Injectable Drug Delivery Market Trends, Growth Drivers and Leading Companies 2024
Injectable Drug Delivery Market Size
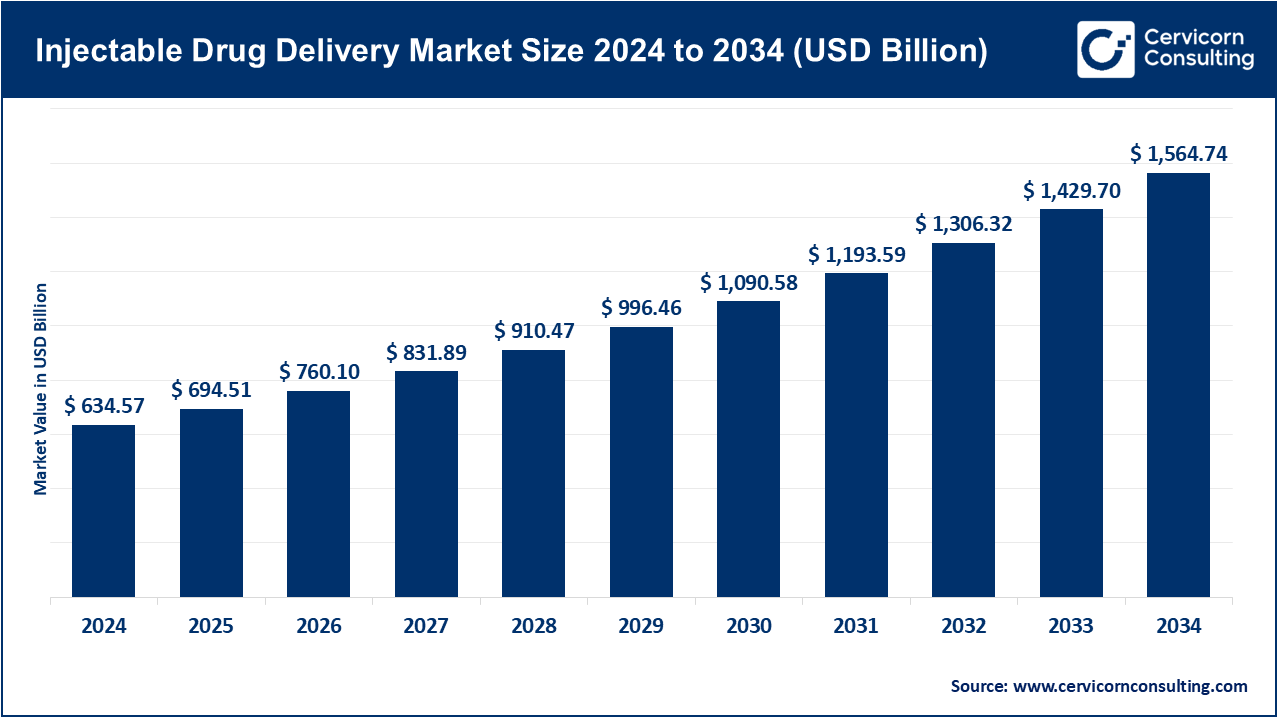
The global injectable drug delivery market size was worth USD 634.57 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 1,564.74 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.45% from 2025 to 2034.
What is the Injectable Drug Delivery Market?
The injectable drug delivery market encompasses both the medicines administered by injection and the devices or systems used to deliver them. It includes vials and ampoules, syringes and needles, prefilled syringes (PFS), autoinjectors, insulin pens, wearable injectors, safety needles, infusion pumps, and connected or “smart” delivery systems. Ancillary products such as needle-safety devices, reconstitution systems, and cold-chain packaging required for biologics also fall under this category.
Demand is driven by the rising dominance of biologics in pharmaceutical pipelines—since most biologics require parenteral administration—alongside increasing prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Growing acceptance of self-injection, expansion of biologics manufacturing capacity, and advances in smart connected injectors all contribute to market expansion. The segment therefore bridges two industries: pharmaceuticals and medical devices, combining biological innovation with engineering precision to improve patient outcomes worldwide.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2766
Growth Factors
The injectable drug delivery market is expanding due to multiple converging factors: the increasing global prevalence of chronic diseases requiring long-term injectable therapy; rapid growth in biologic and biosimilar drug approvals; technological advancements in autoinjectors, prefilled syringes, wearable injectors, and smart drug delivery systems; rising patient preference for home-based care and self-administration; supportive government and regulatory initiatives promoting safe injection practices; growing healthcare infrastructure investments; and the push for enhanced cold-chain logistics for temperature-sensitive biologics. These drivers collectively enhance accessibility, safety, and convenience, leading to strong growth projections for the global injectable drug delivery market through 2034.
Why the Injectable Drug Delivery Market Is Important
- Essential for Biologics – Most modern biologic and biosimilar therapies cannot be administered orally because they degrade in the digestive tract. Injectable delivery remains the most effective way to ensure the efficacy and stability of these complex molecules.
- Ensures Precision and Bioavailability – Injections deliver medication directly into the bloodstream or targeted tissues, ensuring rapid onset and accurate dosing, especially for drugs with narrow therapeutic windows.
