance, and energy service contracts.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2796
Why Is CHP Important?
CHP systems are crucial because they provide immediate, practical benefits for energy efficiency and sustainability. By capturing and reusing waste heat, they drastically reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. CHP also enhances energy reliability, providing backup power during grid outages—a feature vital for hospitals, universities, and data centers. Economically, CHP helps facilities cut operating costs by producing electricity and thermal energy onsite, reducing reliance on utility grids. For countries striving toward net-zero emissions, CHP represents a mature, scalable technology that bridges the gap between fossil-fueled systems and fully renewable grids. It complements renewable energy deployment by providing stable baseload power and flexible thermal energy management.
Top Companies in the Combined Heat and Power Market
Below are detailed profiles of leading CHP market companies, highlighting their specialization, focus areas, notable features, revenues, market positioning, and geographic footprint.
2G Energy AG (2G Energy Inc.)
- Specialization: Small- to medium-scale gas engine CHP systems, including biogas and biomethane-fueled solutions.
- Key Focus Areas: Decentralized energy solutions, biogas plants, engine-based CHP systems, lifecycle services, and digital monitoring.
- Notable Features: Strong reputation in Europe for modular, pre-engineered CHP systems and biogas integration. Offers turnkey packages combining design, construction, and maintenance.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately €375.6 million.
- Market Share: Prominent in the European small- to mid-scale CHP segment, especially for biogas applications.
- Global Presence: Operations in over 50 countries, including strong markets in Germany, the UK, and North America.
General Electric Company (GE)
- Specialization: Large-scale power generation systems including gas turbines, steam turbines, and integrated CHP and combined-cycle plants.
- Key Focus Areas: Industrial-scale CHP solutions, turbine technology, plant integration, grid connectivity, and digital optimization.
- Notable Features: Pioneering R&D in high-efficiency turbines and grid-interactive technologies. Offers comprehensive maintenance and digital analytics for improved asset performance.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately $38.7 billion (total company revenue).
- Market Share: Strong in large industrial and utility-scale CHP installations.
- Global Presence: Extensive global footprint across North America, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Aegis Energy Services Inc.
- Specialization: Design, installation, and operation of small-scale gas-fired CHP systems for commercial and institutional buildings.
- Key Focus Areas: Turnkey CHP systems for hotels, hospitals, multi-family housing, and educational facilities.
- Notable Features: Regional leader in the Northeastern United States, known for reliability and tailored service contracts. Offers energy performance contracting and long-term operations support.
- 2024 Revenue: Estimated between $50 million and $100 million.
- Market Share: Strong regional player in the U.S. commercial CHP segment.
- Global Presence: Primarily serves the U.S. Northeast, with growing influence in other regions.
Caterpillar Inc.
- Specialization: Global manufacturer of power generation equipment, including engines, generator sets, and CHP systems.
- Key Focus Areas: Engine-based CHP plants for industrial and large commercial use, integrated energy systems, and service networks.
- Notable Features: Renowned for durability and extensive service network. Offers modular CHP packages using natural gas, biogas, and other fuels.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately $64.8 billion.
- Market Share: Major supplier in large-engine CHP applications worldwide.
- Global Presence: Operations and dealer networks in more than 190 countries.
Curtis Engine & Equipment Co. Inc. (Curtis Power Solutions)
- Specialization: Regional supplier and integrator of power generation and CHP solutions.
- Key Focus Areas: Turnkey CHP projects, backup and standby power, equipment rentals, and maintenance services.
- Notable Features: Strong regional presence in the Mid-Atlantic U.S.; known for responsive customer service and system integration capabilities.
- 2024 Revenue: Estimated between $20 million and $35 million.
- Market Share: Small but influential regional player.
- Global Presence: Primarily U.S.-based operations with regional project deployments.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Fuel Diversification
CHP systems are evolving beyond natural gas. Biogas, biomethane, and hydrogen blends are being introduced to reduce lifecycle emissions. This trend is particularly evident in agricultural and waste management sectors, where renewable gases are readily available. The impact is a more sustainable and flexible CHP landscape compatible with circular economy principles.
2. Integration with Cooling and Storage Systems
Tri-generation systems (combined cooling, heat, and power) and thermal storage are gaining traction, particularly in commercial and institutional facilities. These configurations enhance system utilization, reduce peak loads, and enable facilities to participate in demand response programs. The result is greater energy independence and cost optimization.
3. Digitalization and Energy-as-a-Service Models
The adoption of digital monitoring and predictive maintenance tools has improved operational reliability. Combined with performance-based service contracts, these innovations lower barriers to entry for customers and attract investors to third-party ownership models. Digital solutions also allow for remote optimization, improving asset lifespan and reducing downtime.
4. Policy and Incentive-Driven Adoption
Governments worldwide are promoting CHP as part of energy efficiency and resilience strategies. Incentives, rebates, and grants make CHP projects more financially attractive. The policy shift toward localized, low-carbon energy generation continues to enhance CHP’s relevance in national and regional decarbonization plans.
