ESG Investing Market Size
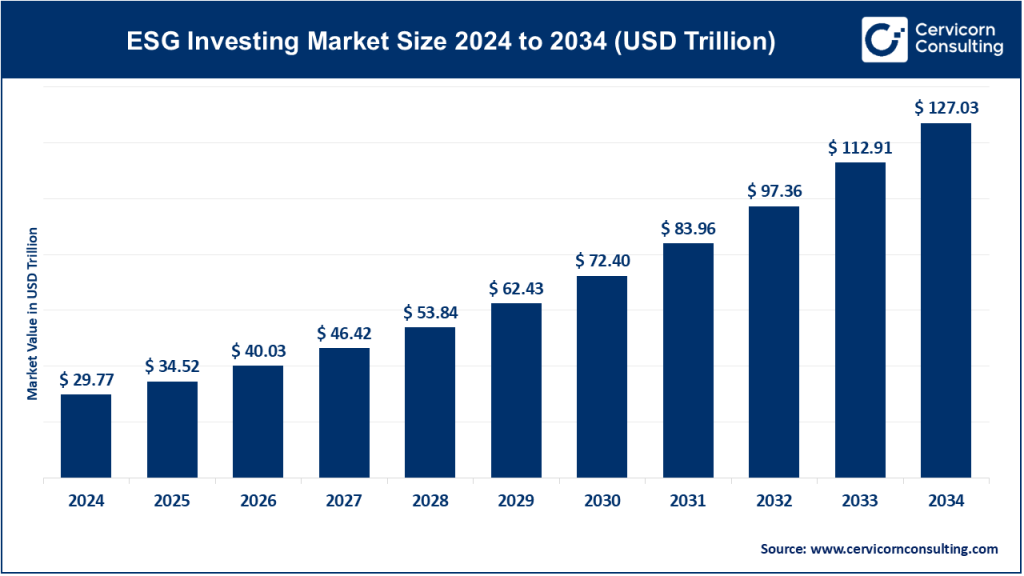
The global ESG investing market size was worth USD 29.77 trillion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 127.03 trillion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.96% from 2025 to 2034.
ESG Investing Market — Growth Factors
The ESG investing market is expanding rapidly due to a convergence of economic, regulatory, and investor-driven forces. Investors are increasingly prioritizing portfolios that manage climate risks, uphold social responsibility, and maintain strong governance practices, which has significantly increased inflows into ESG-labelled funds. Regulatory bodies across the world have introduced new sustainability disclosure requirements, improving transparency and making ESG data more comparable across companies and sectors.
Additionally, the financial materiality of ESG factors — such as climate-related risks, supply-chain disruptions, diversity metrics, and corporate governance quality — has become more evident, pushing investors to consider ESG as a core part of risk management. The declining cost of renewable energy, rapid growth of sustainable finance instruments (green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, ESG ETFs), and global commitments to decarbonization have further accelerated market expansion. As asset managers continue to integrate technology, data analytics, and stewardship strategies into their investment processes, the ESG market is transitioning from a niche segment into a mainstream investment paradigm.
What is the ESG Investing Market?
The ESG investing market encompasses all financial products, strategies, and assets that consider environmental, social, and governance factors as part of the investment decision-making process. These strategies go beyond traditional financial analysis by assessing sustainability risks and opportunities that may impact long-term financial performance. ESG investing can take many forms: exclusionary screening (avoiding certain industries), positive screening (favoring companies with strong ESG practices), ESG integration (embedding ESG criteria into core financial analysis), thematic investing (such as renewable energy or gender diversity funds), and impact investing (targeting measurable environmental or social outcomes).
The market includes equities, fixed income, ETFs, private equity, real assets, and alternative investment vehicles. As sustainability considerations become more deeply embedded in global capital markets, ESG investing is now used by institutional investors, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, retail investors, and financial advisors worldwide.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2395
Why is ESG Investing Important?
ESG investing is important because it connects financial returns with responsible corporate behavior, creating a more resilient economic system. Environmental criteria help investors assess climate-related risks, carbon exposure, pollution, water use, and energy efficiency — all of which can impact corporate profitability. Social factors evaluate employee welfare, community relations, human rights practices, diversity, and product safety, helping investors identify companies that manage human capital effectively.
