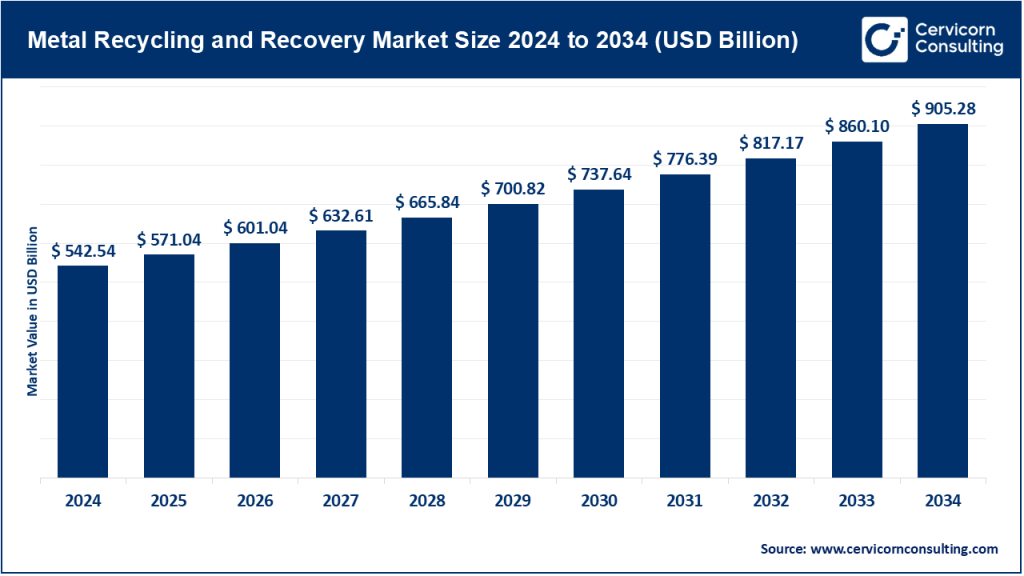
Metal Recycling and Recovery Market Size
What is the metal recycling & recovery market?
At its simplest, the metal recycling and recovery market comprises the collection, sorting, processing, and re-refining of end-of-life or scrap metals into secondary raw materials that can be re-used in manufacturing. That includes ferrous metals (steel and iron), non-ferrous base metals (aluminum, copper, lead, zinc), and precious and critical metals (gold, silver, platinum group metals, rare earths). “Recovery” emphasizes extracting valuable metal from complex matrices — e-waste, industrial residues, slag, automotive shredder residue and the like — using mechanical, hydrometallurgical, pyrometallurgical, and chemical separation technologies. The market spans small local scrap yards and global smelting/rolling operations to specialized recyclers who reclaim rare or battery-grade materials for advanced industries.
Why it is important
Metal recycling is central to resource security, emissions reduction, and cost management. Producing metals from recycled feedstock typically uses a fraction of the energy required to make them from virgin ore (e.g., aluminum via recycling can save >90% of the energy compared with primary production). Recycling reduces mining demand, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and buffers manufacturers from raw-material price shocks. For critical and strategic metals (copper, nickel, cobalt, rare earths), recycling becomes a domestic supply solution and a geopolitical hedge. Finally, growing electrification (EVs, batteries, cables) and electronics proliferation mean more metal is locked in waste streams that, when recovered, become valuable feedstock for the low-carbon transition.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2739
Growth factors
The metal recycling and recovery market is expanding due to rising demand for metals from electrification and renewable energy (copper, nickel, aluminium), higher commodity prices that make secondary sources economically attractive, stricter circular-economy and waste-management regulations (extended producer responsibility, deposit-return schemes, and national recycling targets), technology advances—improved shredding, sensor-based sorting, and hydrometallurgical processes that enable recovery of complex and low-concentration metals (including rare and battery metals), corporate sustainability commitments and procurement policies favouring recycled content, and growing incentives and investments (public and private) to build local recycling/refining capacity to reduce import dependence and carbon footprints.
These drivers are amplified by policy moves in regions such as the EU and by the commercial value unlocked when telecoms, utilities, and OEMs harvest metals from decommissioned assets.
