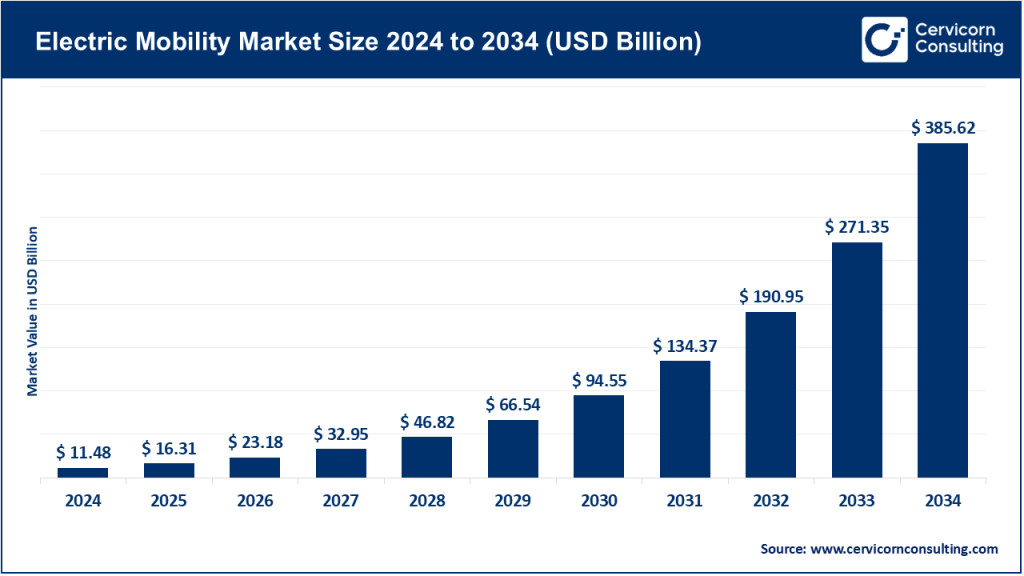
Electric Mobility Market Size
The global electric mobility market size was worth USD 11.48 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around USD 385.62 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.5% from 2025 to 2034.
What is the Electric Mobility Market?
The electric mobility (e-mobility) market represents the growing ecosystem of vehicles, technologies, infrastructure, and services that enable the transportation of people and goods powered by electricity. It includes battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, buses, and trucks, as well as charging infrastructure, battery manufacturing, recycling systems, and grid integration. The market also extends into digital platforms for shared and autonomous mobility, fleet management software, and energy storage solutions. Electric mobility is reshaping global transportation by replacing internal combustion engines with clean, energy-efficient electric drivetrains, reducing environmental impact, and driving innovation across automotive and energy industries.
Growth Factors Driving the Electric Mobility Market
The growth of the electric mobility market is driven by multiple interconnected factors. Stringent emissions regulations and fuel-efficiency standards across major economies are pushing automakers toward full or partial electrification. Government incentives, such as subsidies, tax rebates, and infrastructure investments, continue to encourage both manufacturers and consumers to adopt electric solutions. Declining battery costs, alongside advances in energy density and charging speed, have significantly lowered the total cost of ownership, making electric vehicles more accessible to mass consumers. The emergence of gigafactories and localized supply chains has improved production efficiency and reduced dependence on imports.
Moreover, corporate fleet electrification initiatives, combined with sustainability commitments, are driving bulk procurement of EVs for logistics and ride-hailing services. Urbanization, coupled with zero-emission transport mandates, is further accelerating electric adoption. Additionally, innovations like vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, fast-charging networks, and battery recycling are creating a robust, circular, and interconnected electric mobility ecosystem globally.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2783
Why Electric Mobility is Important
Electric mobility is central to the global transition toward sustainability, energy independence, and technological progress. First, it plays a pivotal role in decarbonizing transportation, one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. By using electricity—especially from renewable sources—EVs drastically reduce carbon footprints compared to traditional fossil-fueled vehicles. Second, e-mobility contributes to energy security by reducing dependence on imported petroleum and diversifying national energy portfolios.
Third, electric mobility improves urban air quality, minimizing pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter that cause respiratory diseases. Finally, the e-mobility transition creates new industrial and economic opportunities, including high-skilled jobs in manufacturing, battery development, software, and smart grid management. Governments and companies alike view electric mobility not only as a climate solution but also as a driver of economic modernization and competitive advantage.
Electric Mobility Market — Top Companies
Tesla, Inc.
Specialization: Tesla focuses on designing, manufacturing, and selling electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and renewable energy products.
