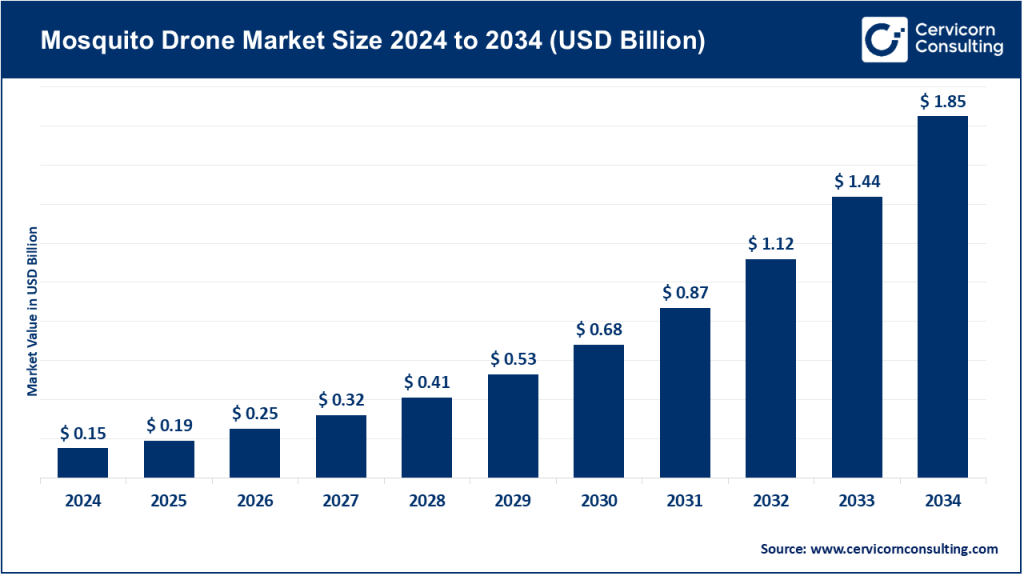
Mosquito Drone Market Size
What is the mosquito drone market?
The mosquito drone market covers hardware (multi-rotor and fixed-wing UAVs adapted for vector control), software (flight planners, GIS and AI for habitat detection), payloads (tank/spray systems for larvicides/adulticides, release mechanisms for sterile or symbiont-infected insects, sensor and trap payloads), and services (drone-based vector surveillance, contract spraying and data analytics). End users include municipal and regional vector control districts, public-health agencies, military and humanitarian organizations, agriculture & land managers (where mosquito populations overlap with farms), and private pest-control operators.
Market offerings range from off-the-shelf agricultural sprayer drones repurposed for larviciding, to specialized light-weight release platforms for sterile male programs and integrated surveillance platforms that combine imagery, machine vision, and mapping. Several market research firms now treat “drone-based mosquito control” as a sub-segment of agricultural and pest-control drones and of the broader “drone-based vector control” space.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2744
Mosquito drone market — Growth Factors
The mosquito drone market is expanding rapidly because of (1) escalating public-health pressures from dengue, malaria and other vector-borne diseases that force agencies to look for scalable, targeted interventions; (2) advances in UAV platform endurance, payload capacity and low-cost mass production that make larvicide/adulticide application by drone cheaper and more precise than traditional helicopters or backpack sprayers; (3) breakthroughs in sensing and AI that let drones detect likely breeding habitats from aerial imagery and prioritize treatments; (4) growth in integrated pest-management funding and targeted grants by health agencies and foundations that fund demonstration projects.
(5) regulatory liberalization in many jurisdictions that created clearer certification and operational pathways for commercial spraying operations; and (6) new biological control methods (sterile-male release, Wolbachia infection) that need safe, distributed aerial release systems — together these technical, regulatory, and programmatic factors create both demand and supply momentum for mosquito-specific UAV solutions.
Why the mosquito drone market is important
- Precision and reach. Drones can treat wetlands, marshes and fragmented breeding habitats without the logistics, cost or ecological footprint of manned helicopters or heavy ground equipment. That’s especially useful in protected areas and rough terrain.
- Cost and speed. Small teams with sprayer drones can cover more ground for specific tasks, reduce labor hours, and respond faster to surveillance triggers.
- Safer, targeted chemistry. Low-volume, ultra-low-volume (LV/ULV) drone applications can localize doses and reduce non-target exposure compared with large-scale blanket spraying.
- Data and integration. Remote sensing and AI can move vector control toward prevention (identifying breeding hotspots) instead of only reactive adulticide campaigns.
