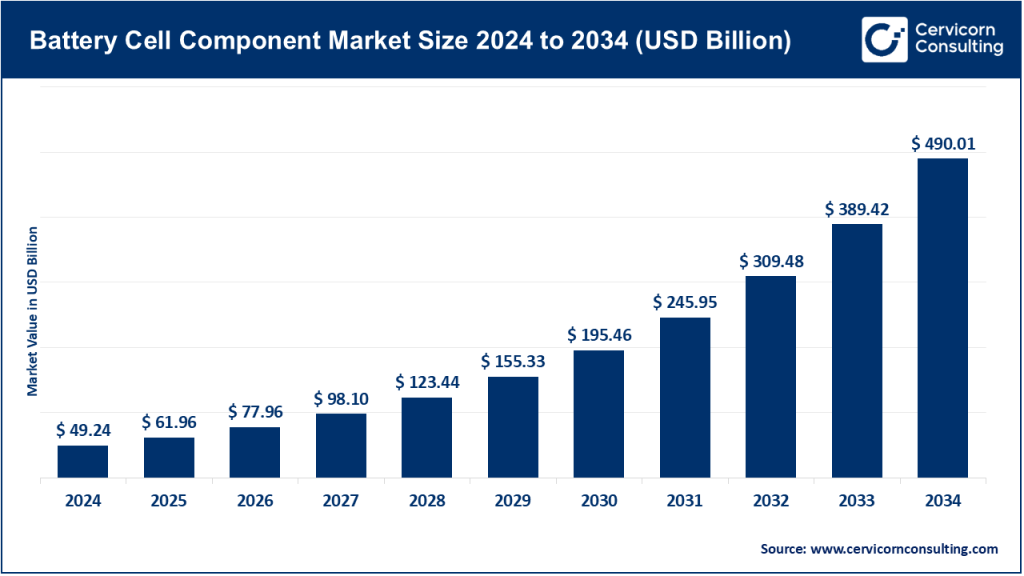
Battery cell component market size
Battery cell component market — Growth Factors
Rapid electrification (EVs, e-buses, commercial fleets), exponential growth in energy storage systems (utility and behind-the-meter), falling cell-level costs enabled by learning curves and scale, advances in cell chemistries (higher-nickel NMC, silicon-enhanced anodes, solid-state R&D), intense vertical integration by OEMs and battery makers, regulatory pressure for recyclability and responsible sourcing, capital flows into giga-scale manufacturing, and geopolitical industrial policy (subsidies, local content rules and tax credits) together create a high-momentum market where demand growth, technology differentiation (energy density, cycle life, safety) and supply-chain resilience are the dominant commercial levers.
These drivers accelerate investments into upstream component refinement (high-purity cathode materials, synthetic graphite anode grades, next-gen separators and electrolyte additives), while simultaneously forcing suppliers to meet stringent traceability, sustainability and localization requirements — in short, demand + technology + policy are co-driving expansion across the entire value chain.
What is the battery cell component market?
Put simply: it’s the ecosystem that supplies the ingredients and subsystems used to build individual battery cells. That covers:
- Active materials: cathode powders (NMC, NCA, LFP), anode materials (graphite, silicon blends), electrolyte salts and solvents, additives.
- Passive components: separators (polymeric membranes), current collectors (copper/aluminum foils), cell casings and welding-tabs.
- Cell assembly & quality: electrode coating, calendaring, roll-to-roll assembly, formation, aging and testing equipment.
- Intelligence & safety: battery management systems (BMS), temperature sensors, fuses and safety vents.
The market spans raw-materials refiners, specialty chemical firms, precision metal and polymer suppliers, industrial machinery manufacturers, and electronics/software firms that provide sensing and control.
Why the battery cell component market is important
Battery cells are the single most value-adding subassembly in electrified systems: energy density, cost per kWh, charging speed and safety all originate at the cell level. Improvements in cathode chemistry, anode microstructure, separator robustness and electrolyte additives directly translate to longer vehicle range, smaller stationary storage footprints, faster charging and lower total system cost. This makes cell-component suppliers strategic partners for automakers, appliance makers and grid operators. Moreover, because battery manufacturing is capital-intensive and tightly coupled to national industrial strategies, the battery component market is both an economic lever (jobs, exports) and a national-security priority (critical minerals, domestic production).
