Smart Gas Meter Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034
Smart Gas Meter Market Size
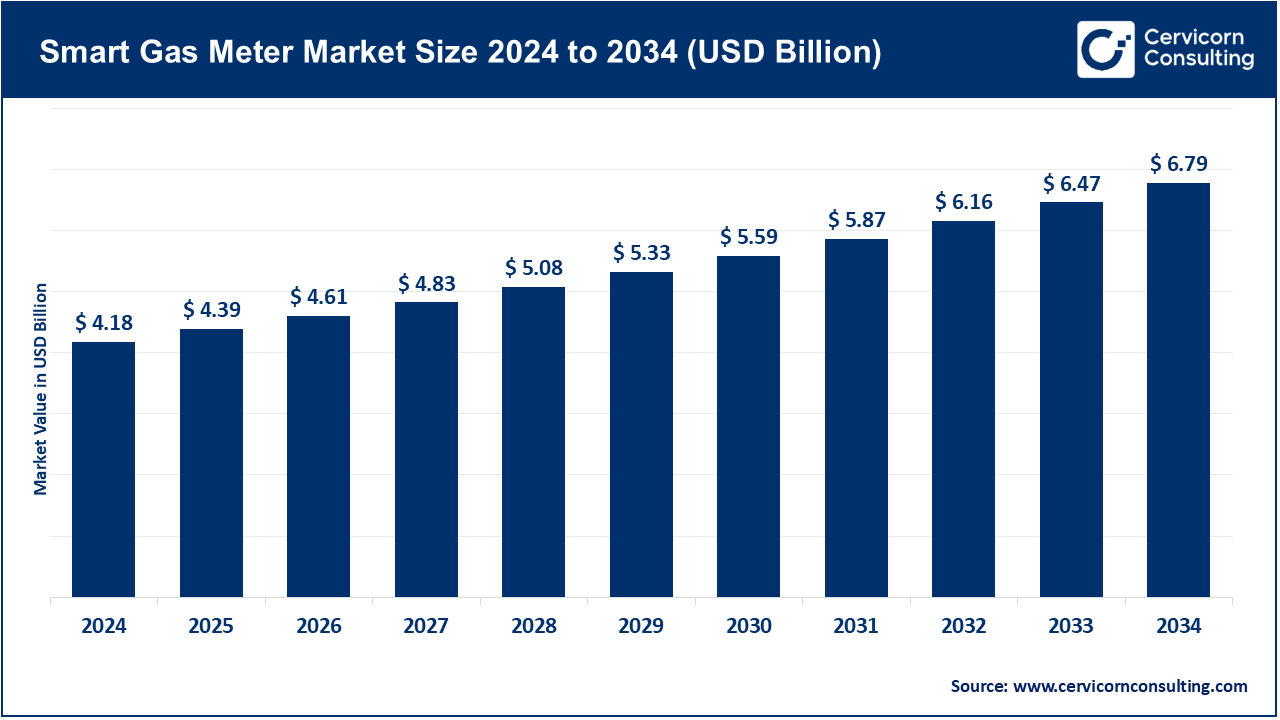
The global smart gas meter market size was worth USD 4.18 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 6.79 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.97% from 2025 to 2034.
What Is the Smart Gas Meter Market?
The smart gas meter market encompasses manufacturers, software and platform providers, communications network suppliers, and system integrators who design and deploy meters capable of remotely measuring gas consumption, sending data in near real time, and supporting two-way communications for functions such as leak detection, tamper alerts, and remote shut-off. These meters are integral to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and Internet of Things (IoT) networks.
Smart gas meters come in several types — from retrofitted electronic modules that upgrade mechanical meters to fully integrated ultrasonic or diaphragm meters with embedded connectivity using radio frequency (RF) mesh, cellular, or power-line carrier (PLC) technologies. The market includes revenues from meter hardware, communications modules, software (meter data management, AMI head-end systems), installation, maintenance, and analytics services.
