Healthcare ERP Market Size
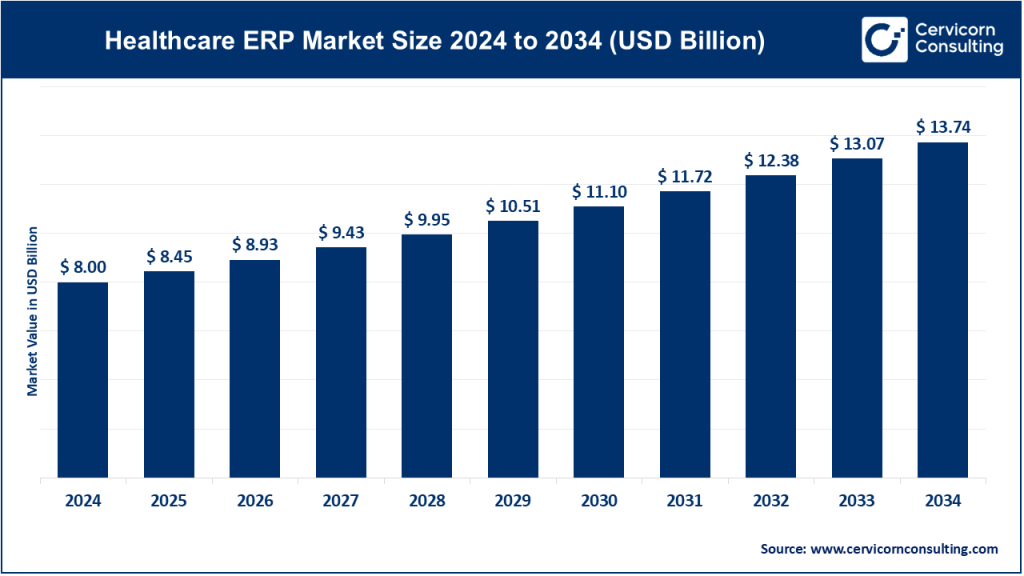
The global healthcare ERP market size was worth USD 8 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 13.74 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.56% from 2025 to 2034.
What is the Healthcare ERP Market?
Healthcare Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to integrated software suites designed specifically for hospitals, health systems, clinics, long-term care facilities, and other healthcare providers. These systems centralize and automate critical back-office and operational functions such as finance, billing, procurement, supply chain management, human resources, inventory, fixed assets, analytics, and sometimes clinical integrations with EHRs/EMRs. Healthcare ERP platforms can be deployed on-premises, through private or public clouds, or as hybrid solutions, increasingly delivered via Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models.
The primary goal of ERP in healthcare is to provide a unified source of truth across administrative and operational domains, enabling providers to reduce waste, enhance financial performance, ensure compliance, and achieve better decision-making. In doing so, healthcare organizations can streamline business operations, reduce inefficiencies, and ultimately support improved patient care outcomes.
Healthcare ERP Market Growth Factors
The healthcare ERP market is witnessing strong growth driven by multiple converging factors. Rising pressure on healthcare organizations to control operational costs while managing increasing patient loads and complex reimbursement structures is pushing hospitals to embrace integrated systems. The growing need for streamlined financial control, real-time analytics, and cost transparency is fueling demand for ERP modernization. Cloud-based ERP solutions have gained traction due to their scalability, lower total cost of ownership, and flexibility. The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotic process automation (RPA), and predictive analytics further enhances ERP capabilities, enabling smarter forecasting, workforce optimization, and inventory management.
In addition, regulatory demands for data protection, audit trails, and interoperability—combined with value-based care initiatives—are encouraging providers to adopt modern ERP platforms. Together, these drivers are propelling the global healthcare ERP market toward steady, double-digit growth through the next decade.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2435
Why is Healthcare ERP Important?
Healthcare ERP systems are transforming the operational backbone of healthcare providers. Their importance lies in several key areas:
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Control: ERP centralizes purchasing, inventory, and financial processes, reducing redundancy and waste. This results in better supply management, reduced procurement costs, and improved resource allocation.
- Revenue Optimization: With integrated billing and revenue-cycle management, ERPs reduce claim denials and accelerate reimbursements, leading to healthier cash flow and better financial stability.
- Workforce Management: HR and scheduling modules help manage workforce allocation, reduce overtime costs, and ensure staff credentialing compliance.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERPs provide built-in governance and traceability features that simplify audit processes and support compliance with data protection regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Unified, real-time data across departments supports strategic planning, cost analysis, and performance improvement initiatives.
In essence, ERP transforms fragmented healthcare operations into connected, data-driven environments that support better patient outcomes and financial sustainability.