Battery Cell Component Market — Top Companies (Key profiles & 2024 snapshot)
Below are concise profiles of the global leaders. For transparency I include specialization, focus areas, and the best available 2024 revenue/market share snapshots from company releases and market research.
1. CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited)
- Specialization: Integrated battery cell manufacturer and vertically integrated supplier of cathodes, cell modules, packs, and energy storage systems.
- Key focus areas: High-energy automotive cells, LFP and high-nickel chemistries, cell-to-pack and cell-to-chassis innovations, battery swapping infrastructure and global gigafactory expansion.
- Notable features: Industry leader in scale and vertical integration; large R&D investments, strong OEM partnerships (Tesla, Volkswagen, Stellantis and many Chinese OEMs), and rapidly expanding overseas manufacturing footprint.
- 2024 revenue: Approximately ¥362 billion.
- 2024 market share: Roughly ~38% of global EV battery installations in 2024.
- Global presence: Headquartered in Ningde, China, with manufacturing and R&D sites across China, Germany, Hungary, and partnerships supplying automakers worldwide.
2. LG Energy Solution (LGES)
- Specialization: Automotive and ESS lithium-ion cell and module manufacturing with a large focus on pouch and prismatic formats.
- Key focus areas: Automotive battery cells (EV), stationary energy storage, safety and cathode/anode supply partnerships; localization of production in the U.S. and Europe.
- Notable features: Spin-out from LG Chem with deep chemical-materials expertise; strong ties to global OEMs and large investments in North American capacity to capture IRA benefits.
- 2024 revenue: About KRW 25.6 trillion in consolidated revenue.
- Market share / position: Top multinational competitor (generally ranked in the 2–4 range globally in shipped GWh in 2024).
- Global presence: Major plants in Korea, the U.S., Poland and China; customer base includes Hyundai-Kia, General Motors and other global automakers.
3. Panasonic Energy Co., Ltd.
- Specialization: Cylindrical lithium-ion cells (notably long-standing partnership with Tesla), industrial and consumer batteries, and energy storage solutions.
- Key focus areas: High-reliability cylindrical cells, scaling North American production (Nevada), diversification into energy storage for data centers and industrial use.
- Notable features: Deep manufacturing know-how for cylindrical cells, close OEM partnerships, and steady product evolution toward higher energy density and manufacturing efficiency.
- 2024 revenue: Around ¥873.2 billion (battery unit level).
- Market position: A leading Japanese supplier particularly strong in cylindrical cell formats with important North American facilities.
- Global presence: Japan, US (Nevada), planned expansions and supply operations globally to serve automakers and stationary storage customers.
4. Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
- Specialization: Automotive pouch/prismatic cells, energy storage systems and materials for electronic materials.
- Key focus areas: Automotive and ESS cells, advanced electrode materials, and expansion of production capacity outside South Korea.
- Notable features: Strong R&D, collaborations with global automakers and investments into ESS and specialty battery markets.
- 2024 revenue: Approximately KRW 16.59 trillion in total annual revenue.
- Market position: A major global supplier among non-Chinese leaders, with particular strength in mobility and ESS sectors.
- Global presence: Facilities and investments in South Korea, Europe and the United States; expanding U.S. footprint to serve local OEM demand.
5. BYD Company Limited (FinDreams Battery / BYD Auto ecosystem)
- Specialization: Vertically integrated EV maker and large battery producer (BYD’s battery arm supplies cells used inside the BYD vehicles and sells externally).
- Key focus areas: LFP and blade-cell formats optimized for cost, scale and safety; synergy between vehicle assembly and captive cell supply that improves cost control.
- Notable features: Massive vehicle production scale plus in-house cell manufacturing gives BYD an integrated cost advantage; BYD’s “blade” LFP innovation is a prominent example.
- 2024 revenue: About ¥777.1 billion in consolidated revenue.
- 2024 market share: Estimated ~15–17% of the global battery market.
- Global presence: Headquartered in Shenzhen with expanding exports and manufacturing footprints; BYD combines battery, vehicle and EV component manufacturing in a vertically integrated model.
Leading trends and their impact
- Cell format & chemistry diversification (LFP vs high-Ni NMC/NCA vs future solid-state): LFP regained favor in many mass-market EVs because of cost and safety advantages, while high-nickel chemistries continue to chase higher energy density for premium EVs and long-range applications.
