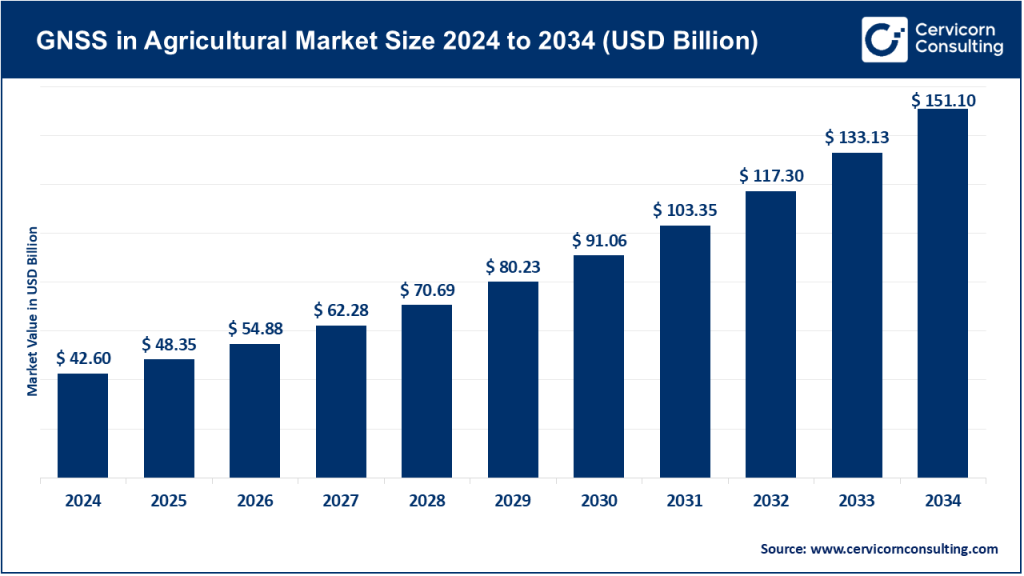
GNSS in Agricultural Market Size
Growth factors
The GNSS-in-agriculture market is being pulled forward by a confluence of forces: falling receiver costs and more capable multi-constellation chips, expanding high-accuracy services such as Galileo High Accuracy and regional SBAS, growing farmer awareness of precision-ag returns through input savings and yield gains, rising farm labor scarcity pushing automation, broader adoption of digital farm management platforms that rely on geospatial accuracy, and strong public funding for precision-ag research and deployments across the world. Climate pressure and regulatory incentives for sustainable, traceable farming further accelerate precision investments, while business consolidation and aftermarket retrofit strategies make GNSS tools accessible across farm sizes.
What is “GNSS in the agricultural market”?
“GNSS in agriculture” refers to the ecosystem of hardware, firmware, software and services that use satellite positioning and time signals to enable farming applications: auto-steer guidance, machine control, precision planting, yield mapping, variable-rate application of seed, fertilizer, and chemicals, field mapping, fleet and asset tracking, RTK/PPP and SBAS augmentation delivery, and data services that integrate GNSS-produced geolocation with sensors, imagery and farm management systems. GNSS capabilities vary by accuracy (meter-level to centimeter-level) and latency (real-time RTK versus post-processed), which determines suitability for different tasks — from parcel mapping to automated implement guidance.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2758
Why is GNSS important for agriculture?
GNSS is the precision needle that lets modern agriculture move from blanket, “one-size” operations to site-specific management. With accurate position and timing, farmers can cut overlap in spraying and planting, apply fertilizers and pesticides exactly where needed, trace input and harvest provenance, run implements autonomously to reduce labor needs, and combine GNSS with sensors and imagery for decision support. These changes boost input efficiency, reduce costs and environmental footprint, and enable compliance with traceability and sustainability standards. Evidence from OEM impact studies shows measurable cost savings and fuel/time reductions when guidance and variable-rate application are correctly implemented.
GNSS in Agricultural Market — Top Companies
John Deere (Deere & Company)
- Specialization: Full-line OEM (tractors, combines, sprayers) with integrated precision ag technology such as AutoTrac guidance, JDLink telematics, ExactApply, and Operations Center.
- Key focus areas: Factory-fit precision, autonomy, integrated data platforms, partnerships for connectivity and services.
- Notable features: AutoTrac auto-steering, GreenStar displays, integrated machine-to-farm-cloud ecosystem delivering end-to-end workflows and ROI calculators. Deere emphasizes system-level integration of hardware, software, and financing.
- 2024 Revenue: Deere reported consolidated net sales and revenues of about $51.7 billion for fiscal 2024; Production & Precision Agriculture was a major contributor at over $20 billion.
- Market share / Global presence: Market leader in large machinery and integrated precision systems; very strong in North America, large footprint in Europe, Latin America, and Asia-Pacific via dealer networks and manufacturing.
Trimble
- Specialization: Positioning hardware, guidance, field computers, agronomy software, and geospatial solutions; historically strong in GNSS receivers/RTK and precision guidance.
- Key focus areas: Positioning accuracy, recurring software revenue, integrations with OEMs and third parties.
- Notable features: High-quality GNSS/INS receivers, field-level software, integrated workflow; strong emphasis on subscription models.
