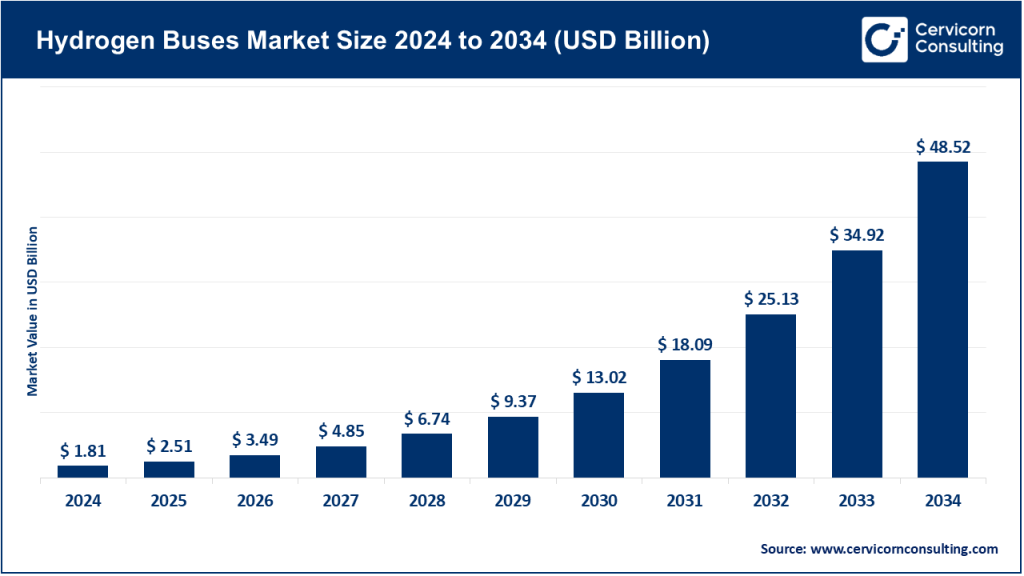
Hydrogen Buses Market Size
Growth factors
The hydrogen buses market is being driven by multiple converging forces: decarbonisation targets and clean-air regulations that push cities to replace diesel fleets; growing public and private funding for zero-emission public transit that makes higher-upfront hydrogen buses financially tractable via subsidies and total-cost-of-ownership (TCO) analyses; technology improvements and scale-up in fuel cells, hydrogen storage and electrolyser capacity that are gradually lowering component costs; commitments from fleet operators and OEMs to diversify beyond battery-electric buses (especially for high-mileage, long-range routes and extreme-climate operations where batteries are less attractive.
the parallel expansion of hydrogen refuelling infrastructure and integrated project models (vehicle + refueller + green hydrogen supply); and, finally, strategic moves by oil & gas and industrial gas companies to develop hydrogen value chains that can offer bundled supply and financing — all of which together are catalysing pilot fleets, fleet conversions and procurement pipelines worldwide.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2736
What is the hydrogen buses market?
The hydrogen buses market covers manufacturers, component suppliers (fuel-cell stacks, hydrogen tanks, balance of plant), system integrators, refuelling infrastructure providers, fuel suppliers (green/low-carbon hydrogen), fleet operators, and the services and financing models that tie these together. Product-level offerings vary from city single-decker and double-deck buses to coaches and articulated vehicles, each integrating a proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell (or hybrid fuel-cell + battery architectures), high-pressure composite hydrogen storage tanks, power electronics and conventional bus subsystems. The market includes not just vehicle sales but service contracts, fuel supply agreements, depot refuelling installations and government-sponsored pilot programs. Industry market forecasts model a nascent but extremely fast projected CAGR over the next decade as early projects scale into commercial deployments.
Why is it important?
Hydrogen buses matter because they offer a zero-tailpipe-emission option with rapid refuelling and long range — attributes that address two practical gaps battery buses sometimes struggle with: (1) routes requiring very high daily mileage or continuous operation where overnight charging is insufficient, and (2) cold-climate or heavy-duty applications where battery efficiency and payload can be limiting. From a policy perspective, hydrogen buses let cities decarbonise public transit without massive grid upgrades at depots and provide an industrial pathway to scale green hydrogen production (electrolysers) and storage, stimulating broader hydrogen value chains.
In addition, hydrogen buses can reduce local air pollutants (NOx, particulates) in dense urban corridors, contributing to public-health objectives. However, their net climate benefit depends on hydrogen’s source — green/renewable hydrogen offers true emissions reductions, while grey hydrogen does not — which is why policy and procurement increasingly link hydrogen buses to low-carbon hydrogen supply.
Hydrogen Buses Market — Top Companies (profiles)
Below are concise company profiles tailored to hydrogen bus market relevance: specialization, key focus areas, notable product/features, latest (available) 2024 revenue figure, market share context where available, and global presence.
Hyundai Motor Company
- Specialization: OEM (light and heavy commercial vehicles), fuel-cell powertrains and integrated hydrogen-vehicle platforms.
