3D Printing Construction Market Size
3D Printing Construction Market Growth Factors
The global 3D printing construction market is experiencing rapid expansion driven by multiple converging factors. Growing housing shortages across the world, combined with labor shortages and rising construction costs, have created an urgent demand for faster and more cost-effective building methods. The technology enables significant reductions in construction time—from months to mere days—while minimizing material waste and improving sustainability. Additionally, innovations in robotics, software, and printable materials have enhanced precision, scalability, and design flexibility. Government initiatives promoting affordable housing and carbon neutrality further accelerate adoption. Together, these factors are propelling 3D printing from niche experimentation into a transformative force in global construction.
What Is the 3D Printing Construction Market?
The 3D printing construction market encompasses all technologies, equipment, materials, and services that enable buildings and infrastructure to be created layer by layer through additive manufacturing. This includes large-scale printers (gantry or robotic arm systems), specialized concrete or composite materials, software platforms that translate digital designs into printable instructions, and the construction and design services that bring these innovations to life. The approach eliminates traditional formwork, reduces waste, and allows for intricate geometries that are difficult or expensive to achieve through conventional methods. Applications range from single-family homes and social housing to bridges, schools, and industrial facilities.
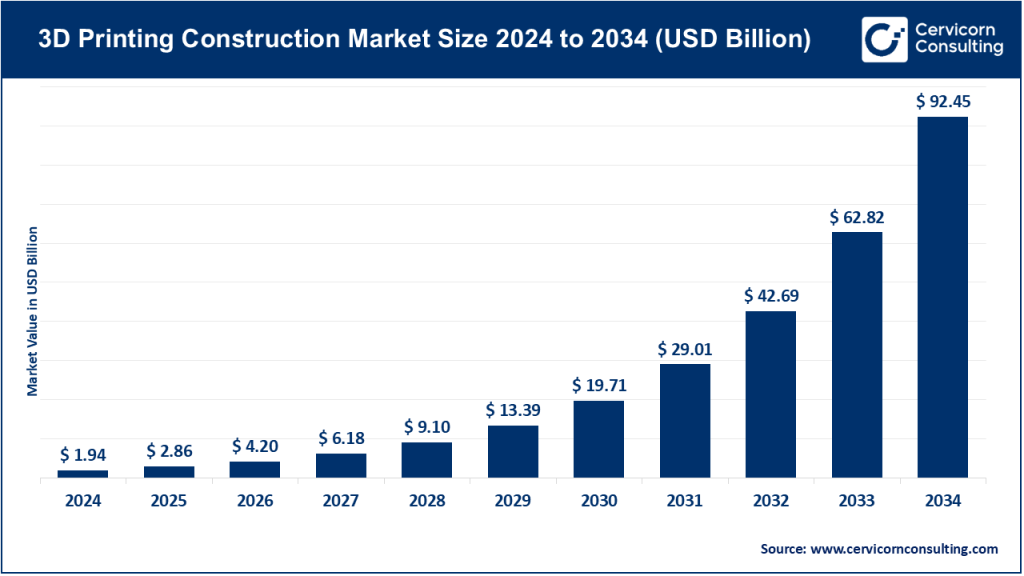
While the market is still emerging, it has already attracted significant investments from construction firms, governments, and venture capital. Analysts project exponential growth over the next decade as materials improve, standards are established, and regulatory frameworks catch up to the technology’s potential.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2792
Why 3D Printing Construction Is Important
The importance of 3D printing in construction lies in its ability to address some of the industry’s most pressing challenges. Conventional construction faces cost overruns, delays, and material inefficiencies. 3D printing offers solutions on all fronts:
- Speed: Automated printing drastically reduces build times, enabling rapid housing deployment after natural disasters or in rapidly urbanizing areas.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced labor and material waste lower overall project costs.
- Design Flexibility: Architects can create organic and complex shapes that would otherwise be prohibitively expensive.
