Electric Vehicle Battery Swapping Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034
Electric Vehicle Battery Swapping Market Size
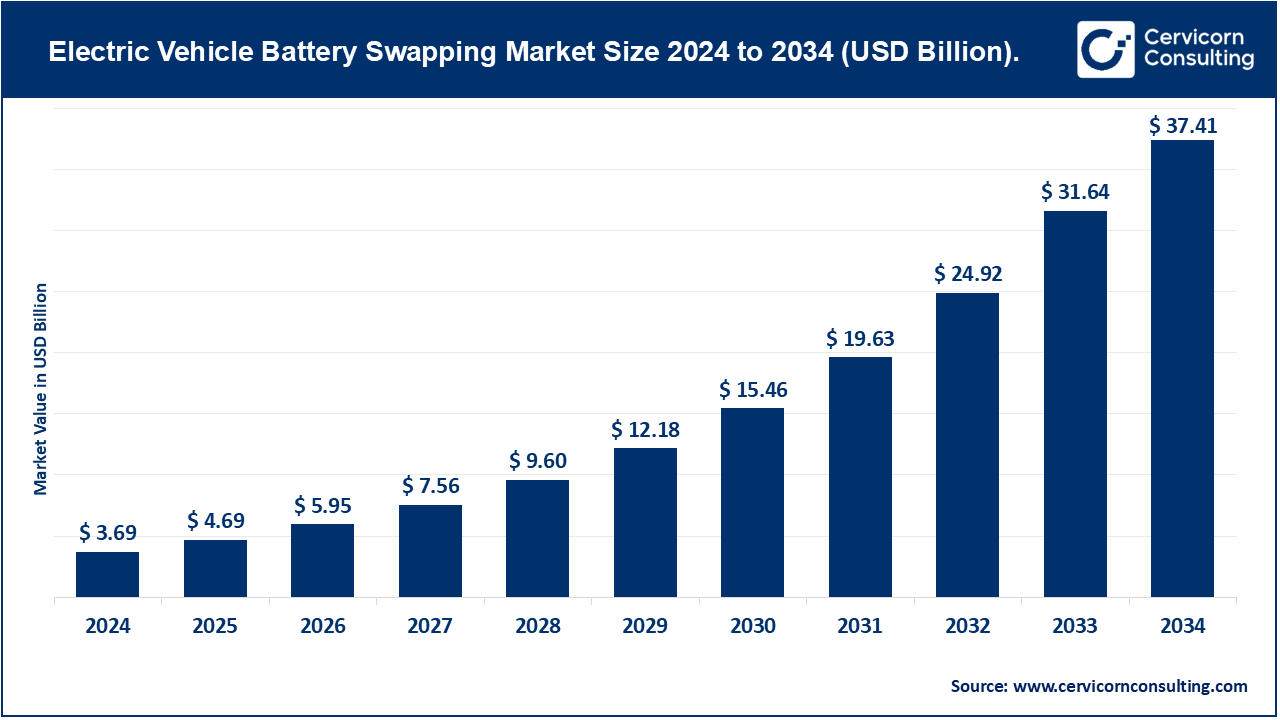
The global electric vehicle battery swapping market size was worth USD 3.69 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 37.41 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.07% from 2025 to 2034.
Growth factors
The battery-swapping market is accelerating due to rapid EV adoption, the operational needs of high-utilization fleets requiring minimal downtime, government support for decarbonization, and expanding battery infrastructure targets. Falling battery costs are making swap-pool economics more viable, while rising investments from startups and large OEMs are increasing scale, standardization, and interoperability. Centralized swap stations also enable more efficient grid integration by charging batteries during off-peak hours. Additionally, business-model innovation—Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS), subscription plans, and modular swap hardware—reduces upfront costs and enhances battery lifecycle management. Together, these factors are driving strong double-digit market growth worldwide.
What is the electric vehicle battery-swapping market?