- 2024 Revenue: $3.68 billion. Trimble completed major ag-business transactions that reshaped its precision agriculture segment.
- Market share / Global presence: Strong in precision guidance and aftermarket GNSS equipment globally; partnerships and joint ventures such as PTx with AGCO target mixed-fleet adoption.
AG Leader
- Specialization: Aftermarket precision ag electronics and software — guidance controllers, seed and fertilizer application controllers, data platforms.
- Key focus areas: Cost-effective retrofit precision systems, data collection and analytics, yield mapping and VRA controllers suited to small-to-mid farms.
- Notable features: Reputation for open connectivity and farmer-centric aftermarket solutions that retrofit older machines.
- 2024 Revenue (estimate): Private company; industry estimates place revenue in the $50–75 million range.
- Market share / Global presence: Niche leader in retrofit electronics, strong in North America, growing exports to Latin America and Asia-Pacific.
Topcon Agriculture (Topcon Positioning Group)
- Specialization: GNSS and machine control systems for precision agriculture, surveying, and construction; guidance, auto-steer, correction services.
- Key focus areas: High-precision positioning, aftermarket and OEM solutions, integrated workflows between geospatial and ag applications.
- Notable features: Robust RTK and SBAS implementations, machine control integrations, and cross-sector expertise from surveying and engineering.
- 2024 Revenue (Parent): Topcon Corporation reported Positioning Business net sales at ¥140,386 million (around $1.4 billion).
- Market share / Global presence: Significant share in GNSS receivers and machine control across Europe, Japan, North America, and Asia-Pacific.
Hexagon Agriculture (Hexagon AB — Autonomous Solutions / Agriculture focus)
- Specialization: Hexagon is a large tech group offering geospatial software and autonomy tech; its Autonomous Solutions business provides GNSS-enabled guidance, fleet optimisation and autonomy solutions adaptable to agriculture.
- Key focus areas: Autonomy, sensor fusion, high-precision positioning, software for fleet and operations including digital twins and mapping.
- Notable features: Strong R&D, sensor fusion platforms, industrial deployments across sectors leveraging Hexagon’s broader location intelligence portfolio.
- 2024 Revenue: Hexagon reported net sales of approximately €5.4 billion (≈ $5.8 billion USD) for 2024 across the group.
- Market share / Global presence: Global reach across Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific with strong enterprise and industrial customer base.
Leading trends and their impact
- Multi-constellation and multi-frequency receivers become standard.
Devices that use GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, and GLONASS yield better signal availability and resilience, improving uptime for guidance and RTK solutions. - Augmentation services expand and commercialize.
Regional SBAS services and commercial PPP reduce the cost of achieving sub-decimetre accuracy, broadening adoption of tasks such as precision planting and controlled-traffic farming. - Shift from hardware to software and recurring revenue.
Companies emphasize subscription models and data platforms — farmers now pay for positioning and services, not just equipment. - OEM-first factory integration versus aftermarket retrofit.
Large OEMs increasingly ship factory-installed GNSS, while aftermarket players serve mixed fleets and cost-sensitive buyers. - Consolidation and partnerships.
Strategic moves like Trimble and AGCO’s PTx joint venture unify precision stacks, simplify interoperability, and accelerate rollouts. - Autonomy layering on top of accurate positioning.
GNSS combined with RTK, INS, and perception sensors enables autonomous implements, reducing labour dependence and improving timeliness.
Successful examples around the world
- United States: John Deere AutoTrac delivers measurable input savings for large farms, with evidence of reduced herbicide, fertilizer, fuel, and time costs.
- Europe: EGNOS and Galileo adoption has brought affordable, accurate guidance systems into mainstream use across the EU, enabling both small and large farms.
- Brazil & Latin America: Large-scale farms adopt Trimble and Topcon GNSS solutions for precision planting and VRA, integrated with local agronomy expertise.
- India: The Digital Agriculture Mission integrates GNSS mapping and satellite data for advisories to smallholders, enabling nutrient management and soil mapping across diverse regions.
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives & policies shaping the market
North America
The USDA supports precision agriculture adoption through Conservation Innovation Grants and climate-smart programs. Federal RTK networks and SBAS (WAAS) improve accuracy and coverage. Large commercial farms dominate adoption, with public programs offsetting costs.
Europe
EU space programs actively promote GNSS applications in agriculture. The Common Agricultural Policy incentivizes digital tools and sustainable practices. Widespread use of EGNOS-enabled receivers supports both small and large farms.
Asia-Pacific
India’s Digital Agriculture Mission builds public digital infrastructure, integrating GNSS with satellite imagery. China and Australia support BeiDou and GNSS-enabled agriculture through national initiatives. These programs enhance smallholder participation and broaden adoption.
Latin America & Africa
Brazil and Argentina lead adoption in large-scale farming with private investment and OEM partnerships. In Africa, donor-funded programs expand GNSS-based digital agriculture services, though adoption remains uneven. Large-scale and high-value crop producers benefit most, while smallholders gradually integrate low-cost solutions.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Regenerative Agriculture Market Growth Drivers, Key Players, Trends and Regional Insights by 2034