- Vertical integration and captive supply: OEMs pushing for tighter control over battery supply (either via captive cell plants or long-term contracts) compress margins for independent suppliers, but create stable demand streams for dedicated partners.
- Localization driven by policy: Governments incentivizing domestic manufacture (U.S. IRA; India PLI; EU strategic support + regulation) are shifting where components are made, boosting demand for local material processing and high-precision component manufacturing in non-China regions.
- Recycling / circularity pressure: New rules (notably in the EU) and rising raw-material costs push for design-for-recycling and increased secondary supply of cathode metals, creating new business models for reclaimed materials and advanced recycling tech.
- Battery system intelligence & safety: More sophisticated BMS, cell-level monitoring and thermal management solutions are being embedded at the cell and pack level; suppliers of sensors and software become strategic technology vendors.
- Manufacturing automation & equipment upgrades: Better coating, drying, and formation systems are needed to hit narrower tolerances as energy density and cycle-life targets tighten, favoring advanced machinery vendors and digital-twin approaches.
Impact: Taken together these trends compress time-to-market for new chemistries, raise capital intensity for flexible factories, and increase the premium placed on suppliers that can deliver consistent quality, traceability and compliance with emerging regulations.
What are some successful examples of battery cell component market deployment around the world?
- CATL’s global scaling + blade battery commercialisation: CATL’s blade LFP design and rapid capacity expansion (including European investments) is a textbook example of combining chemistry innovation with scale and OEM partnerships to reshape cost dynamics in EVs and commercial fleets.
- BYD’s vertically integrated model: BYD’s combination of in-house cell production, vehicle assembly and modular design lowered unit costs and helped it scale vehicle shipments rapidly — proving vertical integration can outperform in capital-intensive categories.
- LGES and Samsung SDI localization in North America/Europe: These firms invested rapidly in western plants to secure OEM contracts and to access policy-driven incentives (IRA), demonstrating how policy can accelerate non-China manufacturing.
- Panasonic’s longevity in cylindrical cells + tie-ups with vehicle OEMs: Panasonic’s long-term collaboration with Tesla and steady product improvements illustrate the value of stable, quality-focused supply in premium segments.
Each example shows a different strategic route: chemistry-led scale (CATL), vertical integration (BYD), regionalization/localization (LGES, Samsung SDI), and OEM partnership depth (Panasonic).
Global regional analysis — Government initiatives and policies shaping the market
China — industrial champions + domestic demand
China remains the powerhouse for cell components and upstream refinement. While central purchase subsidies for NEVs were phased down at national level, Beijing’s broader industrial policy, local incentives and sizeable domestic market continue to favor large, vertically integrated players. China also extends tax breaks and targeted support in areas such as battery swapping and charging infrastructure. Chinese firms have benefited from long-term industrial subsidies and ecosystem clustering that reduced cost and accelerated scale.
United States — Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) & supply-chain reshaping
The IRA introduced manufacturing and production tax credits and incentives intended to accelerate domestic cell assembly and materials processing. That policy created a “Battery Belt” investment wave as firms sought to qualify for tax credits and local content bonuses; it has materially shifted investment pipelines but also introduced sensitivity to policy changes, with manufacturers monitoring legislative shifts closely.
European Union — sustainability regulation and defensive measures
The EU’s new Batteries Regulation (entered into force 2024) requires stricter sustainability, traceability and recycling obligations; at the same time the EU has looked at trade remedies and countervailing duties on subsidised imports to protect nascent local capacity. These twin pressures push suppliers to improve lifecycle reporting and recycling partnerships while accelerating investments in European gigafactories.
India — PLI and capacity building
India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells aims to kick-start local cell production with grant-style incentives and capacity tenders, attracting large industrial players and new entrants. The PLI objective is to establish giga-scale ACC capacity and reduce import dependence — an urgent strategic goal given India’s EV adoption targets. Recent tenders and allocations show active government management to meet capacity and localization goals.
Rest of Asia & ROW
Japan focuses on high-quality manufacturing and strategic partnerships (Panasonic is an example), South Korea supports its global champions through export assistance and R&D, while ASEAN and Latin American markets are targeting battery projects tied to local mineral processing and EV assembly. Policy heterogeneity creates both opportunities (incentives, partnerships) and complexity (different standards, local content rules).
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Consumer Healthcare Market Growth Factors, Key Players, and Global Presence by 2034