- Sustainability: The process uses less material and supports environmentally friendly concrete alternatives.
- Resilience: Printed structures can be designed for durability and disaster resistance.
For governments and NGOs, 3D printing offers a promising tool for addressing housing shortages and sustainability goals. For developers, it represents a competitive advantage through innovation and cost savings.
Top Companies in the 3D Printing Construction Market
Below is an overview of five leading companies shaping the 3D printing construction market—ICON, Apis Cor, COBOD International, Mighty Buildings, and CyBe Construction—covering their specialization, focus areas, notable features, estimated 2024 revenue position, and global presence.
ICON
Specialization:
ICON is recognized as a global leader in large-format, on-site concrete 3D printing. Its proprietary Vulcan printers and advanced cementitious materials enable rapid, durable, and architecturally flexible construction.
Key Focus Areas:
Affordable housing, disaster-resilient construction, large-scale residential developments, and experimental projects such as extraterrestrial habitats in collaboration with NASA.
Notable Features:
ICON’s printers use its proprietary “Lavacrete” material and are capable of producing complex curvilinear designs. The company partners with developers, governments, and designers to deliver fully integrated solutions.
2024 Revenue & Market Share:
While exact figures are private, ICON is widely reported as the market’s most capitalized player, backed by strong funding and large-scale U.S. housing projects.
Global Presence:
Headquartered in Austin, Texas, with growing projects in the U.S. and international collaborations, ICON is considered a benchmark for large-scale additive construction.
Apis Cor
Specialization:
Apis Cor specializes in mobile, on-site construction printing solutions that allow entire houses to be printed directly at the build location.
Key Focus Areas:
Affordable housing, modular printed homes, and mobile printer technology for remote and disaster-affected regions.
Notable Features:
Apis Cor gained global recognition by printing a full house within 24 hours in Russia, demonstrating the feasibility and speed of the technology.
2024 Revenue & Market Share:
As a privately held firm, revenue figures are undisclosed, but Apis Cor is a well-known pioneer in mobile 3D printing systems and holds a strong reputation in early-stage commercialization.
Global Presence:
Originating in Russia and now based in the U.S., Apis Cor operates globally with projects and partnerships across North America, the Middle East, and Europe.
COBOD International
Specialization:
COBOD International develops and supplies modular gantry-style construction printers (the BOD series) used by contractors and partners worldwide.
Key Focus Areas:
Hardware manufacturing, training, and turnkey solutions for commercial printing operations.
Notable Features:
COBOD’s BOD2 printer is one of the most widely adopted in the industry, capable of producing multi-story structures. The company’s modular design allows flexibility and scalability for diverse construction needs.
2024 Revenue & Market Share:
COBOD reported strong growth and profitability in 2024 within its segment, establishing itself as a market leader among printer manufacturers.
Global Presence:
Headquartered in Denmark with operations across Europe, North America, the Middle East, and Asia, COBOD partners with construction firms globally to implement large-scale printing projects.
Mighty Buildings
Specialization:
Mighty Buildings focuses on off-site, factory-based 3D printing of modular housing units using advanced polymer composite materials.
Key Focus Areas:
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), single-family modular homes, and sustainable neighborhood developments.
Notable Features:
Unlike most concrete-based systems, Mighty Buildings uses lightweight composite materials that allow faster assembly and excellent finish quality. Its factory-controlled environment ensures precision and compliance with building codes.
2024 Revenue & Market Share:
Although private, Mighty Buildings has achieved multimillion-dollar revenues and continues to expand manufacturing capacity in the U.S. Its modular business model positions it as a high-growth company within the prefabricated housing segment.
Global Presence:
Headquartered in California with expansion into international markets through joint ventures, the company targets eco-friendly and high-speed housing production.
CyBe Construction
Specialization:
CyBe Construction is a Dutch company offering a comprehensive ecosystem of 3D printing solutions, including hardware, materials, and on-site construction services.
Key Focus Areas:
Social housing, commercial projects, and sustainability-driven innovations in printable concrete mixtures.
