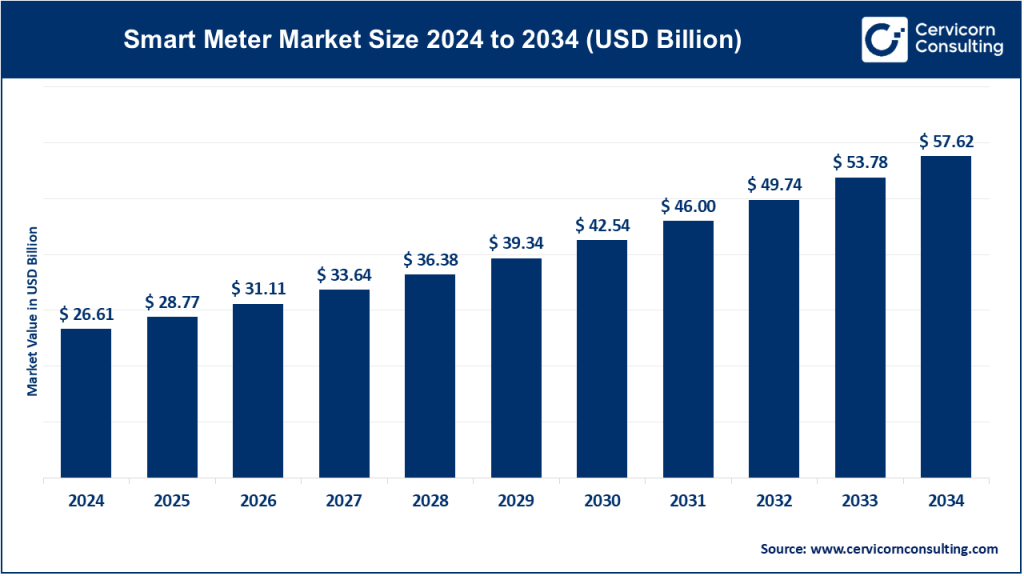
Smart Meter Market Size
What Is the Smart Meter Market?
The smart meter market encompasses the design, manufacturing, and deployment of digital meters that record and communicate energy, gas, or water consumption data in real time. Unlike conventional meters, which require manual readings, smart meters automatically transmit data to utilities through advanced communication networks such as radio frequency (RF) mesh, cellular IoT, or power-line communication.
These meters form the backbone of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)—a digital ecosystem that includes data management software, communication networks, and analytics platforms. AMI enables two-way communication between utilities and consumers, offering detailed insights into energy usage, improving billing accuracy, and helping utilities manage peak demand and grid stability.
Why Is the Smart Meter Market Important?
Smart meters are a critical component of modern energy management systems. They bridge the gap between power generation and consumption, enabling utilities to optimize energy distribution and consumers to manage their usage more effectively.
For utilities, smart meters reduce power theft, enhance billing accuracy, and allow quicker identification and restoration of outages.
For consumers, they offer real-time visibility into energy consumption, enabling behavioral changes and participation in time-of-use pricing programs.
For governments, smart meters help in achieving sustainability goals by supporting renewable integration, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting efficient resource utilization.
Overall, smart meters are foundational to achieving grid modernization, resilience, and decarbonization.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2444
Smart Meter Market Growth Factors
The global smart meter market is experiencing rapid growth in 2024 due to a combination of regulatory, economic, and technological factors. Governments around the world are mandating or incentivizing the adoption of smart meters to enhance energy efficiency and transparency. Utility companies are investing heavily in smart infrastructure to reduce operational costs and improve customer service.
The rise of distributed energy resources—such as solar, wind, and electric vehicles—requires granular data for effective grid management, which smart meters provide. In addition, the cost of enabling technologies such as NB-IoT and LTE-M has fallen significantly, making smart metering more affordable for utilities in both developed and developing nations.