Battery swapping—also known as Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) when paired with subscription models—is a system in which depleted EV batteries are quickly exchanged at automated stations for fully charged units. This eliminates long charging times and reduces costs by separating battery ownership from the vehicle. The market encompasses swap stations, robotics, swappable battery packs, software systems, infrastructure operators, and compatible vehicle OEMs across segments such as two-wheelers, three-wheelers, passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and heavy-duty trucks. Although market size estimates vary globally, nearly all major analyses indicate rapid growth from the early-2020s baseline.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/electric-vehicle-battery-swapping-market
Why it is important
The EV battery-swapping market is important because it solves key challenges associated with conventional EV charging. First, it dramatically reduces time-to-charge, enabling drivers to get back on the road in minutes. Second, BaaS improves affordability by removing the battery from the vehicle’s purchase price, while also reducing long-term maintenance and lifecycle concerns. Third, swapping enhances fleet availability for taxis, logistics operators, and delivery services that operate continuously. Finally, centralized battery charging reduces pressure on electrical grids, supports renewable energy integration, and simplifies large-scale electrification strategies. Together, these advantages make swapping a critical complement (and in some markets, superior alternative) to plug-in charging infrastructure.
Company profiles
Below are detailed profiles for the major players shaping global battery-swapping networks.
NIO (China)
Specialization:
Premium EV manufacturer offering an integrated battery-swapping system and Battery-as-a-Service subscription program.
Key focus areas:
Rapid network expansion, next-generation automated swap stations (4.0+), partnerships with global energy companies, and deeper integration of BaaS into vehicle sales.
Notable features:
Large installed base of Power Swap Stations, fast swap speeds, high automation, multi-generation station improvements, and the industry’s most mature passenger-car battery-swapping service.
2024 revenue:
Approximately RMB 65.7 billion (≈ USD 9 billion), representing total company revenue including vehicle sales and services.
Market position:
Considered the global leader in passenger EV battery swapping, with the largest and most advanced swap-station network.
Global presence:
China, with expanding presence in Europe and pilots across select global markets.
Gogoro (Taiwan)
Specialization:
Battery-swapping networks for two-wheelers, primarily electric scooters, and licensing of its platform to regional partners.
Key focus areas:
Subscriber growth for its swapping service, geographic expansion across Asia, and partnerships enabling localized deployment of the Gogoro Network.
Notable features:
Highly dense urban swap network, fast swap times, strong recurring service revenue, and market-leading unit economics.
2024 revenue (swap services only):
Approximately USD 137.9 million from battery-swapping services.
Market position:
The world’s most successful two-wheeler battery-swapping ecosystem, dominating Taiwan’s market.
Global presence:
Taiwan headquarters; partnerships expanding across Southeast Asia, India, and beyond.
Ample (USA / global fleets)
Specialization:
Modular battery-swapping systems for fleets, designed for quick station deployment and compatibility with multiple vehicle types.
Key focus areas:
Electrification of delivery fleets, taxi and ride-hailing vehicles, lightweight commercial trucks, and retrofittable modular battery technology.
Notable features:
Rapid station deployment with minimal civil works, modular battery units, partnership-driven model with OEMs and cities, and multi-vehicle compatibility.
2024 revenue:
Not publicly disclosed (private company), but supported by significant venture funding and multiple commercial-scale pilots.
Market position:
Leading modular-swap innovator outside China, gaining traction in fleet applications.
Global presence:
Headquartered in the U.S., active deployments in Japan, trials in Europe, and collaborations with logistics companies and energy providers.
Aulton (China)
Specialization:
Large-scale battery-swapping operator with a focus on commercial fleets, taxis, and passenger EVs.
Key focus areas:
Expansion of nationwide swap stations, supporting multi-brand vehicle compatibility, and building fleets of swap-ready taxis and ride-hailing cars.
Notable features:
High-speed swapping systems, strong partnerships with energy companies and OEMs, and considerable historical swap volume.
2024 revenue:
Not publicly disclosed; primarily reports operational growth and station deployment numbers.
Market position:
One of the largest battery-swapping networks in China after NIO, especially strong in taxi and fleet markets.
Global presence:
Primarily within China, with collaborations involving international energy companies.
BAIC BluePark (China)
Specialization:
EV manufacturing and R&D under BAIC Group, supporting production of swap-capable electric vehicles.
Key focus areas:
Development of EV platforms compatible with battery swapping, partnerships with swap operators, and scaling China’s NEV ecosystem.