Mosquito Drone Market — Top companies
1) DJI Technology Co., Ltd.
- Specialization: Global leader in consumer and commercial multirotor UAVs; produces platforms that are frequently adapted for payload spraying and sensors. DJI’s Matrice/AGR series & agricultural adaptations are widely used as a base for mosquito-control sprayer builds.
- Key focus areas: Robust flight controllers, mature supply chain, large global dealer network, payload integration for agriculture and public-safety customers.
- Notable features: Market-leading vehicle reliability, extensive OEM ecosystem (third-party sprayer mounts and software), high manufacturing scale and spare-parts support. DJI is also the dominant force in many commercial drone markets, giving operators familiar, readily-supported platforms.
- 2024 revenue / market share (summary): Public reporting on DJI is limited (private company), but industry coverage and market trackers put DJI’s overall drone revenue in the multi-billion dollar range in 2024 (media reporting cited revenues exceeding RMB 80 billion / ~USD 11.2 billion in 2024 across DJI’s business lines), and DJI holds a dominant share of the global consumer/commercial drone market (often cited >70% in consumer segments). Specific mosquito-drone market share is not separately published.
- Global presence: Worldwide (except partial bans or restrictions in some government procurement markets); dealer networks in Asia, Europe, North America, Latin America.
2) XAG Co., Ltd.
- Specialization: China-based agricultural drone maker focused on heavy-duty field sprayers and precision agriculture UAVs that are frequently repurposed or adapted for mosquito larvicide application. XAG systems are used for high-capacity spraying.
- Key focus areas: Large-area crop spraying, autonomous flight systems for agriculture, international expansion in Asia/Africa/Latin America.
- Notable features: Strong product suite for liquid application, thriving service network for agricultural spraying, and emphasis on autonomous farm workflows. XAG publicly reports rapid overseas growth and has large installed fleets (reports noted over 130,000 units in operation across more than 60 countries at recent points).
- 2024 revenue / market share (summary): XAG has signaled improving profitability and significant overseas revenue (company-reported percentages), but exact 2024 consolidated revenue figures for the mosquito segment are not isolated in public disclosures. XAG’s position in agricultural spraying makes it a natural supplier for large-scale vector-control spraying programs.
- Global presence: Large footprint in China, fast expansion across Southeast Asia, Africa and other emerging markets; sizeable installed base internationally.
3) PrecisionVision
- Specialization: The name “PrecisionVision” is used by multiple firms in different sectors (imaging, medical devices, robotics). Public evidence directly tying a particular PrecisionVision company to mosquito-specialized drones is limited in primary sources. As a result, revenue and precise market share for a mosquito-drone-focused PrecisionVision entity are not publicly documented. Where PrecisionVision appears in industry lists it is typically in the context of imaging, sensors or bespoke UAV integrations rather than as a major sprayer OEM.
4) VectorDrone
- Specialization: Small, niche UAV integrators and custom OEMs have emerged to provide mosquito-specific payloads (e.g., low-volume larvicide tanks, sterile-insect release systems). The exact firm named “VectorDrone” shows scant public footprint at scale — this is common for highly specialized startups or local integrators (many operate as regional service providers rather than global brands). Where public detail is scarce, county mosquito districts often contract local integrators or retrofit agricultural sprayers for mosquito work.
5) Aerial Response Solutions
- Specialization: Drone services and emergency response UAV operator that can offer spraying and aerial interventions for public utilities and pest control. Some service operators target multi-use contracts (utilities, emergency response, vector control).
- Key focus areas: Contract drone services, rapid deployment, localized operations for municipal clients.
- Notable features: Often hold local approvals and pilot certifications; some public profiles indicate modest revenue scale as a services firm rather than large hardware OEM (data sources show company revenue estimates in the low-millions USD range, indicative of a services posture rather than large manufacturing scale).
- 2024 revenue / market share (summary): Public estimates indicate small-to-mid single-digit millions USD revenue levels for 2024; no public evidence of significant global market share as a manufacturer — instead a regional services presence.
Leading trends and their impact
- Shift from blanket spraying to targeted, data-driven interventions. AI and high-resolution imagery enable habitat detection and larval hotspot mapping. Impact: reduced pesticide volumes, better cost-efficiency and improved ecological outcomes.
- Biological control + aerial release platforms. Drones are increasingly used to distribute sterile or Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes (for population suppression) and to seed beneficial biocontrols. Impact: opens non-chemical strategies and enables releases in remote or island ecosystems.
