Ethanol Market Size
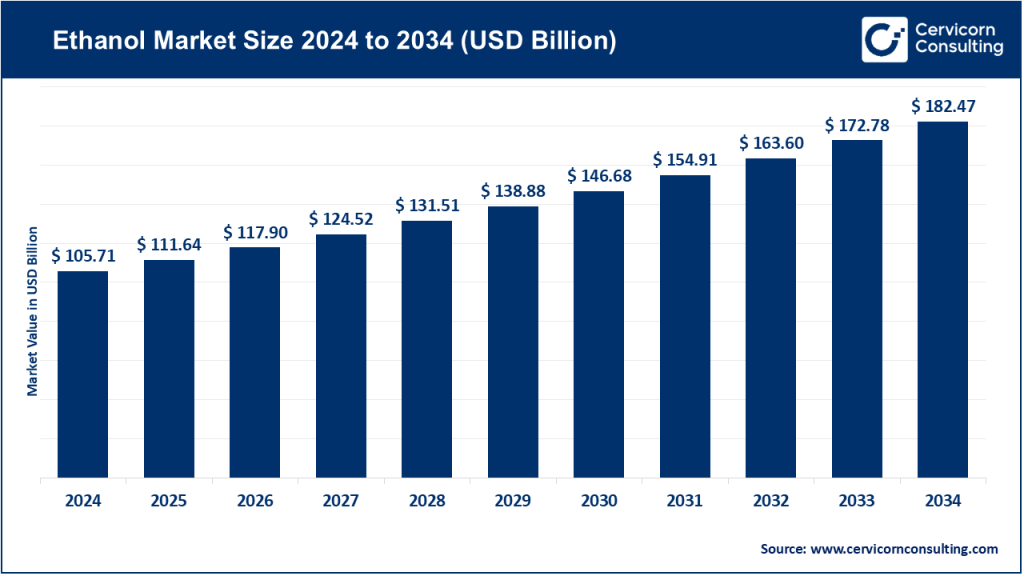
The global ethanol market size was worth USD 105.71 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 182.47 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.61% from 2025 to 2034.
What is the Ethanol Market?
The ethanol market represents the global production, distribution, and consumption of ethyl alcohol (C₂H₅OH), typically produced through the fermentation of biomass feedstocks such as sugarcane, corn, molasses, and increasingly cellulosic materials like agricultural residues and waste. Ethanol is primarily used as a biofuel—blended with gasoline in ratios like E10, E15, E20, and E85—to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. It is also widely utilized in industries including pharmaceuticals, beverages, cosmetics, and chemicals as a solvent and key feedstock.
In 2024, the global ethanol market was estimated to be worth between USD 70–110 billion, reflecting steady growth from 2020 levels. The market is composed of several segments, including fuel-grade ethanol (the largest), industrial ethanol, and beverage-grade ethanol. The industry’s structure spans from feedstock cultivation to biorefining, blending, distribution, and co-product utilization, creating a vast value chain that supports millions of jobs globally.
Why is the Ethanol Market Important?
Ethanol holds strategic importance in global energy and economic systems for several reasons:
-
Energy Security and Diversification – Ethanol allows nations to reduce dependence on imported oil by substituting gasoline with domestically produced biofuels. This is particularly critical for developing economies like India and Brazil, which seek to strengthen energy independence.
-
Climate Change Mitigation – Ethanol combustion emits fewer greenhouse gases than conventional gasoline, especially when derived from low-carbon feedstocks like sugarcane or agricultural waste. Its integration into fuel systems helps countries meet their carbon reduction and renewable energy goals.
-
Rural Development and Agricultural Value – Ethanol production enhances rural economies by creating stable demand for agricultural crops such as corn and sugarcane, increasing farmer incomes, and fostering job creation in rural processing industries.
-
Industrial and Chemical Applications – Beyond fuel, ethanol is vital in the production of sanitizers, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemicals, making it a versatile industrial input.
-
Economic Stability and Trade – As a globally traded commodity, ethanol contributes to international trade balances and provides developing countries with export opportunities.
In essence, ethanol is a cornerstone of the global transition toward low-carbon, sustainable energy systems while simultaneously driving economic and agricultural growth.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2799
Ethanol Market Growth Factors
The global ethanol market’s expansion is driven by a combination of regulatory support, economic incentives, and technological innovation. Governments worldwide are increasing biofuel blending mandates to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy security. The U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard, India’s Ethanol Blending Programme, and Brazil’s long-standing Proálcool initiative have collectively accelerated ethanol consumption. Technological advances in fermentation efficiency, enzyme development, and feedstock diversification (including cellulosic and waste-based ethanol) are improving production yields and reducing costs. The growing focus on low-carbon intensity fuels and carbon capture integration is attracting new investments, while industrial demand for ethanol in sanitizers and beverages remains robust.