- Supports Self-Care and Adherence – Autoinjectors and insulin pens have empowered patients to manage chronic conditions independently, improving adherence, convenience, and quality of life while reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
- Critical for Public Health Programs – Large-scale immunization efforts, emergency responses, and pandemic preparedness depend on robust injectable delivery infrastructure, including manufacturing, cold chain, and trained personnel.
- Economic and Strategic Value – For pharmaceutical companies, integrating the right drug-device combination extends product lifecycle, improves differentiation, and enables premium pricing. For health systems, efficient injectables reduce hospitalization and improve patient management.
Top Companies in the Injectable Drug Delivery Market
Below are profiles of leading companies shaping the global injectable drug delivery landscape, focusing on their specialization, key focus areas, notable features, 2024 revenues, market share relevance, and global presence.
Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- Specialization: BD is a global leader in medical devices, particularly in syringes, safety needles, prefilled syringes, medication management systems, and infusion technologies.
- Key Focus Areas: The company focuses on medication delivery systems, autoinjector technology, prefilled syringes, and needle safety innovations. BD also integrates its devices with hospital IT systems for medication management and error reduction.
- Notable Features: BD manufactures billions of syringes annually, serving pharmaceutical firms, hospitals, and public-health agencies. It also plays a central role in global vaccination logistics.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 20 billion in fiscal 2024, with strong growth in its medication management and pharmaceutical systems divisions.
- Global Presence: BD has operations in over 190 countries, with major manufacturing hubs in the United States, Europe, India, and China.
Pfizer Inc.
- Specialization: Pfizer is one of the largest pharmaceutical manufacturers in the world, with strengths in vaccines, biologics, and specialty injectable drugs.
- Key Focus Areas: The company focuses on vaccines, oncology biologics, anti-inflammatory injectables, and specialty therapeutics.
- Notable Features: Pfizer’s global COVID-19 vaccine production showcased its capacity for large-scale injectable logistics, cold-chain management, and rapid distribution networks.
- 2024 Revenue: Reported approximately USD 63.6 billion in 2024, with strong contributions from vaccines and specialty injectables.
- Global Presence: Active in more than 125 countries, with R&D centers and manufacturing facilities spread across North America, Europe, and Asia.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Specialization: Teva is a global leader in generic drugs with a strong portfolio of injectable generics, biosimilars, and hospital injectables.
- Key Focus Areas: Development and manufacturing of cost-effective generic injectables, hospital products, and complex parenteral formulations.
- Notable Features: Teva combines large-scale production capacity with expertise in sterile manufacturing, making it a preferred partner for healthcare systems seeking affordable injectables.
- 2024 Revenue: Reported approximately USD 16.5 billion in 2024.
- Global Presence: Operations in over 60 countries with production and distribution networks in North America, Europe, and emerging markets.
Eli Lilly and Company
- Specialization: Eli Lilly focuses on innovative biologics, particularly in diabetes, obesity, oncology, and immunology. Many of its leading drugs are injectables, such as insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
- Key Focus Areas: Injectable diabetes therapies, weight-management drugs, and biologic treatments for autoimmune and oncological conditions.
- Notable Features: Lilly’s portfolio includes globally recognized injectable products like insulin pens and GLP-1 injectors, which have reshaped diabetes and obesity management.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 45 billion in 2024, driven by rapid growth in diabetes and obesity injectables.
- Global Presence: Active in more than 120 countries, with expanding manufacturing and research operations in the U.S., Europe, and Asia.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Rise of Self-Administration and Home Care
Patients increasingly prefer home-based therapy due to convenience and lower costs. The proliferation of prefilled syringes, insulin pens, and autoinjectors has empowered individuals to self-inject safely. The impact is a shift from hospital-centric to patient-centric care, reducing clinical workloads and improving adherence.
2. Dominance of Biologics and Biosimilars
The biopharmaceutical pipeline is dominated by biologics and biosimilars, all of which require parenteral administration. This drives demand for high-quality injectors, prefilled systems, and cold-chain logistics. Pharmaceutical firms are partnering with device makers early in drug development to optimize delivery performance.
3. Wearable and Large-Volume Injectors
Wearable injectors capable of delivering larger doses over extended periods are gaining traction, especially for oncology, autoimmune, and rare diseases. These devices enable patients to receive treatment at home, reducing hospital visits and improving quality of life.
4. Smart and Connected Devices
Integration of connectivity features such as Bluetooth or NFC allows injectors to track dosing, send reminders, and share adherence data with healthcare providers. This digitalization of drug delivery is fostering data-driven disease management, particularly in diabetes and chronic-care programs.
5. Surge in Prefilled Syringes and Safety Devices
Prefilled syringes offer reduced contamination risk, accurate dosing, and shorter preparation time. Safety syringes with retractable needles or shielding mechanisms are becoming mandatory under stricter health and occupational safety regulations, especially in North America and Europe.
6. Regulatory and Safety Standards
Government policies mandating the use of safety-engineered injection devices are boosting adoption. Regulatory authorities have issued guidelines for combination products (drug + device), ensuring product consistency and patient safety, though compliance costs have risen.