Cybersecurity advancements, improved communication protocols, and integration with cloud-based analytics platforms have further accelerated adoption. The market is also expanding as utilities upgrade from first-generation to second-generation meters, which offer enhanced connectivity, remote firmware updates, and better data management.
Smart Meter Market Top Companies
1. Itron Inc.
Specialization: Itron designs and manufactures smart electricity, gas, and water meters, along with advanced communications modules and data analytics solutions.
Key Focus Areas: Grid-edge intelligence, data management systems, cloud-based analytics, and energy optimization software.
Notable Features: Itron is a pioneer in offering integrated AMI platforms that combine hardware, software, and services. The company focuses on enabling real-time insights for utilities through grid-edge computing.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 2.4 billion.
Market Share: Among the top global players in North America and Europe, with a strong portfolio in data-driven energy management.
Global Presence: Headquartered in the United States, Itron operates across more than 100 countries with a diverse customer base of electric, gas, and water utilities.
2. Landis+Gyr
Specialization: A Swiss multinational specializing in electricity, heat, and water metering systems, AMI platforms, and energy management services.
Key Focus Areas: Large-scale smart metering deployments, low-power communication technologies (NB-IoT), and managed utility services.
Notable Features: Landis+Gyr has successfully implemented some of the world’s largest smart meter rollouts, providing utilities with end-to-end metering solutions that integrate seamlessly with grid systems.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 1.7 billion.
Market Share: One of the top global suppliers with a strong presence in Europe, North America, and the Asia-Pacific region.
Global Presence: Operating in over 30 countries with manufacturing and research centers in Switzerland, the U.S., and Asia.
3. Honeywell International Inc.
Specialization: A diversified industrial technology company with significant operations in smart metering and automation through its acquisition of Elster.
Key Focus Areas: Building automation, industrial IoT, and integrated metering for gas and electricity networks.
Notable Features: Honeywell combines its metering expertise with broader energy management and building control systems, providing holistic digital solutions for industrial and utility clients.
2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 38–39 billion (corporate total).
Market Share: A major player in industrial and gas metering solutions with a strong global footprint.
Global Presence: Operates in more than 70 countries with robust R&D facilities across North America, Europe, and Asia.
4. Schneider Electric
Specialization: A global leader in energy management and automation, providing solutions that connect smart meters with advanced distribution systems.
Key Focus Areas: Digital energy management, distribution automation, and integration of smart metering with sustainability analytics platforms.
Notable Features: Schneider Electric incorporates smart metering data into its EcoStruxure platform, helping businesses and utilities monitor, control, and optimize energy use.
2024 Revenue: Around €38–39 billion.
Market Share: A leading provider of smart energy and grid automation systems across Europe, North America, and Asia.
Global Presence: Headquartered in France, Schneider Electric operates in more than 100 countries, supporting major smart grid and industrial automation projects.
5. Siemens AG
Specialization: A multinational engineering and technology company focused on smart infrastructure, grid automation, and energy digitalization.
Key Focus Areas: Smart grids, distributed energy management, and integration of metering data with wider grid systems.
Notable Features: Siemens plays a critical role in providing infrastructure and software that connect smart meters to broader energy management ecosystems.
2024 Revenue: Approximately €75.9 billion (group total).
Market Share: A leading system integrator and solution provider for smart grid and AMI projects worldwide.
Global Presence: Operating in nearly 190 countries, Siemens has a significant market presence across Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Second-Generation Smart Meters
Many early adopters are now upgrading to next-generation meters that feature enhanced cybersecurity, improved communication modules, and interoperability with distributed energy resources. This trend is driving a new wave of hardware sales and service opportunities.
2. Cellular IoT Connectivity
The shift toward NB-IoT and LTE-M communication networks allows for greater scalability and reduced infrastructure costs. These technologies are especially valuable in rural or hard-to-reach areas where RF mesh networks are less effective.