- Key focus areas: development and mass-production of fuel-cell buses (Elec City FCEV), fuel-cell trucks (XCIENT), integration of hydrogen supply/refuelling business lines, and local manufacturing hubs for hydrogen vehicles.
- Notable features: Hyundai’s Elec City FCEV (urban bus) and Universe FCEV (coach) use Hyundai’s fuel-cell stacks and high-pressure tanks; proven long-range configurations and fleet deployments in Korea and parts of Europe; Hyundai invests along the value chain (vehicles + refuelling ecosystems).
- 2024 revenue (company-wide): Hyundai reported consolidated revenue of KRW 175.2 trillion for 2024.
- Market share: There is no single global market share metric publicly reported that isolates hydrogen-bus revenue; the hydrogen-bus market remains fragmented and nascent, but Hyundai is widely cited as a leading vehicle OEM for fuel-cell bus supply, particularly in South Korea where government programs have accelerated procurement.
- Global presence: South Korea (major deployments), targeted sales and partnerships across Asia, Europe and selected trials elsewhere; Hyundai is active in hydrogen truck demonstrations and is investing in production and refuelling partnerships.
Wrightbus
- Specialization: Bus OEM with a strong portfolio of zero-emission buses — battery electric and hydrogen fuel-cell variants (including double-deckers).
- Key focus areas: zero-emission bus R&D, localised manufacturing in Northern Ireland, building hydrogen and battery fleets for UK and European operators.
- Notable features: Wrightbus produced the world’s first hydrogen double-deckers and has a run of projects that combine local manufacturing with export orders; the company is investing in next-gen zero-emission tech.
- 2024 revenue: Wrightbus is privately held and does not publish a comprehensive public 2024 revenue figure; public reporting focuses on orders, investment and economic impact (company statements highlight strong order books and supply-chain activity).
- Market share: As a specialist bus OEM focused on the UK and select European markets, Wrightbus is a notable player in hydrogen double-deck and zero-emission city bus niches; exact global market share numbers are not publicly disclosed.
- Global presence: UK-based manufacturing (Ballymena), supply and trial contracts across the UK and Europe; recent R&D investments and large contracts with major UK operators (illustrating deep domestic presence and expanding exports).
ITM Power
- Specialization: PEM electrolyser manufacturer (green hydrogen production equipment), enabling hydrogen supply for transport applications including bus fleets.
- Key focus areas: modular PEM electrolysers (TRIDENT platform), factory scale-up, project delivery for industrial and transport hydrogen demand.
- Notable features: ITM reports a commercially proven TRIDENT stack, gigafactory production strategy, and an increasing project pipeline for industrial, transport and power applications. ITM’s transport sector revenue indicates direct engagement in hydrogen projects that feed mobility applications.
- 2024 revenue: ITM Power reported consolidated revenue of approximately £16.5 million for FY 2024.
- Market share: As an electrolyser supplier rather than a bus OEM, ITM competes in the electrolyser market rather than vehicle manufacturing. Its role is critical to the supply side of green hydrogen for buses. Market share in electrolysers is competitive and regionally varied.
- Global presence: UK headquarters and Sheffield manufacturing; sales and projects across Europe and partnerships for large-scale electrolyser plants.
Chart Industries
- Specialization: Cryogenic and cryo-processing equipment, storage and transfer systems — including high-pressure hydrogen storage and cryogenic tanks used in hydrogen value chains.
- Key focus areas: hydrogen storage, processing equipment for industrial hydrogen and cryogenic gas handling, and supply of key hardware to hydrogen refuelling and production projects.
- Notable features: Chart’s expertise in low-temperature gas handling, customized hydrogen storage solutions and recent strategic moves make it a supplier across the hydrogen value chain.
- 2024 revenue: Chart reported full-year 2024 sales of approximately $1.11 billion.
- Market share: Chart is a leading industrial supplier in cryogenic and gas-handling equipment with strong market positions in hydrogen handling; the hydrogen-bus market depends on suppliers like Chart for refuelling and storage solutions.
- Global presence: US-headquartered with operations worldwide; active in major hydrogen projects and supply agreements globally.
Shell (Shell plc)
- Specialization: Integrated energy major with downstream retail, fuels, and a growing hydrogen and low-carbon energy portfolio (including refuelling, hydrogen production and mobility services).
- Key focus areas: hydrogen supply (including low-carbon hydrogen projects), refuelling network development, partnerships with OEMs and fleet operators to provide refuelling + supply contracts.
- Notable features: Shell leverages retail and energy infrastructure expertise to trial and commercialise hydrogen refuelling at scale; Shell’s investments can bundle hydrogen supply commitments for fleets.
- 2024 revenue (company-wide): Shell’s 2024 annual report shows group revenues in the range of several hundred billion dollars.
- Market share: As an energy supplier, Shell does not manufacture buses but is an influential player in hydrogen fuel supply and depot/refueller deployment; market share in refuelling services varies by region and contract portfolio.
- Global presence: Global footprint across retail, fuels and energy projects — engaged in hydrogen projects and refuelling pilots in Europe, Asia and elsewhere.
