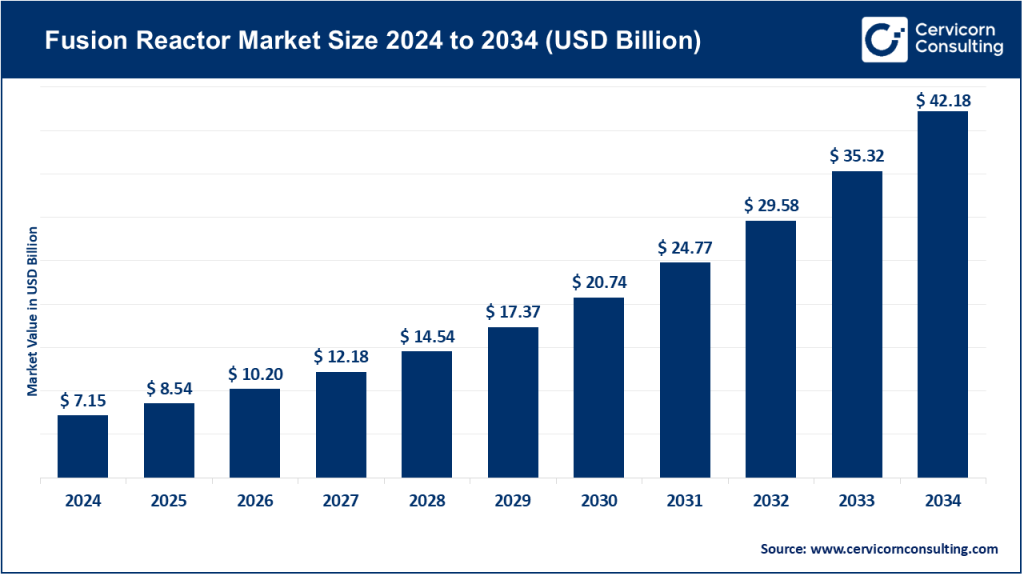
Fusion Reactor Market Size
Fusion Reactor Market Growth Factors
Several key growth drivers are propelling the fusion reactor market: rapidly expanding demand for clean and low-carbon energy to combat climate change; breakthroughs in plasma confinement, superconducting magnet technologies, and tritium-breeding systems that make fusion increasingly feasible; surging public and private investment—including billions in venture funding and substantial government R&D spending; rising international collaboration and policy frameworks that encourage commercialization; expansion in modular and compact reactor designs enabling flexible deployment; and heightened interest from strategic investors, including tech giants, which is accelerating commercialization timelines. Together, these factors form a robust foundation for the fusion reactor market’s steep projected growth.
What Is the Fusion Reactor Market?
The fusion reactor market encompasses the development, manufacturing, and commercialization of nuclear fusion systems—devices that replicate the sun’s power-generating process by fusing light atomic nuclei under extreme conditions. These reactors aim to harness clean, virtually limitless energy by fusing isotopes like deuterium and tritium, generating immense heat and energy in the process.
Participants in this market include a mix of innovative startups, national research institutions, industrial powerhouses, and government agencies. Key offerings range from experimental tokamak reactors to next-gen plasma confinement systems, magnet technologies, superconductors, and integrated reactor control systems. The value chain spans from component R&D, prototyping, and reactor construction to integration into power grids and commercialization at utility scale.
Why Is It Important?
Fusion power has long been regarded as the “holy grail” of energy. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atoms and produces long-lived radioactive waste, fusion merges light elements and creates far less hazardous byproducts. It is inherently safer—no meltdown risk—and fuel sources like deuterium and lithium are abundant in nature.
Its importance lies in its ability to deliver:
- Zero-carbon electricity
- Virtually limitless fuel supply
- 24/7 baseload power (unlike intermittent solar/wind)
- No long-lived nuclear waste
- Greater energy independence
As countries seek to meet their decarbonization goals while maintaining energy security, fusion presents a transformative solution capable of powering economies with minimal environmental footprint.
Top Companies in the Fusion Reactor Market
1. General Fusion
- Specialization: Magnetized target fusion using mechanical pistons to compress plasma.
- Key Focus Areas / Features: Utilizes a proprietary system where liquid metal is used to compress plasma into fusion conditions, reducing engineering complexity.
- 2024 Revenue & Market Share: Revenue figures are not publicly disclosed, but the company is recognized among the leading fusion developers globally.
- Global Presence: Headquartered in Canada, with demonstration projects under way in the UK and strategic partnerships across Europe and North America.
2. Tokamak Energy
- Specialization: Compact spherical tokamaks with high-temperature superconducting magnets.
- Key Focus Areas / Features: Achieved major milestones like 100-million-degree plasma temperatures. Aims to combine spherical tokamak efficiency with compact design.
- 2024 Revenue & Market Share: Private company with undisclosed revenues; among the top five privately funded fusion firms globally.
- Global Presence: Based in the UK, engaged in international collaboration and joint development efforts.
3. Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS)
- Specialization: SPARC tokamak with high‑temperature superconducting (HTS) magnets, aiming for net-positive energy generation.