3. Software-Driven Business Models
Vendors are moving from selling standalone devices to offering subscription-based software and analytics platforms. Utilities increasingly rely on predictive analytics, cloud data management, and machine learning to optimize operations and forecast demand.
4. Enhanced Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As smart meters become central to national energy systems, the focus on secure communication and data integrity has intensified. Utilities are investing heavily in encrypted communication, firmware updates, and regulatory compliance systems.
5. Policy-Driven Growth
Governments are using policy frameworks to accelerate adoption. National mandates and incentive programs, such as those in the EU, the U.S., and India, are creating massive deployment pipelines and stable long-term demand.
6. Renewable Integration and Grid Flexibility
Smart meters enable the integration of renewable energy sources and support new business models like demand response and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) energy trading. This aligns with global sustainability targets and carbon reduction strategies.
Successful Examples of Smart Meter Deployment
United Kingdom
The UK’s nationwide smart meter rollout is one of the most extensive in Europe. Millions of meters have been installed as part of the government’s energy modernization initiative. Despite challenges with interoperability and installation logistics, the program remains a benchmark for large-scale smart grid implementation.
Italy
Italy’s smart metering initiative led by Enel is a global success story. As one of the first countries to achieve near-universal smart meter coverage, Italy demonstrated how large-scale deployments can enhance billing efficiency and consumer participation in energy savings.
Nordic Region
Sweden and other Nordic countries are leading the next generation of smart metering. Utilities like Ellevio have upgraded to advanced meters that improve communication reliability and support renewable integration, reflecting the region’s commitment to sustainable energy systems.
India
India’s government has embarked on one of the world’s largest smart metering rollouts under national programs such as the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS). These initiatives aim to install hundreds of millions of meters, reduce distribution losses, and strengthen grid efficiency.
United States
The U.S. has one of the most mature AMI ecosystems globally, with over 130 million advanced meters in operation. Federal and state programs continue to support the expansion of smart metering, particularly in the context of grid resilience and renewable integration.
Regional Analysis: Government Initiatives and Policy Influence
Europe
The European Union’s Clean Energy Package mandates widespread smart meter deployment across member states. These initiatives aim to empower consumers, promote renewable adoption, and improve energy efficiency. Countries like Italy, France, and the UK are nearing full coverage, while others are scaling up using EU funding and regional investment programs.
North America
In the U.S. and Canada, state-level regulations and federal grants have driven high adoption rates. Funding from infrastructure programs and smart grid grants supports ongoing modernization and replacement of older AMI systems. Utilities are also integrating smart meters with distributed energy management and microgrid systems.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market, led by India, China, Japan, and South Korea. India’s government has committed to complete smart metering across all distribution networks by the end of the decade. China continues to expand its smart meter network alongside local manufacturing initiatives. Japan and South Korea are integrating smart metering into nationwide smart city and renewable energy programs.
Latin America and Africa
These regions are leveraging smart meters primarily to reduce energy theft and improve billing accuracy. Government-supported modernization projects and multilateral funding are promoting adoption in countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa. Vendors offering turnkey solutions and financing options are gaining traction in these markets.
Implications for Stakeholders
For Vendors
The market’s evolution favors vendors offering comprehensive ecosystems—combining meters, communication networks, cloud analytics, and cybersecurity services. Companies that shift from hardware-centric models to service-based offerings are positioned for sustained profitability.
For Utilities
Utilities must move beyond installation toward data utilization. By leveraging real-time consumption data, utilities can improve demand forecasting, outage management, and customer engagement. The integration of metering data with renewable sources and EV infrastructure will become essential to maintaining grid balance.
For Governments and Regulators
Governments play a vital role by setting clear regulatory frameworks, ensuring data privacy, and providing financial incentives. Well-designed policies encourage innovation while safeguarding consumer interests, paving the way for sustainable and efficient energy distribution systems.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Solid-State Battery Market Trends, Growth Drivers and Leading Companies 2024