5. Modular and Fuel Cell CHP Systems
Smaller, modular CHP units and fuel cell-based CHP systems are gaining attention for their low emissions and high efficiency. Fuel cells, in particular, are being deployed in data centers and commercial buildings, offering quiet operation and near-zero NOx emissions. This diversification in technology broadens CHP’s appeal to new sectors.
6. Microgrids and Distributed Energy Integration
CHP is increasingly integrated into microgrid frameworks, supporting grid stability and renewable integration. These hybrid systems combine CHP with batteries, solar PV, and demand management technologies, enhancing resilience against grid disruptions and optimizing energy economics.
Successful Examples of CHP Around the World
1. District Heating in Scandinavia
Denmark and Sweden have long championed CHP in district heating networks. Nearly all major cities utilize CHP to supply both electricity and heat to residential and commercial consumers. These projects achieve exceptionally high fuel efficiency and serve as global models for sustainable urban energy systems.
2. Campus Microgrids in the United States
Universities and hospitals across the U.S. have adopted CHP as the backbone of resilient microgrids. For example, several Ivy League campuses operate gas-turbine-based CHP systems that provide reliable power and heating while reducing carbon emissions by up to 30%. These installations also support demand-side flexibility.
3. Industrial CHP in Europe and Asia
Industrial facilities—especially in chemicals, food processing, and pulp & paper—rely heavily on CHP for steam and power. Many of these plants use waste fuels or process byproducts to drive turbines or engines, significantly lowering operational costs and emissions.
4. Biogas CHP at Wastewater Plants
Cities worldwide are capturing biogas from wastewater treatment and converting it into power through CHP units. The recovered heat is reused for digestion processes, closing the energy loop and transforming wastewater treatment from an energy consumer into a producer.
5. Commercial CHP in Japan
Japan’s hospitality and healthcare sectors are notable for deploying compact CHP systems. The government’s long-standing efficiency programs have made CHP adoption common in urban buildings, improving energy security and reducing operational costs.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Initiatives
North America
In the United States and Canada, CHP growth is fueled by resilience planning and energy efficiency initiatives. State and federal programs provide tax credits, grants, and technical support for CHP installations. Key markets include universities, hospitals, and industrial facilities. Regional developers like Aegis Energy and utilities are central to deploying packaged CHP systems. Policies encouraging energy independence and microgrids also drive market expansion.
Europe
Europe leads globally in CHP deployment due to stringent efficiency targets, district heating infrastructure, and carbon pricing mechanisms. Countries like Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands have integrated CHP into national energy strategies. The European Union’s “Fit for 55” package and emissions trading schemes incentivize efficient heat recovery and low-carbon fuels. Companies like 2G Energy benefit from these favorable frameworks, especially in biogas and biomethane applications.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is experiencing robust growth in industrial and urban CHP installations. In China, CHP forms a major part of industrial energy policy, particularly for large manufacturing clusters. Japan promotes micro-CHP for commercial buildings under its energy security programs. Meanwhile, Australia and India are exploring gas- and biomass-based CHP for distributed industrial energy.
Middle East and Africa
In this region, CHP is tied to industrial complexes, desalination plants, and petrochemical operations. Countries are exploring CHP as a means to improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon intensity in heavy industries. While adoption remains in early stages, increased awareness of sustainability and efficiency is expected to drive future investment.
Latin America
Latin America presents emerging opportunities for biomass and biogas CHP projects, particularly in agriculture-based economies like Brazil and Argentina. Policies promoting renewable energy and waste-to-energy initiatives are gradually creating a favorable landscape. However, challenges such as financing constraints and inconsistent regulations slow broader adoption.
Market Overview and Future Outlook
The global CHP market was valued at approximately USD 28–30 billion in 2024 and is expected to expand steadily through 2034, supported by industrial demand, efficiency mandates, and fuel-flexible technologies. Industrial and commercial users remain the primary end-users, while institutional facilities are emerging as strong growth segments due to resilience and cost-efficiency needs. The integration of CHP into microgrids, district heating networks, and renewable hybrid systems positions it as a foundational technology in the global transition toward sustainable, decentralized energy.
Key Insights
- CHP provides a direct, proven route to reducing carbon emissions and improving energy efficiency.
- Technological innovations such as hydrogen-ready engines and digital optimization are reshaping the CHP landscape.
- Regional diversity defines the market—Europe leads in policy-driven adoption, the U.S. in resilience-focused systems, and Asia in industrial scale deployment.
- Companies like 2G Energy, GE, and Caterpillar dominate globally, while regional firms such as Aegis and Curtis Power provide tailored local expertise.
- Government incentives, net-zero commitments, and decentralization trends will continue to shape the CHP market trajectory through 2034.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Electric Air Taxi Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034