- Key Focus Areas / Features: Utilizing breakthrough HTS magnet tech that enables compact but powerful magnetic confinement; developing ARC, a grid-scale fusion power plant.
- 2024 Revenue & Market Share: Estimated at approximately USD 148 million; valuation around USD 8 billion; holds a major share in the private fusion market.
- Global Presence: US-based with strategic partners including MIT, Italian energy firms, and tech companies. Planning the first commercial fusion plant in Virginia, USA.
4. TAE Technologies
- Specialization: Field-reversed configuration (FRC) technology focused on aneutronic fusion.
- Key Focus Areas / Features: Innovating toward fusion using hydrogen-boron fuels for clean energy with zero neutron activation, enabling direct electricity conversion.
- 2024 Revenue & Market Share: Revenues not publicly disclosed; TAE has raised over USD 1 billion in funding, backed by major investors like Google and NEA.
- Global Presence: Based in the United States with partnerships across Europe and Asia.
5. Helion Energy
- Specialization: Plasma-based fusion using pulsed field-reversed configurations and direct energy conversion.
- Key Focus Areas / Features: Uses electromagnetic compression to accelerate and collide plasma targets; focuses on cost-effective, scalable fusion solutions.
- 2024 Revenue & Market Share: Exact revenue not disclosed; has secured large-scale funding and made significant scientific progress.
- Global Presence: US-based, working with energy utility partners and state governments for grid integration.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
1. Commercial Prototypes Under Construction
Companies like CFS and Helion are building prototype reactors aiming to demonstrate energy gain. These projects signal a critical transition from R&D to pre-commercial testing.
2. Surge in Private Investment
More than USD 8 billion has flowed into fusion startups, highlighting increased confidence from venture capitalists and institutional investors. Funding is enabling the acceleration of R&D timelines and expansion of facilities.
3. Policy and Regulatory Shifts
Governments like the United States have adopted new regulations that classify fusion facilities differently than fission ones, reducing regulatory hurdles and incentivizing private fusion plant development.
4. Technology Diversification
Multiple fusion pathways—tokamaks, stellarators, field-reversed configurations, magnetized target fusion, and inertial confinement—are being simultaneously pursued. This diversification improves the likelihood of technological success.
5. Rise of Corporate Partnerships
Energy firms, tech companies (such as Google), and government agencies are forming joint ventures with fusion startups to secure long-term clean energy supplies and co-develop solutions.
Successful Examples of Fusion Reactor Development
1. ITER (France)
ITER is the world’s largest fusion project, a collaborative effort among 33 countries. It is designed to prove the feasibility of nuclear fusion at scale. Although not intended for power production, it will demonstrate the viability of large-scale magnetic confinement systems.
2. National Ignition Facility (USA)
In 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy announced a historic breakthrough at the National Ignition Facility, where laser-driven inertial confinement achieved net energy gain. This demonstrated that fusion ignition is possible in controlled laboratory settings.
3. SPARC and ARC (USA)
Commonwealth Fusion Systems is constructing SPARC, a compact high-field tokamak, with the goal of achieving net-positive fusion energy. ARC, the follow-up commercial plant, is expected to deliver energy to the grid.
4. Tokamak Energy (UK)
This company has successfully built and operated a series of spherical tokamaks, achieving world-first milestones in compact reactor design and superconductor deployment.
5. General Fusion’s Demonstration Plant (UK)
General Fusion is constructing a demonstration facility in the UK with support from the government. This plant aims to show how magnetized target fusion can be scaled commercially.
Global Regional Analysis: Government Initiatives and Policy Support
North America
The United States leads the global fusion market with over 40% share in private sector fusion activity. The Department of Energy has launched initiatives like the Milestone-Based Fusion Development Program, committing over USD 1 billion to support prototype development. Fusion projects now benefit from a reclassification of regulations, treating them like particle accelerators rather than nuclear fission plants, thus reducing costs and approval timelines.
Canada supports General Fusion through innovation grants and partnerships. States like Washington and Virginia are offering site support and tax incentives for plant development.
Europe
Europe is home to the ITER project in France and a growing number of private fusion ventures in the UK, Germany, and Spain. The European Fusion Association (EFA) is coordinating efforts to fast-track commercial fusion plants, while countries like the UK are offering public funds to private companies like Tokamak Energy and First Light Fusion.
Germany’s Wendelstein 7-X stellarator continues to contribute to fundamental research, while Spain is emerging as a host for future fusion pilot plants through companies like Gauss Fusion.
Asia-Pacific
China is aggressively investing in fusion R&D, reportedly spending around USD 1.5 billion annually—almost double the U.S. allocation. It operates the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), which has achieved multiple record-breaking plasma operations.
Japan and South Korea are supporting fusion innovation through academic and industry collaboration. South Korea’s KSTAR reactor recently maintained plasma at over 100 million degrees Celsius for several seconds.
Rest of the World
Other regions are catching up. Australia has startups exploring laser-driven fusion. Middle Eastern countries like the UAE are investing in future-oriented energy initiatives, which could include fusion partnerships. Latin America remains in early exploration stages but is participating in international fusion networks.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market Top Players, Trends, and Regional Insights by 2034