Key Focus Areas: Tesla’s core priorities include expanding mass-market EV adoption through models like the Model 3 and Model Y, developing full self-driving capabilities, and scaling battery production via Gigafactories in the U.S., Europe, and China.
Notable Features: The company’s vertically integrated ecosystem includes proprietary software, in-house batteries, and the globally recognized Supercharger network. Tesla’s vehicles feature over-the-air updates and advanced driver-assistance systems.
2024 Revenue: Approximately $97.7 billion, reflecting a strong market presence despite increased competition.
Market Share: Around 10–11% of global EV sales in 2024.
Global Presence: Strong foothold in North America, China, and Europe, with expanding manufacturing capacity and charging infrastructure worldwide.
BYD (Build Your Dreams)
Specialization: BYD is a global leader in new energy vehicles (NEVs), offering BEVs, PHEVs, electric buses, and trucks, alongside its in-house battery technology.
Key Focus Areas: BYD emphasizes cost-effective mass production, proprietary Blade Battery innovation, and aggressive expansion into international markets.
Notable Features: The Blade Battery offers superior safety, long life cycles, and lower production costs. BYD’s vertical integration covers everything from battery cells to vehicle assembly.
2024 Revenue: Approximately $107 billion, driven by surging domestic and export sales.
Market Share: Around 25% of global EV/NEV sales, making BYD the largest manufacturer by volume in 2024.
Global Presence: Dominant in China, expanding into Europe, Southeast Asia, South America, and the Middle East with new production facilities.
Geely Auto Group
Specialization: Geely operates a multi-brand portfolio that includes Geely, Volvo, Polestar, Lynk & Co, and Zeekr, focusing on both ICE-to-EV transition and premium electric mobility.
Key Focus Areas: The company is committed to developing shared EV architectures, enhancing smart connectivity, and scaling exports.
Notable Features: Geely leverages shared platforms across brands, such as the Sustainable Experience Architecture (SEA), to reduce costs and accelerate model launches.
2024 Revenue: Approximately RMB 240.2 billion, marking record growth and profitability.
Market Share: Among the top five Chinese NEV producers, with rapidly expanding global sales through Volvo and Polestar.
Global Presence: Strong in China with a growing presence in Europe and Southeast Asia through brand diversification and partnerships.
General Motors (GM)
Specialization: GM is transforming its global portfolio toward electric and autonomous mobility through its Ultium battery platform.
Key Focus Areas: Electrification of SUVs, trucks, and commercial fleets; partnerships for battery manufacturing; and software integration.
Notable Features: The Ultium platform underpins GM’s new lineup, offering scalable architecture and advanced battery performance. GM also focuses on fleet electrification and autonomous driving technologies through Cruise.
2024 Revenue: Approximately $187.4 billion, reflecting stable financials during EV transition.
Market Share: A leading U.S. player in electric trucks and SUVs, expanding its EV footprint rapidly.
Global Presence: Strong in North America, with growing activities in Latin America, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East.
Volkswagen Group
Specialization: Volkswagen is one of the largest global automakers with a strong focus on full-scale electrification under its “NEW AUTO” strategy.
Key Focus Areas: Expanding EV production capacity, introducing modular electric platforms (MEB and PPE), and building a European battery ecosystem.
Notable Features: Volkswagen’s EV lineup spans all major price points through brands like Audi, Porsche, and Cupra. The company is investing heavily in software-defined vehicles and sustainable manufacturing.
2024 Revenue: Approximately €324.7 billion, underscoring its vast global scale.
Market Share: One of Europe’s top EV producers and among the global leaders in BEV sales.
Global Presence: Strong across Europe, North America, and China, with expanding production facilities dedicated to EVs.
Leading Trends and Their Impact on the Electric Mobility Market
1. Battery Innovation and Cost Reduction
Advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state batteries are reducing costs while enhancing range and safety. These improvements make EVs more affordable and attractive to mainstream consumers. Lower battery costs also drive higher production margins and allow manufacturers to diversify their product offerings.
2. Modular EV Platforms
Automakers are investing in flexible, scalable platforms that can underpin multiple models, reducing production complexity. These modular architectures, such as VW’s MEB or GM’s Ultium, cut manufacturing costs and accelerate time to market, fostering rapid expansion across vehicle segments.
3. Expansion of Fast-Charging Infrastructure
Ultra-fast charging technologies and growing interoperability between networks are addressing range anxiety. Widespread public charging infrastructure supports long-distance travel and encourages EV ownership in regions lacking home charging facilities.
4. Rise of Chinese Automakers
Chinese brands like BYD, Geely, and NIO are leading the global EV revolution, offering competitive pricing, advanced features, and large-scale production. Their success has pushed global OEMs to innovate faster and lower costs to maintain competitiveness.