7. Localization and Supply Chain Resilience
Post-pandemic strategies emphasize regional manufacturing of syringes, needles, and autoinjector components to ensure supply security. Several governments are offering tax benefits and incentives to boost domestic production of critical injectable components.
These trends are reshaping the competitive landscape. Drug manufacturers must integrate delivery considerations into early product design, while device makers are focusing on patient experience, digital health integration, and sustainable materials.
Successful Examples Around the World
1. Global Vaccination Campaigns:
The mass COVID-19 vaccination drives between 2020 and 2022 demonstrated the scalability and importance of injectable drug delivery systems. Billions of doses were produced, filled, and distributed worldwide, supported by partnerships among governments, pharmaceutical giants, and device manufacturers. This event accelerated innovation in vial design, safety syringes, and cold-chain distribution networks.
2. Self-Injectable Contraceptives in Developing Regions:
Several countries in Africa and South Asia have successfully introduced self-administered subcutaneous contraceptives (DMPA-SC). Supported by global health organizations, these initiatives improved accessibility for women in rural areas, reduced dependency on clinic visits, and proved that safe self-injection can be achieved at scale through training and policy alignment.
3. Insulin Pen Revolution:
The introduction of insulin pens transformed diabetes management globally. Patients gained portability, accurate dosing, and improved quality of life. The widespread adoption of disposable and reusable pens shows how patient-centric design can achieve both commercial success and clinical improvement.
4. Wearable Injectors for Oncology Care:
Wearable devices used for subcutaneous administration of large-molecule drugs in oncology are helping hospitals shift infusion-based therapies to at-home administration. This reduces treatment costs and enhances patient comfort while maintaining efficacy.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Initiatives
North America
North America leads the injectable drug delivery market due to its strong biologics pipeline, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory clarity for combination products. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides detailed guidance on the approval process for drug-device combinations, encouraging innovation. Government vaccine procurement programs and reimbursement frameworks for self-administered biologics continue to drive demand. The region also benefits from high patient awareness, strong insurance coverage, and adoption of smart connected injectors for chronic-care monitoring.
Europe
Europe’s market is shaped by strict regulatory compliance under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which ensures high safety standards. The region is also witnessing growth in prefilled syringes, safety devices, and autoinjectors for biologics and biosimilars. Public health systems emphasize value-based procurement, encouraging devices that improve adherence and outcomes. The European Union actively funds research on sustainable materials and recyclable injection systems, aligning with environmental goals.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market due to rising healthcare expenditure, expanding chronic disease prevalence, and government support for local manufacturing. China and India have announced initiatives to strengthen domestic production of syringes and biologics under industrial incentive programs. Japan continues to lead in high-precision delivery systems for insulin and biologics. Meanwhile, increasing adoption of self-injection devices in countries such as South Korea and Singapore reflects growing patient empowerment and digital-health readiness.
Latin America
Latin American countries, including Brazil and Mexico, are focusing on expanding immunization programs and improving access to affordable injectables through partnerships with global manufacturers. Government tender systems for vaccines and chronic-disease therapies are major demand generators. However, import dependency and fluctuating exchange rates pose challenges for long-term supply consistency.
Middle East and Africa
This region is driven by large-scale immunization initiatives and donor-supported programs. Governments are adopting WHO-recommended policies to promote safe injection practices and local training programs for healthcare professionals. The introduction of self-injectable contraceptives and expansion of public–private vaccine partnerships are improving healthcare access in rural areas. As healthcare infrastructure develops, the demand for affordable yet high-quality injectables continues to rise.
Government Policies Shaping the Injectable Drug Delivery Market
- Reimbursement and Procurement Policies: In many developed markets, reimbursement for self-administered injectables drives adoption. In developing regions, centralized government procurement for vaccines and chronic diseases ensures large-volume demand.
- Regulatory Support for Drug-Device Combinations: Streamlined approval processes and clear regulatory guidance for combination products reduce barriers to innovation and market entry.
- Safety Legislation: Mandates requiring safety-engineered devices, such as retractable syringes, have accelerated industry innovation and improved healthcare worker safety.
- Domestic Manufacturing Incentives: Governments in India, China, and parts of Europe offer financial incentives to boost local production, reducing import dependency and enhancing supply chain resilience.
- Public Health Programs: Large-scale initiatives, including immunization drives, chronic disease control programs, and family-planning projects, directly influence market demand for injectable products and delivery devices.
Strategic Insights for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Integrating drug-device development early ensures smoother regulatory approval, improved user experience, and competitive advantage. Combination products can extend patent life and strengthen brand loyalty.
- Medical Device Manufacturers: Focus areas include miniaturization, human-factor engineering, and digital connectivity. Developing reusable or eco-friendly devices will meet both sustainability and cost objectives.
- Healthcare Providers: Emphasize training programs for patients adopting self-injection technologies to ensure safety, adherence, and effective outcomes.
- Investors and Policymakers: Support infrastructure development and digital-health ecosystems that enable real-time monitoring and data-driven care.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Hydrogen Polygeneration System Market Trends, Growth Drivers and Leading Companies 2024