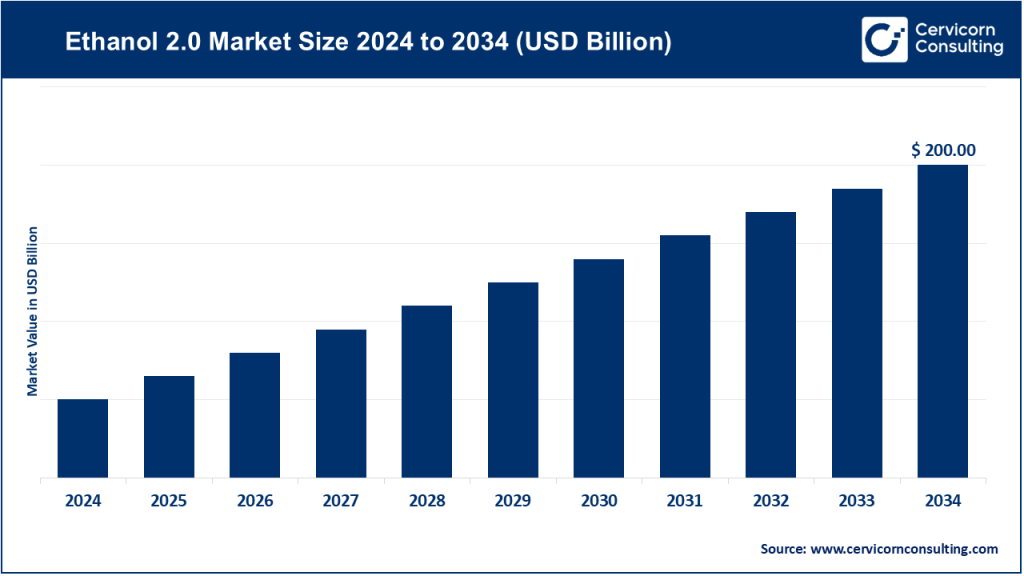
Ethanol 2.0 Market Size
The global ethanol 2.0 market size is anticipated to expand to around USD 200 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6% from 2025 to 2034.
Ethanol 2.0 Market Growth Factors
The Ethanol 2.0 market is being propelled by a convergence of favorable government policies, advances in cellulosic and enzyme technologies, and the growing need for sustainable and low-carbon fuels. Blending mandates, low-carbon fuel standards, and subsidy programs are encouraging the shift toward next-generation bioethanol. Improvements in pretreatment, fermentation efficiency, and feedstock optimization—using agricultural residues, waste biomass, and energy crops instead of food grains—are lowering production costs.
Simultaneously, global decarbonization targets, rising demand for renewable aviation and transport fuels, corporate sustainability commitments, and new co-product markets for biochemicals and renewable oils are reinforcing investment. As large producers integrate carbon-capture systems and renewable power sources into operations, the overall carbon intensity of ethanol 2.0 declines further, making it a key enabler of circular and climate-neutral energy systems.
What Is the Ethanol 2.0 Market?
“Ethanol 2.0” refers to the next evolutionary stage of bioethanol production that utilizes non-food biomass feedstocks—such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and industrial organic by-products—to produce second-generation (2G) or advanced ethanol. Unlike traditional first-generation ethanol, which is derived primarily from starch or sugar-rich crops like corn and sugarcane, Ethanol 2.0 minimizes the food-versus-fuel dilemma and provides significant lifecycle greenhouse-gas (GHG) reductions. This version of ethanol leverages advanced biotechnologies, innovative enzymes, integrated biorefinery models, and carbon-management systems to generate cleaner, more sustainable fuel options.
Ethanol 2.0 is also expanding into new applications—such as sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), renewable diesel blending, and biochemical feedstocks—beyond traditional gasoline blending, establishing itself as a vital component of the global clean-energy transition.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2798
Why Is Ethanol 2.0 Important?
Ethanol 2.0 plays a crucial role in the global transition toward carbon neutrality. First, it offers substantial climate benefits—its lifecycle carbon intensity is markedly lower than both fossil fuels and conventional bioethanol, helping nations meet emission-reduction targets and low-carbon fuel mandates. Second, by utilizing non-food biomass, it alleviates pressure on agricultural land and avoids direct competition with food supply chains. Third, Ethanol 2.0 contributes to energy diversification and rural economic growth, enabling countries to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels while fostering domestic industries for residue collection, bio-processing, and co-product manufacturing. The scalability of second-generation ethanol technologies and their integration with renewable energy and carbon-capture systems position Ethanol 2.0 as an indispensable part of a sustainable industrial ecosystem.
Ethanol 2.0 Market — Top Companies
1. Archer-Daniels-Midland Company (ADM)
- Specialization: ADM is a global agribusiness leader specializing in agricultural origination, processing, and nutrition solutions, with deep involvement in starch-based ethanol and renewable fuel production.
- Key Focus Areas: Feedstock optimization, enzyme and fermentation innovation, bio-refining integration, and large-scale supply-chain management.