Notable features:
Significant backing from BAIC Group, modern EV product lines (Arcfox, Beijing brand), and involvement in national battery-swapping pilot cities.
2024 revenue:
Reported RMB 3.714 billion for H1 2024.
Market position:
Key OEM participant in China’s expanding swap ecosystem, contributing vehicles rather than operating stations.
Global presence:
China-centric, with ambitions for broader EV exports.
Leading trends and their impact
1. Swap-focused fleet electrification
Fleets—taxis, delivery vans, logistics trucks—value uptime. Swapping provides near-zero downtime compared to charging, enabling fleets to electrify faster, reduce operational cost, and improve vehicle utilization.
2. Growth of Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS)
BaaS helps reduce the upfront EV price and shifts battery maintenance and replacement risk to operators. It also enables battery upgrades without replacing the vehicle, boosting long-term customer value.
3. Standardization of batteries and interfaces
Battery makers and industry groups are pushing standard sizes and interfaces. Standardization increases station utilization, reduces capital expenditure, and enables multiple OEMs to share infrastructure.
4. Modular and low-footprint swap stations
Startups such as Ample are leading modular swap station designs that require minimal land and simpler permitting—crucial for dense cities where building permanent structures is costly and slow.
5. Integration with energy systems
Swap stations double as distributed energy assets. By charging during off-peak periods and storing power, they help stabilize grids, reduce peak loads, and integrate renewable energy generation.
6. Segment-based evolution
Two-wheeler swapping is already profitable in Asia, while passenger cars and trucks are growing through fleet-first strategies. Over time, multi-segment integration is expected to create hybrid swapping-charging ecosystems worldwide.
Successful examples around the world
NIO’s Power Swap Stations (China & Europe)
NIO’s network demonstrates that passenger-car battery swapping can scale to thousands of stations and millions of swaps annually. Its BaaS model is widely seen as the most mature globally.
Gogoro’s two-wheeler network (Taiwan)
Gogoro’s scooter battery-swapping system showcases strong economics and widespread adoption, with hundreds of thousands of active subscribers.
Ample’s fleet swaps in Japan
Ample’s deployment in cities such as Kyoto and Tokyo has proven the effectiveness of modular swapping for delivery fleets, in collaboration with major companies and utilities.
Aulton’s taxi swapping model (China)
Aulton’s network supports large taxi and ride-hailing fleets, demonstrating how swapping significantly reduces operational downtime in high-mileage applications.
Consortium-based approaches in Japan & Europe
Collaborative, multi-stakeholder projects—often including OEMs, logistics companies, and energy providers—are becoming a successful model for rapid pilot and deployment.
Global regional analysis — government initiatives and policies shaping the market
China
China leads the world in battery-swapping deployment, supported by national-level pilot programs, municipal subsidies, incentives for swap-capable EVs, and partnerships between automakers, battery suppliers, and energy companies. Swap-focused pilot cities have accelerated adoption across taxis, ride-hailing fleets, commercial vehicles, and passenger EVs.
Taiwan & Southeast Asia
Taiwan is the global epicenter for two-wheeler swapping, having created a supportive policy environment that enabled Gogoro’s success. Southeast Asian governments are exploring swapping for scooters and three-wheelers to support urban mobility and reduce oil dependence.
Japan
Japan supports swapping pilots for both passenger and commercial vehicles through government coordination with utilities, OEMs, and technology companies. Projects in Kyoto, Tokyo, and other cities focus on logistics fleets and last-mile delivery.
India
India has been working toward a national battery-swapping policy emphasizing two- and three-wheelers, asset standardization, and interoperability. State governments are supporting pilots, subsidies, and simplified grid access for swapping networks.
Europe
Europe focuses more on fast charging but increasingly acknowledges the role of battery-swapping for fleets. Regulations around sustainable batteries, digital battery passports, and alternative fuels infrastructure create a conducive environment for swap technologies to evolve.
North America
The U.S. and Canada are beginning to explore swapping for commercial fleets, especially delivery vehicles. While the region is charging-dominant, fleet-focused swapping is gaining traction due to high vehicle utilization and growing electrification mandates.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Digital Logistics Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034