Governance considerations such as board structure, executive pay, ethics, transparency, and shareholder rights influence corporate stability and accountability. With rising climate risks, social inequality, and regulatory pressures, ESG investing offers a framework for mitigating long-term risks while capitalizing on opportunities like clean energy, sustainable supply chains, and inclusive business models. Moreover, consumers and younger generations are increasingly aligning investments with personal values, pushing financial institutions to offer ESG-aligned products. Ultimately, ESG investing supports both financial performance and positive societal outcomes.
Top Companies in the ESG Investing Market
Below is a detailed overview of the major global players leading ESG investing efforts.
1. BlackRock, Inc.
Specialization:
World’s largest asset manager with expertise in equity, fixed income, multi-asset funds, ETFs, and alternatives.
Key Focus Areas:
Sustainable ETFs, climate-aware strategies, decarbonization portfolios, stewardship, and corporate engagement.
Notable Features:
Advanced ESG analytics integrated into its risk-management platform; strong global stewardship and sustainability-focused voting strategies.
2024 Revenue / AUM:
BlackRock reported strong overall revenue growth in 2024 with total assets under management exceeding USD 11 trillion.
Market Share:
Largest share of ESG-labelled ETFs globally and a leading position in sustainable index funds.
Global Presence:
Extensive operations across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and emerging markets.
2. Vanguard Group, Inc.
Specialization:
Global leader in low-cost index funds and ETFs.
Key Focus Areas:
ESG index funds, low-cost sustainable ETFs, stewardship and proxy voting focused on climate and governance risks.
Notable Features:
Wide retail investor base, accessible ESG options, and influential stewardship activities.
2024 Revenue / AUM:
Vanguard’s total AUM reached multiple trillions in 2024, with stewardship covering a large share of its equity holdings.
Market Share:
One of the largest passive managers competing heavily in ESG ETF adoption.
Global Presence:
Strong presence in the U.S., Europe, Australia, and Asia with significant index-based ESG adoption.
3. State Street Global Advisors (SSGA)
Specialization:
Institutional asset management, indexing solutions, and SPDR ETFs.
Key Focus Areas:
ESG-integrated index strategies, climate-aligned ETFs, and stewardship initiatives targeting corporate governance.
Notable Features:
Large footprint in institutional investing, influential governance initiatives, strong ESG data integration.
2024 Revenue / AUM:
SSGA maintained significant AUM in 2024, including strong growth in ESG-labelled ETFs.
Market Share:
A top global ETF provider with considerable influence over ESG indexing.
Global Presence:
Operations across North America, Europe, Middle East, and Asia-Pacific.
4. JPMorgan Chase & Co. — Asset Management Division
Specialization:
Global active and passive investment solutions across equities, fixed income, alternatives, and ETFs.
Key Focus Areas:
Active sustainable strategies, green financing, decarbonization advisory, and impact-driven investments.
Notable Features:
Large institutional client base, strong research insights, and a growing sustainable finance offering.
2024 Revenue / AUM:
JPMorgan reported robust 2024 performance with significant growth in sustainable products and stewardship engagements.
Market Share:
Expanding influence in ESG ETFs and sustainable fixed-income products.
Global Presence:
Global operations in the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Middle East.
5. Goldman Sachs Asset Management (GSAM)
Specialization:
Active strategies, private markets, sustainable infrastructure, and impact investing.
Key Focus Areas:
Climate transition finance, sustainability-linked investments, impact funds, and ESG risk analytics.
Notable Features:
Combines investment banking expertise with sustainable finance capabilities to drive capital mobilization.
2024 Revenue / AUM:
Goldman Sachs reported strong overall financial performance in 2024 and continues to scale sustainable finance commitments.
Market Share:
Growing share in institutional sustainable finance and private-market ESG strategies.
Global Presence:
Active across North America, Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and emerging economies.
Leading Trends in the ESG Investing Market
1. Transition from Exclusion to Full ESG Integration
Traditional negative screening is increasingly being replaced by integrated ESG analysis across sectors and asset classes. Investors now incorporate climate, social, and governance metrics into fundamental financial models, improving risk assessment.
2. Growth of Sustainable Bonds and Debt Instruments
Green, social, sustainability, and sustainability-linked bonds have surged. Corporations and governments are issuing these instruments to finance renewable energy, housing, health infrastructure, and low-carbon transport.