In 2024, the global smart gas meter market is valued in the low-to-mid billions of U.S. dollars, growing steadily as governments and utilities replace legacy mechanical systems with digital, connected infrastructure.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2802
Why Is the Smart Gas Meter Market Important?
Smart gas meters play a critical role in transforming gas utilities into efficient, data-driven enterprises.
- Operational Efficiency: They automate readings, reduce the need for manual meter inspection, enable remote valve control, and allow for proactive maintenance through real-time diagnostics.
- Customer Empowerment: End-users receive accurate bills and real-time insights into consumption patterns, promoting energy conservation and transparency.
- Safety Enhancement: Integrated sensors can detect leaks, abnormal consumption, or tampering and trigger alerts or shut-off mechanisms instantly.
- Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability: Many governments require precise metering for environmental reporting, loss reduction, and decarbonization goals.
Smart meters are thus the cornerstone of smart energy grids — vital for managing distributed energy resources, minimizing losses, and enabling a greener, more efficient energy ecosystem.
Growth Factors
The smart gas meter market is expanding due to rapid digitalization of utility networks, widespread adoption of IoT and AMI technologies, increasing regulatory mandates for accurate billing and leak detection, and growing investments in grid resilience and remote management. Decreasing costs of communication modules, especially those using NB-IoT and LTE-M cellular technologies, have made deployment more affordable. Additionally, the surge in data analytics applications, evolving consumer awareness about energy efficiency, and strong government programs to replace outdated meters are fueling sustained growth. Partnerships between meter manufacturers, telecom operators, and data-platform providers are creating new recurring-revenue ecosystems, accelerating global adoption.
Top Companies in the Smart Gas Meter Market
1. Itron, Inc.
Specialization:
Itron is a global leader in smart metering and grid management solutions across electricity, gas, and water. It provides metering hardware, network communications infrastructure, and advanced analytics platforms that enable utilities to optimize operations.
Key Focus Areas:
Itron focuses on end-to-end AMI solutions, open communications standards, and interoperability between devices and networks. It emphasizes software integration, edge intelligence, and data-driven grid optimization.
Notable Features:
- Modular meter platforms adaptable to multiple network technologies.
- Integration with advanced data-management and analytics systems.
- Proven large-scale deployments worldwide.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 2.4 billion.
Market Share and Global Presence: Strong presence in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Itron leads in AMI deployments and system integration projects.
2. Landis+Gyr Group AG
Specialization:
Landis+Gyr designs and manufactures smart meters and AMI systems for electricity, gas, and heat. It delivers hardware, software, and services to help utilities transition to digital operations.
Key Focus Areas:
Its primary emphasis is on scalable AMI infrastructure, energy data analytics, and sustainable energy management. The company provides tailored solutions that integrate seamlessly with national and regional utility systems.
Notable Features:
- Robust, high-accuracy meters and modular communication solutions.
- Strong interoperability with major AMI platforms.
- Extensive experience managing national rollouts.
2024 Revenue: Around USD 1.7 billion.
Market Share and Global Presence: Particularly dominant in Europe, especially the United Kingdom’s national smart-meter rollout, and maintains operations in over 30 countries.
3. Elster Group GmbH (Honeywell)
Specialization:
Elster, now a part of Honeywell, specializes in high-precision gas, electricity, and water metering. Its integration within Honeywell enables combined offerings in industrial automation and safety systems.
Key Focus Areas:
Focuses on durable, industrial-grade meters for utilities and industries, integration with Honeywell’s control systems, and ensuring safety and compliance in gas distribution networks.
Notable Features:
- Proven reliability and long service life.
- Integration with Honeywell’s industrial Internet-of-Things ecosystems.
- Advanced remote monitoring and leak-detection capabilities.
2024 Revenue: Honeywell’s total 2024 revenue was about USD 50 billion+; the Elster unit represents a substantial portion of its energy-related operations.