Metal Recycling & Recovery — Top companies
Note: the five companies you listed are primarily large packaging and materials/packaging firms. They are active in recycling and sustainable-materials initiatives (packaging recycling, recycled content targets), but they are not traditional scrap-metal recyclers or smelters. Below I profile each firm with public 2024 figures and their sustainability / recycling relevance.
Amcor plc
- Specialization: Flexible and rigid packaging for food, beverage, healthcare and other sectors.
- Key focus areas: Recyclable packaging solutions, increased recycled content, and circular packaging systems. Amcor’s sustainability programs target design for recyclability and partnerships to improve collection and recycling infrastructure.
- Notable features: Large global footprint, major M&A activity (notably the announced Berry Global deal in 2024/25 that changes company scale and footprint).
- 2024 revenue: Amcor reported net sales of about USD 13.6 billion for fiscal 2024 (FY ended June 30, 2024).
- Market share & presence: Global — operations in 40+ countries and a major supplier to multinational FMCG firms. While Amcor is a packaging leader, its role in metal recycling is typically as a buyer/supplier in packaging circularity (e.g., multilayer material recovery initiatives), not as a primary metal recycler.
Sealed Air
- Specialization: Protective packaging, food-preservation packaging, and engineered materials (Bubble Wrap, Cryovac).
- Key focus areas: Packaging sustainability, reduced material use, increased recyclability and circular solutions for protective packaging categories.
- Notable features: Strong presence in food service and industrial protective packaging; investment in recycled and recyclable packaging formats.
- 2024 revenue: Sealed Air reported about USD 5.4 billion in sales in 2024.
- Global presence: Large multinational, serving customers in over 100 countries. Again, engagement with recycling is via packaging streams rather than metal scrap processing.
Tetra Pak (part of Tetra Laval group)
- Specialization: Aseptic carton packaging for beverages and liquid food, filling equipment and collection/recycling programs for cartons.
- Key focus areas: Collection and recycling of beverage cartons (which contain paper, polyethylene, and aluminum layers), R&D into paper-based barrier solutions to reduce aluminum content.
- Notable features: Runs carton-collection and recycling schemes in several markets and invests in carton recycling capacity.
- 2024 revenue: Tetra Pak reported net sales of €12.82 billion in 2024 (Tetra Pak / Tetra Laval group figures).
- Relevance to metal recycling: Tetra Pak focuses on recovery of aluminium from multilayer packaging among other materials; this is a niche but important intersection with metal recovery.
Huhtamäki Oyj
- Specialization: Foodservice packaging (paper-based and moulded fibre), consumer packaging solutions.
- Key focus areas: Recyclable fibre-based products, lowering virgin material use, and investment into circular fibre streams.
- Notable features: Strong footprint in foodservice and retail packaging with global operations and sustainability targets.
- 2024 revenue: Huhtamäki reported net sales of EUR 4.1 billion in 2024.
- Relevance: While primarily fibre-focused, Huhtamäki participates in wider packaging circularity programs that interact with metal recycling when multi-material packaging is involved.
Mondi
- Specialization: Paper and packaging—corrugated solutions, kraft paper, industrial bags and sustainable packaging products.
- Key focus areas: Sustainable packaging, recycled content, and efficient paper and packaging value chains.
- Notable features: Large European and global footprint with integrated forestry-to-packaging operations.
- 2024 revenue: Mondi released full-year results for the 12 months to 31 Dec 2024 (reported figures in Feb 2025). The firm reported multi-billion euro sales (company filings provide complete figures).
- Relevance to metal recycling: Mondi’s role is indirect — their packaging solutions intersect with metal recycling primarily through multi-material packaging streams and procurement of recycled fibres.
Leading trends — and their impact
- Urban mining & e-waste recovery accelerate — the electronics and telecom sectors are becoming major secondary-metal suppliers. Telecom decommissioning alone is projected to yield billions from recycled copper and other metals as operators harvest cables and equipment; commercial gains are accelerating recycling investments. Impact: creates new feedstock streams and supports local supply for electrification.
- Battery-grade metal recovery (Ni, Co, Li) grows fast — hydrometallurgy and direct-recycling processes are being commercialized to recover cathode materials at higher value than traditional smelting. Impact: reduces reliance on mining and shortens EV battery supply chains.