- Notable Features: ADM operates one of the world’s most extensive networks for grain procurement and processing. The company’s strong R&D capabilities and vertically integrated infrastructure make it a vital contributor to the ethanol 2.0 ecosystem.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 85 billion (companywide).
- Market Share: Among the top global ethanol producers and a key supplier of raw materials and processing technology to 2G projects.
- Global Presence: Extensive operations across North and South America, Europe, and Asia with a broad logistics and distribution network.
2. POET LLC
- Specialization: POET is the world’s largest dedicated bioethanol producer, focusing on sustainable fuel production, cellulosic ethanol development, and bioproduct diversification.
- Key Focus Areas: Expansion of commercial ethanol plants, advancement of cellulosic technology, and optimization of bioprocessing systems.
- Notable Features: The company’s Project LIBERTY facility in Iowa was among the first large-scale cellulosic ethanol plants, setting the benchmark for next-generation ethanol production.
- 2024 Revenue: Estimated multi-billion-dollar range; POET is privately held and does not publicly disclose detailed figures.
- Market Share: One of the largest ethanol producers globally and a pioneer in 2G ethanol innovation.
- Global Presence: Primarily U.S.-based operations, with global partnerships and export networks for biofuels and co-products.
3. Valero Energy Corporation
- Specialization: A leading integrated energy company combining petroleum refining with renewable fuels and ethanol production.
- Key Focus Areas: Ethanol manufacturing, renewable diesel integration, and low-carbon fuel blending operations.
- Notable Features: Valero operates several large ethanol plants in the U.S. Midwest and integrates production with its extensive refining and distribution system.
- 2024 Revenue: Around USD 125 billion (total company revenue).
- Market Share: A top-tier player in the global biofuel market with significant ethanol production capacity.
- Global Presence: Headquarters in the U.S. with trading and export operations across North America, Europe, and Latin America.
4. Cargill Inc.
- Specialization: One of the world’s largest privately held corporations, active in food, agriculture, and energy, including ethanol and biofuel production.
- Key Focus Areas: Bioenergy investments, sugarcane and corn ethanol production in Brazil, feedstock sourcing, and sustainability integration.
- Notable Features: Cargill’s supply-chain expertise and strategic acquisitions in Brazil strengthen its position in ethanol production and export.
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately USD 160 billion.
- Market Share: A major global player in biofuel feedstock origination and ethanol production, particularly in Latin America.
- Global Presence: Operations in over 70 countries with strong market positions in the Americas, Europe, and Asia.
5. Green Plains Inc.
- Specialization: A pure-play ethanol producer focused on transforming into a value-added bioproduct company.
- Key Focus Areas: High-protein feed development, renewable corn oil extraction, and advanced fermentation technology.
- Notable Features: Green Plains emphasizes innovation to create higher-margin co-products while optimizing ethanol production efficiency.
- 2024 Revenue: Around USD 470 million.
- Market Share: A leading mid-size ethanol producer with growing influence in advanced bioproduct segments.
- Global Presence: Primarily U.S. operations with exports to international fuel and feed markets.
Leading Trends and Their Impact
- Commercialization of Cellulosic Ethanol:
Advances in pretreatment and enzyme efficiency are enabling viable commercial-scale operations. Lower production costs and proven performance encourage wider adoption. - Policy Support and Regulatory Incentives:
Expanding biofuel blending mandates, low-carbon fuel standards, and renewable-energy credits create consistent demand and investment confidence. - Feedstock Diversification and Logistics Innovation:
Efficient aggregation of agricultural residues and waste biomass ensures feedstock availability without affecting food supply, supporting rural economies and farmers. - Integration with Carbon-Capture and Renewable Power:
Ethanol 2.0 facilities increasingly co-locate with renewable energy or carbon-capture systems to reduce lifecycle emissions and generate tradable carbon credits. - Strategic Partnerships and M&A Activity:
Energy companies, agribusinesses, and technology firms are forming alliances to accelerate commercialization and secure supply chains, promoting vertical integration across the ethanol 2.0 value chain. - Rise of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Pathways:
Ethanol 2.0 serves as a precursor for SAF production, meeting aviation decarbonization needs and creating new high-value markets for advanced ethanol producers. - Digitalization and Process Optimization:
Adoption of AI, IoT, and data analytics enhances fermentation control, reduces waste, and improves overall plant performance.
These trends collectively position ethanol 2.0 as a cornerstone of future energy systems, bridging agricultural innovation with industrial decarbonization.