Market Share and Global Presence: Strong heritage and installed base in North America and Europe, with global distribution through Honeywell’s extensive channels.
4. Sensus (Xylem Inc.)
Specialization:
Sensus, part of Xylem Inc., provides smart metering solutions and communication networks for water, gas, and electricity utilities. Its product line includes endpoints, network infrastructure, and data-management systems.
Key Focus Areas:
The company focuses on integrating metering data into larger utility management systems, ensuring secure, reliable communications, and supporting utilities in achieving operational efficiency and sustainability.
Notable Features:
- Reliable, low-latency communication networks.
- Cloud-based data analytics and scalable AMI infrastructure.
- Integration with Xylem’s water-management expertise, enhancing cross-utility solutions.
2024 Revenue: Xylem reported approximately USD 8.6 billion in total revenue, with Sensus contributing a significant portion through metering and network solutions.
Market Share and Global Presence: Major presence in North America and expanding globally through smart-city and water-energy optimization projects.
5. Kamstrup A/S
Specialization:
Kamstrup is a Danish technology company known for high-precision metering solutions for water, heat, and electricity, with growing involvement in smart gas metering.
Key Focus Areas:
Innovation in metering technologies, advanced data analytics, turnkey project delivery, and service excellence. Kamstrup emphasizes sustainability and circular production in its operations.
Notable Features:
- Ultrasonic metering technology offering superior accuracy.
- End-to-end project management and customer support.
- Focus on cybersecurity and future-ready firmware upgrades.
2024 Revenue: Estimated in the hundreds of millions to low-billion USD range, per company filings.
Market Share and Global Presence: Particularly strong in Scandinavia and central Europe; expanding reach into the Asia-Pacific region with major turnkey smart-meter projects.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Cellular LPWAN Adoption (NB-IoT and LTE-M)
Low-power wide-area networks such as NB-IoT and LTE-M are revolutionizing connectivity for smart gas meters. These technologies lower costs and extend coverage into rural or low-density regions, eliminating the need for proprietary mesh networks.
Impact: More utilities can now justify smart metering deployments even in dispersed service areas, accelerating global adoption.
2. Edge Intelligence
Smart gas meters increasingly incorporate onboard processing capabilities to analyze data locally, enabling immediate responses to anomalies or leaks.
Impact: Reduced data-transmission volumes, faster safety responses, and improved system resilience.
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) Models
Utilities are shifting from capital-intensive hardware purchases to service-based models that include meter data management (MDM), analytics, and updates on subscription terms.
Impact: Predictable revenue streams for vendors and faster deployment timelines for utilities.
4. Standardization and Cybersecurity
Regulators are mandating interoperability standards and strict data-protection measures for critical infrastructure.
Impact: Enhanced system reliability, better integration between different vendors, and increased consumer trust.
5. Integration with Decarbonization Goals
Smart gas meters are vital to national energy-efficiency and decarbonization efforts. They enable more accurate emissions tracking, improved demand forecasting, and hybrid energy solutions combining gas and renewables.
Impact: Gas utilities can position themselves as enablers of low-carbon energy systems.
6. Retrofit vs. Full Replacement Strategies
Utilities can either retrofit existing meters with smart modules or replace them entirely, depending on budget, regulatory timelines, and network maturity.
Impact: Expands the total addressable market by allowing phased rollouts rather than complete system overhauls.
Successful Global Examples
Great Britain Smart Meter Program
The United Kingdom’s national smart-meter rollout is one of the largest in the world, encompassing both electricity and gas meters. Landis+Gyr is a key supplier, delivering tens of millions of smart meters. The program demonstrates how strong policy mandates, standardized technologies, and centralized data hubs can achieve mass deployment, cost reduction, and improved customer satisfaction.
Denmark — Kamstrup and Radius Case Study
Kamstrup led a large-scale project for Danish utility Radius, replacing over one million traditional meters with smart devices in a remarkably short time frame. This initiative showcased the benefits of end-to-end project management, precise scheduling, and robust public-private coordination.