5. Commercial Fleet Electrification
Corporations and logistics companies are electrifying their fleets to meet sustainability goals and reduce operational expenses. Electric vans, buses, and trucks are increasingly adopted for last-mile delivery and urban transportation, providing predictable routes ideal for EV operations.
6. Software-Defined Vehicles
Modern EVs function as digital platforms, offering features via over-the-air updates, driver-assistance packages, and connected services. Automakers are monetizing software subscriptions, turning cars into long-term revenue sources and improving customer engagement.
7. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration
V2G technology enables EVs to feed energy back into the grid, stabilizing electricity supply and supporting renewable integration. This trend is opening new energy management markets and creating additional value streams for EV owners.
Successful Examples of Electric Mobility Around the World
China
China has become the global leader in electric mobility, with millions of EVs sold annually. Strong government incentives, local supply chains, and infrastructure investment have enabled Chinese automakers to dominate both domestic and export markets. Cities like Shenzhen have electrified their entire public bus fleets, showcasing the scalability of EV deployment.
Norway
Norway stands as the benchmark for EV penetration, with electric vehicles accounting for over 80% of new car sales. A combination of tax exemptions, toll-free roads, and parking benefits made EV ownership economically attractive. Norway’s model demonstrates how consistent policy support and charging access can achieve nationwide adoption.
United States (California and Beyond)
California’s Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) program, federal tax credits, and infrastructure investment have positioned the U.S. as a major EV growth market. States like New York and Washington are following similar policies. Tesla’s manufacturing leadership and expanding charging network have further solidified America’s role in EV innovation.
Europe (Germany and the Netherlands)
Germany and the Netherlands have aggressively expanded EV adoption through tax incentives, corporate fleet electrification, and widespread charging infrastructure. German automakers, including Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz, are rapidly converting factories to EV production. The Netherlands’ extensive charging network makes EV ownership seamless and convenient.
Emerging Markets
India’s rapid electrification of two-wheelers and three-wheelers is transforming urban mobility. Government incentives and the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme are boosting domestic manufacturing. Latin American countries such as Chile and Colombia are leading in e-bus deployment, improving public transit sustainability.
Global Regional Analysis — Government Initiatives and Policies
China
China’s electric mobility success is built on a mix of financial incentives, industrial policy, and strategic investment. The government has heavily subsidized EV purchases, supported battery manufacturing, and established strict vehicle emission standards. Domestic manufacturers benefit from large-scale R&D funding, while export programs are expanding Chinese EVs into new markets.
Europe
Europe’s electric mobility landscape is driven by stringent emissions targets and carbon neutrality goals. The European Union’s “Fit for 55” initiative and national subsidy programs have spurred mass EV adoption. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK offer tax credits, rebates, and infrastructure funding. The EU is also supporting large-scale battery alliances and recycling networks to strengthen supply chain resilience.
United States
The U.S. federal government’s Inflation Reduction Act provides incentives for EV purchases, manufacturing, and domestic battery sourcing. States such as California and New York enforce zero-emission mandates and fund charging infrastructure. These combined policies are catalyzing both consumer adoption and local manufacturing capacity.
India
India’s approach emphasizes the electrification of affordable transport segments. The FAME II initiative, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, and state-level subsidies are driving EV growth. India’s policies target not only consumer vehicles but also public buses, delivery fleets, and charging networks, paving the way for inclusive electrification.
Latin America
Several Latin American nations are adopting electric buses to reduce emissions in congested urban centers. Public-private partnerships are key drivers, helping to overcome initial infrastructure barriers. Countries like Brazil, Chile, and Mexico are implementing import duty reductions and financing programs for electric fleets.
Africa
Africa’s EV market is in early stages but growing steadily, led by local startups and pilot programs in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa. Governments are introducing incentives for electric motorcycles and buses to reduce fuel import dependence and improve air quality in cities.
Cross-Regional Policy Themes
Across regions, several consistent policy themes are evident:
- Purchase Incentives and Mandates: Successful markets blend consumer subsidies with long-term bans or phase-out dates for internal combustion engines.
- Infrastructure Investment: Governments and private players are co-funding public fast-charging networks to ensure seamless mobility.
- Industrial Development: Nations are investing in local battery production, recycling, and workforce training to capture manufacturing value.
- Sustainability Standards: Lifecycle emissions standards and battery recycling regulations ensure long-term environmental benefits.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Alliances between automakers, energy providers, and technology firms accelerate innovation and deployment.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Industrial Software Market Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034