Healthcare ERP Market Top Companies
Microsoft Corporation
- Specialization: Microsoft provides the cloud infrastructure (Azure), productivity, and data analytics tools that power ERP solutions across industries. While not a traditional ERP vendor, Microsoft is a critical enabler for ERP deployment, integration, and analytics through Azure, Power Platform, and Dynamics 365.
- Key Focus Areas: Cloud hosting for ERP, AI-powered analytics with Power BI, low-code automation with Power Automate, and seamless integration across healthcare applications.
- Notable Features: Global Azure data centers, strong compliance portfolio (HIPAA, GDPR, ISO), and scalable cloud infrastructure.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 245 billion.
- Market Presence: Microsoft is a foundational technology provider for ERP vendors and healthcare organizations globally, offering the backbone for scalable, secure ERP deployments.
Oracle Corporation
- Specialization: Oracle is a global leader in enterprise software and databases, offering cloud ERP solutions with deep financial, procurement, and analytics capabilities tailored for healthcare enterprises.
- Key Focus Areas: Oracle Cloud ERP, Human Capital Management (HCM), procurement, and industry-specific healthcare cloud modules.
- Notable Features: Robust financials, integrated AI and analytics, cloud-native applications, and flexible deployment options.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 53 billion.
- Market Presence: Oracle holds a major share of the healthcare ERP market, particularly among large hospital systems and payers seeking scalable enterprise-grade systems.
SAP SE
- Specialization: SAP SE is a global ERP pioneer known for its SAP S/4HANA suite, offering advanced financial, procurement, and HR modules with real-time analytics. SAP also develops industry cloud solutions for healthcare.
- Key Focus Areas: Enterprise financials, supply chain management, human capital management, and healthcare-specific process templates.
- Notable Features: Real-time analytics via SAP HANA, cloud migration support, and strong partner ecosystem for healthcare customization.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately EUR 34 billion.
- Market Presence: SAP dominates large hospital networks and integrated delivery systems, providing robust, scalable ERP solutions with advanced analytics.
Allscripts Healthcare Solutions, Inc.
- Specialization: Allscripts (now operating under the Veradigm brand for some divisions) provides clinical, financial, and practice management solutions for healthcare organizations.
- Key Focus Areas: Revenue-cycle management, interoperability between EHR and ERP systems, and data-driven practice optimization.
- Notable Features: Seamless integration between clinical and administrative data, flexible deployment for ambulatory and acute-care providers, and strong data exchange capabilities.
- 2024 Revenue: Estimated between USD 620–635 million.
- Market Presence: A strong presence in North America, serving small to mid-sized healthcare organizations with clinical and financial integration needs.
Sage Group Plc.
- Specialization: Sage is a leading provider of financial, payroll, and HR software, catering primarily to small and medium-sized healthcare organizations.
- Key Focus Areas: Cloud-based financial management (Sage Intacct), HR and payroll automation, and compliance management.
- Notable Features: User-friendly interface, scalable SaaS model, and strong mid-market presence.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately GBP 2.33 billion.
- Market Presence: Popular among smaller healthcare organizations and community hospitals seeking cost-effective ERP solutions.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
- Cloud Migration and SaaS Adoption:
Healthcare providers are transitioning from legacy, on-premises systems to cloud-based ERP platforms. Cloud ERP offers reduced infrastructure costs, simplified maintenance, and the ability to scale across multi-facility health systems. However, concerns about data privacy, security, and compliance with healthcare regulations remain key considerations. - Integration with Clinical Systems:
ERP systems are increasingly being integrated with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and laboratory information systems (LIS). This connection bridges clinical and financial data, enabling automated charge capture, accurate billing, and real-time inventory management of medical supplies and pharmaceuticals. - Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics:
AI and ML are being embedded into ERP systems to forecast staffing needs, manage inventory, predict patient demand, and identify billing anomalies. Predictive analytics empower hospitals to optimize operations and prevent supply shortages before they occur. - Focus on Revenue-Cycle Modernization:
Revenue-cycle modules are a major investment area within ERP systems, helping providers automate claims processing, reduce denials, and improve cash flow. This is particularly crucial as reimbursement models shift toward value-based care. - Supply Chain Resilience:
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global medical supply chains. Healthcare ERPs are now emphasizing procurement transparency, vendor collaboration, and demand forecasting to build more resilient supply networks. - Enhanced Compliance and Security Features:
Modern ERP systems now embed compliance frameworks to meet HIPAA, GDPR, and other healthcare regulations. Features like audit logs, data encryption, and access control ensure secure handling of sensitive patient and financial data.
Successful Examples of Healthcare ERP Implementations
Cleveland Clinic, USA
Cleveland Clinic implemented an enterprise ERP system to standardize financial and procurement operations across its multi-site network. The implementation led to improved supply chain visibility, cost savings through consolidated purchasing, and faster financial reporting.