- Policy & industrial strategy create demand for domestic recycling capacity — the EU’s circular and metals/steel action plans plus national measures aim to increase domestic processing and recycled content targets; these policies spur investment in sorting/refining capacity. Impact: potential reshuffling of global scrap flows and new regional players.
- Digital sorting & automation — sensor-based (XRF, eddy current, AI vision) sorting improves material purity and economics. Impact: more materials can be profitably recovered, raising yields and reducing contamination.
- Higher commodity prices and decarbonization goals — these two factors increase the commercial and regulatory incentive to recover metal rather than mine it. Impact: more capital flow into advanced recycling, and rising partnerships between OEMs and recyclers.
- Supply-chain contracting & product take-back — OEMs and utilities increasingly internalize end-of-life asset management (take-back or buy-back schemes). Impact: more reliable feedstock and closed-loop procurement contracts.
Successful examples around the world
- Germany — Deposit-Return and high collection rates. Germany’s deposit (Pfand) system for beverage containers achieves extremely high return rates (often cited in the 90% range for eligible containers), demonstrating how policy design and convenient infrastructure can drive near-complete recovery of aluminum cans and bottles — major inputs to metal recycling.
- Tokyo 2020 — Olympic medals from recycled electronics. Tokyo’s organizing committee collected discarded electronics and produced medals from recovered metals — a high-visibility example of urban mining and public engagement used to promote e-waste collection. While symbolic, it shows what coordinated collection and refining can deliver.
- Telecom decommissioning & copper recovery. Several telecom operators have begun systematic recovery of copper from retired infrastructure, producing meaningful revenue and making copper available for reuse/recycling; this is a model for asset-intensive industries.
- EU strategic metals projects. The EU has listed strategic projects to increase domestic processing of critical materials and recycling capacity, signaling state-backed industrial programs to ensure supply resilience and circularity in metals. These initiatives combine funding, permitting streamlining, and industrial coordination.
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives & policies shaping the market
Europe
The European Commission’s circular-economy agenda and recent Steel & Metals Action Plans aim to spur domestic recycling and secondary raw-material markets. Policies include recycled-content targets, support for secondary-material processing, and scrutiny of scrap exports; some industry groups have also lobbied for measures (e.g., scrap export levies) to keep metal feedstock within Europe for decarbonization goals. Impact: stronger regional demand for local recycling/refining investment and tighter regulation of scrap flows.
North America
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides regulatory clarity on recycling of hazardous secondary materials and offers guidance on safe recycling practices (e.g., checklists for hazardous secondary material recycling). U.S. infrastructure and clean-manufacturing incentives also indirectly support investments in recycling capacity and advanced recovery technologies—especially for battery and critical metals. States have their own diversion and e-waste rules that further shape local markets.
Asia (China, Japan, India, Southeast Asia)
- Japan has led notable collection initiatives (e.g., Olympic medal program) and has advanced e-waste collection systems in many cities.
- India has updated e-waste rules and is strengthening EPR regimes for electronics and packaging, pushing formalization and traceability in recycling — a major step given India’s huge electronics and consumer good market. These rules aim to capture more high-value metals from e-waste and encourage formal recyclers to scale.
Latin America & Africa
Both regions are rich in scrap flows and have growing informal recycling sectors. Policy efforts vary — some countries are strengthening regulation and formalizing informal sectors to improve environmental outcomes and resource recovery. Investment in formal processing is expanding slowly, often tied to commodity cycles and foreign investment.
Policy levers shaping the future
Across regions, governments are using several policy levers that will shape metal recycling economics and capacity: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and recycled-content mandates that create guaranteed demand for secondary metals; Deposit-return schemes and collection targets to improve feedstock quality; Trade and export controls on scrap to protect domestic processing; R&D and industrial subsidies for advanced recycling (particularly battery metals); and Standards and certification to guarantee recycled-content quality for critical applications (e.g., battery-grade materials). Examples include EU circular-economy plans, EPA guidance in the U.S., and evolving EPR rules in India. These policy instruments interact with commodity prices and technology economics to determine investment flows into metal recycling infrastructure.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: AI in the Textile Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2034