Europe-Wide Utility Pilots
Across Europe, utilities have partnered with vendors like Itron and Landis+Gyr to run AMI pilots that test advanced functionalities such as real-time billing, anomaly detection, and dynamic pricing. These pilots have proven that smart gas metering can drastically cut operational losses while enhancing energy management and customer service.
North America — Utility Modernization
In the United States and Canada, major gas utilities have adopted Sensus and Itron smart meters to improve billing accuracy and reduce theft. Many projects are integrated with larger smart-grid initiatives funded by state-level modernization grants.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Initiatives
Europe
Drivers:
Europe leads the global smart gas meter market, driven by stringent EU directives on energy efficiency, consumer rights, and digital infrastructure.
Policies:
The EU Energy Efficiency Directive mandates the rollout of smart meters to promote transparency and demand-side management. National programs in the U.K., France, Italy, and the Nordics offer financial incentives for utilities transitioning to AMI.
Impact:
Europe has achieved some of the world’s highest penetration rates of smart meters, with gas and electricity networks closely integrated into national energy-transition strategies.
North America
Drivers:
Regulated utilities focus on operational cost savings, safety improvements, and customer engagement.
Policies:
The U.S. Department of Energy supports smart-grid initiatives through funding and guidelines, while state public utility commissions oversee implementation.
Impact:
Deployment varies by state; regions such as California, Texas, and parts of Canada show high adoption. Utilities leverage smart gas meters for predictive maintenance and emissions tracking.
Asia-Pacific
Drivers:
Rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and growing gas consumption are spurring modernization efforts.
Policies:
Countries like China and India are investing heavily in smart infrastructure. China’s government promotes smart utility systems as part of its digital economy agenda, while India’s Smart City Mission and Ujjwal Bharat initiative encourage smart metering adoption.
Impact:
APAC represents the fastest-growing market segment, with opportunities for both global and local manufacturers to supply large-scale tenders.
Latin America
Drivers:
Focus on loss reduction and accurate billing in developing gas networks.
Policies:
National energy agencies in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile are experimenting with pilot programs and partnerships with European meter vendors.
Impact:
Though in the early stages, the region’s favorable demographics and expanding infrastructure make it a promising growth frontier for smart gas metering.
Middle East & Africa
Drivers:
Expanding natural-gas networks and growing awareness of energy efficiency.
Policies:
Government initiatives, often supported by international development banks, are funding smart utility projects to improve safety and reduce leakage.
Impact:
Adoption is currently limited to urban and industrial hubs but expected to accelerate as regulatory frameworks mature and connectivity costs decline.
Utility and Vendor Considerations
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Beyond the initial purchase, utilities must factor in communication costs, maintenance, and data-management infrastructure. Long-term operational efficiency often outweighs upfront savings. - Interoperability:
Adopting open standards ensures flexibility in integrating different vendor systems and future upgrades. - Security and Privacy:
Smart gas meters are part of critical infrastructure. Utilities must implement encryption, secure firmware updates, and strict access controls to protect customer data. - Deployment Strategy:
Utilities can choose phased rollouts, pilot projects, or region-wide replacements depending on available funding and policy mandates. - Consumer Engagement:
Educating consumers about the benefits of smart meters — accurate billing, transparency, and safety — is key to achieving public acceptance and minimizing resistance.
Summary
The smart gas meter market stands at the crossroads of digital transformation, sustainability, and energy security. With global leaders such as Itron, Landis+Gyr, Elster (Honeywell), Sensus (Xylem), and Kamstrup driving innovation, the market is set to grow steadily as utilities embrace intelligent infrastructure. Advances in connectivity, analytics, and automation are redefining how gas utilities operate — paving the way for safer, more efficient, and environmentally responsible energy systems worldwide.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: 3D Printing Construction Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034