Leading trends and their impact
- Integrated procurement models (vehicle + fuel + financing): Agencies are increasingly procuring hydrogen buses as part of bundled contracts that include depot refuelling and hydrogen supply agreements. Impact: reduces upfront risk for operators and accelerates adoption because operators don’t need to source hydrogen separately.
- Public subsidy and TCO-focused procurement: Governments subsidize capital costs or offer operational incentives. Impact: short-term financials improve for hydrogen buses (which still have higher capital cost vs diesel or battery buses), encouraging pilot fleets and bulk orders.
- Electrolyser and supply chain scale-up (green hydrogen focus): Greater attention to green hydrogen (electrolysers) to ensure lifecycle emissions reductions. Impact: long-term climate credibility for hydrogen buses improves, but near-term project financing and grid constraints remain a hurdle.
- Fuel-cell + battery hybrids and modularization: OEMs combine fuel cells with battery buffers to optimize efficiency and regenerative braking capture. Impact: better route flexibility and lower fuel consumption, easing TCO comparisons with battery buses.
- Operational realities exposed by early pilots: Several high-profile trials have highlighted supply and maintenance gaps (e.g., refuelling station downtime or gas supply shortages). Impact: demonstrates the need to synchronize vehicle rollouts with reliable refuelling infrastructure and contingency planning.
- Consolidation and strategic moves by incumbents: Industrial gas companies, energy majors and established OEMs are pursuing partnerships, acquisitions or JV structures. Impact: this can accelerate project finance and infrastructure rollouts but creates competitive dynamics across segments (electrolyser suppliers vs energy majors).
Successful examples around the world
- South Korea (Hyundai deployments & national plans): South Korea has been one of the most active markets for hydrogen buses — with large procurement targets and Hyundai supplying substantial parts of the fleet. Korea’s government support and fleet targets have been a major demand pull.
- Aberdeen, Scotland (pioneering double-deckers — operational lessons): Aberdeen pioneered hydrogen double-deck buses and early refuelling infrastructure, demonstrating technical feasibility and local-air improvements — but also exposing a key lesson: refuelling station reliability and supply continuity are critical, as demonstrated when hydrogen supply interruptions put buses out of service. This case is often cited as a “first-mover” success with important operational caveats.
- City pilot programs in Europe and Japan: Multiple European cities and selected Japanese municipalities have run hydrogen-bus pilots (both single and double deck) supported by EU and national funding, providing valuable operational data on range, refuelling cycles and depot integration. These pilots have helped refine specifications and procurement frameworks.
- Fleet scale deals and OEM orders: Large orders and frameworks illustrate how procurement scale can be achieved when local industry, funding and operators align. Wrightbus’s contracts with UK operators and Hyundai’s multiple city orders in Korea are representative.
Global regional analysis — government initiatives and policies shaping the market
Asia (South Korea, Japan, China, India)
- South Korea: Strong national targets and generous subsidies for hydrogen buses; procurement targets in the tens of thousands by 2030 have made South Korea a leading adopter and manufacturing anchor for OEMs supplying hydrogen buses domestically.
- Japan: Policy moves such as the Hydrogen Society Promotion Act and multi-year subsidies for low-carbon hydrogen support pilot fleets and long-term procurement. Japan’s focus leans both to hydrogen supply and mobility demos.
- China & India: China is rapidly scaling hydrogen and electrolyser manufacturing capacity (important for the upstream supply chain), while India has emerging hydrogen strategies and pilot funding aimed at public transit decarbonisation.
Europe (EU countries, UK)
- EU: Funding streams, green public procurement criteria and pilot programs are enabling deployments; the EU’s clean-transport goals encourage member states to support fleets, but member states differ in subsidy levels.
- UK: Active support for Wrightbus and domestic OEM programs; local financing, R&D grants and export-support measures have helped resuscitate local hydrogen bus manufacturing. However, the Aberdeen experience shows infrastructure reliability is a decisive factor.
North America
- The US and Canada run selected pilot programs and focus more on heavy-duty hydrogen for trucks and industry in the near term; hydrogen-bus activity is growing but at a smaller scale compared to battery buses and other regions. Federal incentives (e.g., investment tax credits tied to clean hydrogen production) influence project economics.
Middle East, Australia, Africa, Latin America
- Activity is more project-based: industrial decarbonisation and export-oriented hydrogen projects receive emphasis; transport deployments (including buses) are nascent but interest is growing where renewable resources and strategic hydrogen export plans exist. Australia and some Gulf countries are prioritizing hydrogen production for export, which could eventually enable domestic mobility pilots.
Overarching policy levers shaping adoption
- Purchase subsidies and TCO parity programs (reducing fleet operators’ capital exposure).
- Hydrogen supply incentives (e.g., electrolyser funding and production credits to create low-carbon hydrogen).
- Public procurement mandates and clean-fleet targets (cities requiring a share of new buses to be zero-emission).
- Integrated infrastructure funding (supporting depot refuelling, grid upgrades, or on-site electrolysis).
- Performance and safety standards (ensuring vehicles and refuelling meet operational reliability criteria before subsidies are released — increasingly common in subsidy schemes).
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Power Electronics Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034