3. Standardization of ESG Reporting and Regulation
New reporting frameworks, mandatory disclosures, and sustainability taxonomies have improved transparency. This enables more accurate ESG assessments and reduces greenwashing risks.
4. Technology and AI-Driven ESG Analytics
AI-based tools now track climate metrics, analyze supply-chain risks, and score companies using large datasets. This enhances objectivity and consistency in ESG evaluations.
5. Rise of Retail ESG Investments
Low-cost ESG ETFs and user-friendly digital platforms have expanded ESG investing among retail investors. Younger demographics, in particular, drive demand for sustainable investment options.
Impact of these trends:
They collectively increase capital flows into sustainable sectors, improve corporate accountability, promote low-carbon transition, and transform the responsibilities of asset managers through more active engagement and stewardship.
Successful Examples of ESG Investing Worldwide
1. Rapid Expansion of Green Bond Markets
Countries in Europe, Asia, and the Americas have issued large volumes of green bonds, financing renewable energy, sustainable transport, and climate adaptation projects. Green bonds help investors support climate solutions while earning competitive returns.
2. Corporate Stewardship Initiatives
Large asset managers have successfully influenced companies to adopt climate disclosures, improve board independence, reduce emissions, and strengthen human-rights policies. These stewardship efforts have contributed to meaningful corporate transitions.
3. Global Growth of ESG ETFs
The rise of low-cost sustainable ETFs has democratized ESG investing. Investors can now access diversified sustainable portfolios with ease, leading to large inflows into ESG-labelled index funds.
4. Emerging Market Impact Investments
In Latin America, Africa, and South Asia, blended finance — combining private capital with public guarantees — has mobilized investment into clean energy, sustainable agriculture, healthcare, and education. These projects demonstrate high-impact ESG outcomes.
5. National Sustainable Finance Initiatives
Several governments have created sustainability-focused investment frameworks, national ESG guidelines, and climate finance programs that stimulate private-sector participation.
Global Regional Analysis and Government Policy Influence
North America
Policies and initiatives:
- Movement toward mandatory climate risk disclosures
- Strengthening corporate governance standards
- Public pension funds increasing responsible investment mandates
Impact:
These policies push asset managers to enhance ESG reporting, refine product labelling, and invest in stewardship. The U.S. remains a major hub for ESG ETFs and sustainable fixed-income products.
Europe
Policies and initiatives:
- Strongest global ESG regulatory landscape
- EU Taxonomy for sustainable activities
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
Impact:
Europe leads the world in ESG adoption due to robust regulatory frameworks, high investor awareness, and government-backed climate strategies. Asset managers must comply with detailed sustainability classifications and reporting requirements.
Asia-Pacific
Policies and initiatives:
- National net-zero commitments
- Climate disclosure mandates in Japan, South Korea, and Australia
- Regional green bond guidelines (e.g., China, Singapore)
Impact:
These policies create substantial opportunities for sustainable finance, including renewable energy, low-carbon technology, and sustainable urban development. Asia-Pacific is one of the fastest-growing ESG regions.
Latin America
Policies and initiatives:
- Renewable energy investment incentives
- Social impact mandates in pension systems
- Growing adoption of green bond frameworks
Impact:
Latin America attracts global ESG investors through renewable power projects, sustainable agriculture programs, and public-private blended finance initiatives.
Middle East & Africa
Policies and initiatives:
- Sovereign sustainability initiatives
- National diversification plans such as green hydrogen and solar mega-projects
- Emerging ESG disclosure requirements for listed companies
Impact:
The region is witnessing strong growth in sustainable infrastructure development, financed by both sovereign entities and global impact investors.
Additional Market Insights
Growing Investment in Transition Finance
Capital is increasingly directed toward companies transitioning from high-carbon to low-carbon operations — not just companies already performing well on ESG metrics.
Greater Scrutiny of Greenwashing
Regulators and investors are cracking down on misleading ESG claims, pushing asset managers to adopt clearer methodologies and reporting practices.
Increasing Demand for Impact Measurement
Investors now expect measurable environmental and social outcomes, encouraging more rigorous ESG scoring and impact frameworks across the industry.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Polymers Market Revenue, Global Presence, and Strategic Insights by 2035