NHS Trusts, United Kingdom
Multiple National Health Service (NHS) trusts in the UK have modernized their finance and HR systems under government-supported digital initiatives. Cloud-based ERP rollouts have enabled these trusts to centralize financial management, improve budget accountability, and align with government cost-containment policies.
Apollo Hospitals, India
One of India’s leading healthcare groups, Apollo Hospitals, adopted a cloud ERP solution integrated with its hospital management system. The integration streamlined procurement, payroll, and inventory management across its extensive hospital network, enhancing transparency and operational efficiency.
Academic Medical Centers in Europe
Several European academic medical centers have implemented SAP S/4HANA or Oracle ERP systems to manage their multi-faceted operations—combining clinical care, research, and education. These systems provide real-time analytics for grant management, finance, and hospital operations.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Policies
North America
North America leads the global healthcare ERP market, driven by a high concentration of large healthcare organizations, complex reimbursement systems, and stringent compliance requirements. The U.S. government’s focus on digital transformation, transparency in healthcare pricing, and value-based care reimbursement models has accelerated ERP adoption. Cloud ERP solutions are being rapidly deployed to enhance interoperability between financial and clinical systems. Canada is following similar trends with healthcare IT modernization initiatives supported by provincial governments.
Europe
Europe’s healthcare ERP market is shaped by government-led digital transformation programs, public healthcare system modernization, and strong data protection regulations. The United Kingdom’s NHS Digital initiative encourages shared ERP platforms across regional trusts. In the EU, GDPR compliance has increased demand for ERP systems that ensure data integrity and transparency. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are actively investing in ERP upgrades as part of their broader e-health and interoperability strategies.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific represents one of the fastest-growing regions in the healthcare ERP market. Rapid urbanization, expanding hospital networks, and national healthcare digitization programs are driving growth. Countries such as India, China, Japan, and Australia are witnessing large-scale ERP deployments in both public and private sectors. Government initiatives like India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission promote interoperability and data-driven healthcare, encouraging ERP adoption for better resource management and accountability.
Latin America
Latin American countries are increasingly investing in healthcare infrastructure and IT systems. Brazil and Mexico are leading the way in ERP adoption to improve hospital management and procurement. Economic reforms and public-private partnerships are supporting cloud-based ERP implementations that enhance financial control and reduce administrative burdens in public hospitals.
Middle East and Africa
Healthcare ERP adoption in the Middle East and Africa is steadily rising, supported by large investments in healthcare infrastructure and modernization. Gulf countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are integrating ERP systems as part of their national health digitization and Vision 2030 initiatives. In Africa, ERP adoption is driven by the need for supply chain transparency, especially in donor-funded healthcare programs.
Government Initiatives and Policies Shaping the Market
- Digital Health Policies:
Governments worldwide are emphasizing healthcare digitization to enhance efficiency and accessibility. Initiatives such as the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator (ONC) interoperability rules, the EU’s eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure, and India’s National Digital Health Mission are promoting ERP integration with broader digital ecosystems. - Value-Based Care Models:
Shifts from fee-for-service to value-based care reimbursement models require hospitals to accurately measure cost and performance metrics. ERP systems enable the financial and operational transparency needed to participate in such models. - Data Privacy and Protection Laws:
Regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe mandate stringent data security measures. ERP systems that offer built-in compliance and secure data handling are increasingly favored by healthcare providers. - Public Procurement and Shared Services:
Government-driven centralization of procurement and HR functions, especially in publicly funded systems, encourages ERP adoption. Shared service centers allow multiple hospitals to operate under a unified ERP platform, reducing costs and improving accountability. - Healthcare Infrastructure Funding:
Governments in emerging markets are allocating funds for healthcare digitization projects, including ERP systems. These initiatives aim to modernize public hospitals, streamline operations, and improve access to data-driven healthcare delivery.
Strategic Considerations for Healthcare Leaders
- Define Clear Objectives: Successful ERP implementation begins with well-defined goals such as reducing administrative costs, improving procurement transparency, or enhancing billing accuracy.
- Prioritize Integration: ERP systems should be seamlessly integrated with EHRs, billing systems, and other health IT platforms to ensure data consistency.
- Evaluate Cloud Readiness: Healthcare providers should assess their infrastructure and regulatory environment before adopting cloud ERP solutions.
- Partner with Experienced Vendors: Selecting vendors and implementation partners with proven healthcare expertise is critical for ensuring compliance and operational fit.
- Focus on Change Management: ERP transformation is not just a technical project but an organizational shift. Comprehensive training and stakeholder engagement are vital for success.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: AI Infrastructure Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034