- Regulatory clarity and operational frameworks evolve. Countries like India, the U.S. and others have updated rules that make commercial spraying and ag-drone operations more accessible under defined certification regimens. Impact: faster program deployment and larger commercial opportunities for OEMs and service providers.
- Hybrid partnerships (public health + private drone firms). Grants from public health agencies and collaborations between vector control districts and drone service providers accelerate pilots and create reference cases. Impact: faster real-world validation and greater public acceptance as agencies adopt data from drone programs.
- Environmental & public perception pressures. Communities demand non-invasive, low-chemical solutions. Impact: favors low-volume, targeted approaches and biologics over broad adulticiding.
Successful examples around the world
- Santa Cruz County (California, USA). The county’s Mosquito and Vector Control program documents drone-based larvicide treatments in wetlands as part of an effort to reduce the footprint of vehicle and foot treatments while maintaining precision.
- Metropolitan Mosquito Control District (Minnesota, USA). Large U.S. districts report planned drone treatments and public notices as they integrate UAS into seasonal operations to treat larval habitats with reduced ecological impact.
- Hawaii conservation projects. Experimental programs have used drones to release sterile or modified male mosquitoes to protect native bird populations and reduce disease transmission — demonstrating drones’ unique value in remote/island ecosystems.
- Private service providers and contractors. Companies such as Vector Disease Control International and local integrators have begun integrating drones into wider integrated mosquito management programs to supplement surveillance and treatments.
These are representative programs: many municipal and regional vector control agencies globally are at pilot, demonstration or early-operational stages rather than full replacement of older methods.
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives and policies shaping the market
North America (USA & Canada)
The U.S. sees growing federal and state grants for vector surveillance, and county-level mosquito districts have increasingly adopted drones for surveillance and targeted larviciding. The AMCA (American Mosquito Control Association) funds research and pilot projects. Regulatory pathway: FAA rules govern UAS operations; commercial spraying requires state/local permits and FAA waivers depending on airspace. Impact: steady uptake in municipal & county programs; strong vendor/service demand.
Europe
EU member states align with WHO guidance on vector control; drone operations are regulated at national levels consistent with EASA guidance. Adoption is generally cautious but present in wetland-rich regions and island jurisdictions where helicopters are impractical. Impact: preference for data-driven, low-volume interventions and for pilot risk assessments.
Asia-Pacific (China, India, Southeast Asia)
- China: Large domestic drone OEMs (DJI, XAG and others) supply agricultural spraying platforms that are commonly repurposed for vector control. Government support for ag-drones and fast product iteration create strong supply-side capability.
- India: The DGCA’s Drone Rules (2021) and 2023 amendments liberalized commercial drone use, introduced certification pathways and digital platforms — facilitating agricultural and public-health drone use, though local type-certification and enforcement remain important. Several state-level pilots and ag-drone subsidy schemes indirectly support mosquito-drone capabilities since the same platforms are used for spraying.
- Southeast Asia: High dengue burden and many small municipalities create demand for cost-effective solutions; ag-drone OEMs are expanding regionally. Impact: rapid local deployments in pilot programs and growing interest in low-cost drone services.
Africa & Latin America
Vector-borne disease burden is high in pockets of sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America. International donors and NGOs fund pilot programs, but operational scale can be constrained by logistics, maintenance and training. Drones offer promise for remote wetlands or areas where infrastructure is limited, but long-term adoption hinges on local capacity building and supply chains.
International governance & WHO guidance
WHO and technical resources promote integrated vector management, highlight the potential role of novel tools (including UAVs) as supportive measures, and emphasize the need for monitoring insecticide resistance, environmental impact assessment, and community acceptance. WHO guidance does not prescribe specific drone brands but frames safe, evidence-based deployment as part of national control strategies.
Regulatory, funding, and deployment considerations (practical brief)
- Permits and airspace: Operators must follow local aviation rules (e.g., FAA waivers in the U.S., DGCA rules in India, national aviation administrations in Europe). Spraying also often requires environmental regulators’ approvals.
- Data and privacy: Aerial imagery for habitat mapping raises privacy considerations; community outreach and transparent data use policies help acceptance.
- Training & maintenance: Sustainable programs require trained pilots, maintenance capacity and local spares chains — weaknesses here slow scaling in low-resource areas.
- Evaluation & evidence: Agencies want measurable outcomes (reduction in larval indices, disease incidence) to justify continued spending; many current deployments are still gathering robust impact data.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Data center power market Key Players, Trends, and Global Outlook by 2034