Successful Examples of Ethanol 2.0 Around the World
- United States:
The U.S. leads the ethanol 2.0 transition with several large-scale projects and pilot plants demonstrating commercial cellulosic ethanol. Companies like POET and ADM have successfully integrated residue-based ethanol into their operations. Federal incentives such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and state programs like the California Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) continue to drive expansion. - Brazil:
Brazil’s mature sugarcane ethanol infrastructure and expanding corn-based ethanol industry provide a solid foundation for second-generation development. The country is integrating agricultural waste and bagasse into ethanol production, supported by favorable policies and corporate investments from companies such as Cargill. - India:
India has set ambitious ethanol-blending targets (E20 by 2025-26) and launched the “Ethanol 2.0” initiative to convert agricultural residues into fuel. Numerous 2G plants are under construction, leveraging abundant biomass such as rice straw and sugarcane waste. Government support through soft loans and purchase guarantees is making India one of the fastest-growing ethanol 2.0 markets. - European Union:
The EU’s Renewable Energy Directive promotes advanced biofuels, encouraging 2G ethanol projects that utilize waste and residue feedstocks. European biorefineries are experimenting with lignocellulosic ethanol integrated with SAF production and hydrogen recovery, fostering cross-sector collaboration. - China:
China is expanding biofuel production using non-grain feedstocks to reduce pollution and reliance on oil imports. Pilot programs in northeastern provinces are testing residue-to-ethanol technologies, potentially positioning China as a major player in ethanol 2.0 within Asia.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Initiatives
North America
The U.S. and Canada have established robust frameworks for renewable fuels. The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) mandates blending of renewable components, while the LCFS in California and similar programs elsewhere reward low-carbon ethanol. Federal incentives for Sustainable Aviation Fuel and carbon-capture integration enhance ethanol 2.0’s competitiveness. These measures have led to significant investments in 2G ethanol facilities and supportive infrastructure.
Latin America
Brazil remains the regional leader, leveraging decades of experience in ethanol production. The RenovaBio program encourages decarbonization credits for low-carbon biofuels, spurring expansion of both sugarcane and corn ethanol facilities. Argentina and Colombia are also pursuing advanced ethanol initiatives, focusing on local feedstock utilization and regional export opportunities.
Europe
European nations are investing heavily in advanced biofuel technologies under the Renewable Energy Directive III. Incentives for waste-based ethanol production and strict sustainability criteria have spurred pilot projects across Germany, France, and the Nordic region. The EU’s Fit-for-55 package further encourages the use of advanced biofuels in aviation and transport sectors.
Asia-Pacific
India is emerging as the key Asian hub for ethanol 2.0. Its national biofuel policy promotes residue-based production through viability-gap funding and purchase agreements. China, Thailand, and Indonesia are following suit, leveraging agricultural waste to achieve blending targets and reduce dependence on fossil imports. Japan and South Korea are exploring ethanol imports and co-processing partnerships to meet emission targets.
Africa
Countries like South Africa and Kenya are exploring opportunities for ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse and crop residues. While infrastructure and policy frameworks are still developing, donor-supported programs and private investment are laying the groundwork for regional growth.
Oceania
Australia and New Zealand are investigating second-generation biofuel initiatives aligned with national net-zero goals. Feedstock availability and supportive policy mechanisms will determine the pace of commercialization in these markets.
Government Policies Shaping the Ethanol 2.0 Market
- Blending Mandates:
Many countries are raising blend requirements (e.g., E10, E20, or higher), directly stimulating ethanol demand. - Low-Carbon Fuel Standards:
Programs that reward low-GHG fuels provide a competitive advantage for 2G ethanol producers with verified carbon-intensity reductions. - Tax Credits and Grants:
Financial incentives for biofuel production, carbon capture, and SAF integration reduce capital risk and accelerate plant development. - Research and Development Support:
Public-private partnerships fund innovation in enzyme efficiency, feedstock logistics, and waste-to-energy conversion. - Sustainability Certification:
Governments and industry bodies are implementing certification schemes ensuring that feedstocks are responsibly sourced and meet lifecycle emission standards.
Ethanol 2.0 Market Dynamics
- Feedstock Economics:
The viability of Ethanol 2.0 depends on efficient collection and transportation of residues and waste biomass. Regional differences in agricultural output significantly influence feedstock cost and availability. - Technology Readiness:
While cellulosic ethanol technologies have achieved commercial proof-of-concept, further optimization is needed to scale cost-effectively. Advances in biotechnology, process engineering, and digital control systems are improving yields and plant reliability. - Investment Landscape:
Growing investor confidence, backed by long-term policy commitments and corporate net-zero goals, has encouraged major financing rounds in the biofuel sector. Strategic alliances among technology providers, feedstock suppliers, and energy majors are accelerating market growth. - Competition and Substitutes:
While renewable diesel and synthetic fuels compete for attention, ethanol 2.0 remains more mature in terms of commercial infrastructure, particularly in light-duty transport and blending applications. - Global Trade and Market Integration:
International trade in ethanol and co-products is expected to increase, supported by harmonized sustainability standards and expanding export markets in Asia and Europe.
The Future Outlook
Ethanol 2.0 stands at the intersection of agriculture, biotechnology, and clean energy. Its ability to convert low-value biomass into high-value fuels and chemicals aligns perfectly with global goals for decarbonization, waste reduction, and rural development. As policies tighten around carbon emissions and transportation fuels, the technology’s role will expand beyond traditional blending to become a foundation for next-generation energy carriers such as sustainable aviation fuel and green hydrogen feedstocks.
Industry leaders—ADM, POET, Valero, Cargill, and Green Plains—are expected to spearhead this transformation through continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and regional expansion. The Ethanol 2.0 market thus represents not only a technological upgrade to biofuels but a structural evolution of the global energy economy.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players, and Regional Insights by 2034