Rising oil price volatility further boosts ethanol’s attractiveness as a cost-effective, renewable alternative. Together, these forces are propelling steady market growth despite challenges such as feedstock price fluctuations, land-use debates, and policy uncertainty.
Top Companies in the Global Ethanol Market
Below are profiles of five major companies that dominate the global ethanol landscape, detailing their specialization, key focus areas, notable features, 2024 revenue performance, and global footprint.
1. Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM)
- Specialization & Focus Areas: ADM is one of the largest agricultural processors and food ingredient providers globally. Within ethanol, it operates under its Carbohydrate Solutions division, producing fuel ethanol, industrial alcohols, and related co-products such as corn oil and distillers dried grains (DDGS).
- Key Focus Areas: ADM emphasizes integrated grain sourcing, advanced processing efficiency, and diversification into sustainable and low-carbon bio-based products.
- Notable Features: The company leverages its global supply chain, deep logistics network, and advanced processing facilities to maintain operational resilience. ADM also invests heavily in carbon capture and storage (CCS) and low-carbon ethanol initiatives.
- 2024 Revenue: ADM reported approximately USD 85.5 billion in total 2024 revenue, with about USD 11.2 billion attributed to its Carbohydrate Solutions segment, which includes ethanol operations.
- Global Presence: ADM operates in more than 170 countries with major production sites across North America, South America, Europe, and Asia, maintaining a dominant share of the U.S. ethanol market.
2. POET LLC
- Specialization & Focus Areas: POET LLC is the world’s largest bioethanol producer, focused exclusively on biofuels and bioproducts. Its operations include large-scale ethanol production, DDGS animal feed, renewable carbon dioxide, and corn oil for biodiesel feedstock.
- Key Focus Areas: The company’s core areas include maximizing production efficiency, scaling renewable technologies, and pioneering cellulosic ethanol development. POET is also investing in carbon capture and waste-to-energy projects to lower its overall carbon footprint.
- Notable Features: POET operates more than 30 bioprocessing plants across the U.S. Midwest and produces over 3 billion gallons of ethanol annually. Its Project LIBERTY facility was among the world’s first commercial-scale cellulosic ethanol plants.
- 2024 Revenue: As a private company, POET does not disclose exact figures; however, industry estimates place its 2024 revenue in the range of USD 6–8 billion.
- Global Presence: POET operates primarily in the United States but collaborates globally on biofuel policy advocacy, technology transfer, and sustainability initiatives.
3. Green Plains Inc.
- Specialization & Focus Areas: Green Plains is an integrated biorefining and technology company transforming from traditional ethanol production toward value-added products such as high-protein ingredients, renewable corn oil, and low-carbon fuels.
- Key Focus Areas: The company’s strategic vision focuses on maximizing product diversification, leveraging its patented precision separation technology, and adopting carbon capture to achieve a negative carbon intensity for ethanol.
- Notable Features: Green Plains is at the forefront of biofuel innovation, developing food-grade dextrose and high-protein feed ingredients alongside ethanol.
- 2024 Revenue: Green Plains generated approximately USD 2.1 billion in ethanol segment revenue in 2024, marking steady performance amid fluctuating fuel prices.
- Global Presence: Headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska, Green Plains operates multiple U.S. biorefineries and markets its products globally to the feed, food, and fuel industries.
4. Valero Energy Corporation
- Specialization & Focus Areas: Valero is one of the world’s largest independent petroleum refiners with a robust renewable energy division that includes ethanol and renewable diesel. Its ethanol business consists of 12 U.S. plants with a combined annual capacity of about 1.7 billion gallons.
- Key Focus Areas: Valero’s ethanol strategy centers on cost optimization, feedstock flexibility, and integrating renewable diesel and ethanol operations to capture synergies in low-carbon fuel markets.
- Notable Features: The company’s hybrid energy model allows it to pivot between petroleum-based and renewable fuels, enhancing resilience against market fluctuations.
- 2024 Revenue: Valero’s total revenue exceeded USD 144 billion in 2024, with ethanol contributing a strong share through over 4.5 million gallons per day of production.
- Global Presence: Valero has extensive operations in North America, the U.K., and Latin America, making it a key player in both conventional and renewable fuel markets.
5. Flint Hills Resources
- Specialization & Focus Areas: Flint Hills Resources, a Koch Industries subsidiary, operates across refining, chemicals, polymers, and biofuels. It manages multiple ethanol plants in the U.S. Midwest, contributing significantly to regional supply.
- Key Focus Areas: The company focuses on integrating traditional refining capabilities with renewable fuel production, improving process efficiency, and developing low-carbon technologies.
- Notable Features: Flint Hills emphasizes technological innovation, chemical recycling, and circular economy principles in its renewable fuel operations.
- 2024 Revenue: As part of privately held Koch Industries, Flint Hills’ specific 2024 ethanol revenue figures are not publicly disclosed, but the company is recognized among the top five U.S. ethanol producers by capacity.
- Global Presence: Primarily U.S.-based, with a growing focus on sustainability initiatives and advanced biofuel technologies influencing international markets.
Leading Trends in the Ethanol Market and Their Impact
1. Strengthening Biofuel Blending Mandates
Governments are aggressively increasing blending targets to cut emissions and support agricultural economies. The U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard, Brazil’s 30% ethanol blend, and India’s E20 initiative are prime examples. This trend ensures long-term demand stability for ethanol producers but also requires substantial investment in blending infrastructure and supply chain upgrades.
2. Decarbonization and Carbon Intensity (CI) Reduction
Low-carbon ethanol is gaining premium market value. Producers are integrating carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems, renewable energy inputs, and precision agriculture to reduce lifecycle emissions. This trend is redefining competitiveness in the industry—companies that achieve lower CI scores gain access to lucrative low-carbon credit markets.
3. Feedstock Diversification and Cellulosic Ethanol
Second-generation ethanol derived from crop residues, forestry waste, and municipal solid waste is advancing technologically. Although commercial volumes remain modest, innovations in enzyme efficiency and pretreatment technologies are driving down costs. This trend reduces land-use pressure and addresses food-versus-fuel concerns.
4. Co-Product Innovation and Biorefinery Integration
Companies are moving beyond fuel production to extract high-value co-products such as corn oil, protein feed, and biochemicals. Green Plains’ transformation into a diversified biorefinery model exemplifies this shift. Such integration enhances profitability and resilience during periods of low ethanol prices.
5. Industry Consolidation and Strategic Alliances
The ethanol industry is witnessing consolidation through mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships. Collaborations between biofuel and renewable diesel producers are common, enabling technology sharing and cost reduction. These alliances also facilitate cross-sector growth into sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and bioplastics.
Successful Examples of Ethanol Implementation Around the World
Brazil — The Biofuel Pioneer
Brazil’s ethanol program is the world’s most established and successful. The country has promoted sugarcane ethanol since the 1970s, leading to widespread adoption of flex-fuel vehicles capable of running on pure ethanol or gasoline blends. Ethanol accounts for nearly half of Brazil’s light vehicle fuel consumption, and the industry supports millions of rural jobs. Brazil’s policy stability, coupled with its low-carbon sugarcane feedstock, has positioned it as a global exporter and role model for ethanol integration.
United States — Scaling Efficiency and Policy Support
The United States remains the largest ethanol producer, driven by the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and supported by a mature agricultural base. Corn ethanol dominates, but innovation in carbon capture and diversification into renewable chemicals are creating new growth avenues. The U.S. also leads in ethanol co-products, supplying the global livestock industry with distillers grains and corn oil.
India — Rapid Blending Acceleration
India’s Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP) has transformed the market by rapidly increasing ethanol blending rates from 1.5% in 2014 to nearly 12% in 2024, targeting 20% by 2025. The program incentivizes both sugarcane and surplus grain-based ethanol, enhancing energy security and supporting rural farmers. India’s government-led policy coordination has become a blueprint for other developing nations pursuing biofuel adoption.
Global Regional Analysis — Government Initiatives and Policies
North America
The U.S. and Canada anchor North America’s ethanol production. The U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard mandates minimum biofuel volumes, while California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) incentivizes low-CI ethanol. Federal clean fuel tax credits further drive investment. Canada’s Clean Fuel Regulations similarly promote renewable blending, ensuring steady market demand and technological investment.
Latin America
Brazil dominates ethanol production in Latin America, maintaining a 27–30% blend mandate. Countries like Argentina and Colombia are also scaling up ethanol programs, driven by local feedstock availability and export opportunities. The region benefits from favorable agricultural conditions and long-term government support for bioenergy.
Europe
The European Union regulates ethanol under the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II and RED III), setting renewable transport fuel targets while placing sustainability caps on food-based biofuels. The focus is shifting toward advanced ethanol derived from waste and residues. European producers are aligning operations to meet stricter lifecycle emissions standards and certification requirements.
Asia-Pacific
India’s rapid policy-driven growth leads the region, followed by China, Thailand, and the Philippines, which are implementing blending programs to enhance fuel security and reduce pollution. Australia and Japan are exploring advanced biofuel technologies. The region’s growing population and fuel consumption make it a major future demand hub for ethanol.
Africa and the Middle East
Emerging programs in countries like South Africa and Egypt are exploring ethanol potential to offset fossil fuel imports. However, infrastructural and feedstock challenges remain barriers to large-scale adoption.
Cross-Cutting Policy Themes
- Food vs. Fuel Balance: Governments are increasingly cautious about diverting food crops to fuel, driving research into non-food and waste-based ethanol feedstocks.
- Sustainability Verification: Lifecycle carbon accounting and certification are becoming mandatory for export markets, ensuring only sustainable ethanol qualifies under major programs.
- Carbon Market Integration: Ethanol producers are beginning to monetize carbon reductions through credits and offsets, making low-CI ethanol economically attractive.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Healthcare ERP Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034