Notable Features:
CyBe integrates printers, materials, and engineering expertise into turnkey solutions. Its commitment to sustainable materials and local partnerships has made it a leading name in European additive construction.
2024 Revenue & Market Share:
CyBe is privately held, with revenues derived primarily from project contracts, printer sales, and training services. It remains one of Europe’s most visible players in commercial 3D-printed construction.
Global Presence:
Headquartered in the Netherlands, CyBe operates globally, with projects across Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
Leading Trends and Their Market Impact
1. Shift Toward Industrialized and Modular Construction
Factories that print entire building modules are improving quality control, speed, and scalability. Off-site manufacturing (as used by Mighty Buildings) reduces weather-related delays and integrates easily with conventional supply chains. This trend makes 3D-printed homes more commercially viable for suburban and urban developments.
2. On-Site Large-Format Printing
Companies like ICON, COBOD, and Apis Cor have popularized large robotic printers capable of fabricating entire homes directly on site. This allows quick construction in remote or disaster-hit areas, reducing transport costs and enabling immediate local deployment.
3. Material Innovation and Sustainability
Advances in printable concrete, geopolymer blends, and recycled materials are reducing the carbon footprint of printed buildings. These sustainable materials also enhance structural strength, durability, and insulation, aligning the industry with global green-building goals.
4. Automation and Software Integration
The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM), AI-driven print optimization, and real-time monitoring systems ensures precision and consistency. Automated quality control reduces errors, making the technology more reliable for large-scale adoption.
5. Regulatory Acceptance and Standards Development
Governments and research institutions are developing standards to certify 3D-printed structures. These include guidelines for structural integrity, fire safety, and material testing. As codes evolve, insurance and financing barriers are gradually lifting.
6. Expansion from Prototypes to Communities
The market is moving from single demonstration houses to entire printed neighborhoods. ICON’s Wolf Ranch community in Texas and other multi-home projects worldwide demonstrate scalability, cost efficiency, and livable quality—key factors for mainstream adoption.
Successful Global Examples of 3D-Printed Construction
- ICON’s Wolf Ranch (Texas, USA): One of the largest 3D-printed housing developments in the world, showcasing speed, durability, and architectural variety.
- El Cosmico Hotel (Marfa, USA): ICON and BIG (Bjarke Ingels Group) collaborated to produce striking curved hotel units, merging design excellence with technological innovation.
- Apis Cor’s 24-Hour House (Russia): A landmark demonstration that proved an entire single-story home could be printed on-site within one day.
- Tecla House (Italy): A fully 3D-printed clay home developed by WASP, focusing on sustainability and use of local materials.
- Milestone Project (Netherlands): A series of printed homes created through collaboration between the Eindhoven University of Technology and industry partners, addressing affordable housing needs.
- WinSun’s Multi-Story Buildings (China): One of the earliest large-scale experiments, printing entire apartment blocks to demonstrate industrial scalability.
These projects highlight the global diversity of 3D-printed construction, from luxury designs to social housing and sustainable living.
Global and Regional Analysis: Government Initiatives and Policies
North America
In the United States, 3D printing construction has gained significant traction due to strong venture capital funding and a supportive innovation environment. Federal and state agencies view additive construction as a potential solution for affordable housing and disaster recovery. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) has sponsored research and pilot programs to understand code requirements and encourage adoption. Municipalities in Texas, California, and Alaska have been early testing grounds for printed homes.
Europe
Europe has emerged as a hub for research and sustainable construction innovation. The Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark are leaders in developing printed housing for social and municipal projects. European governments provide funding and land for demonstration projects, particularly those focused on low-carbon materials and energy efficiency. The EU’s emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles aligns perfectly with additive construction’s waste-reduction benefits.
Asia-Pacific
China remains a pioneer with early large-scale experiments and continuing innovation in multi-story printed structures. Other countries like India and Australia are piloting 3D-printed homes as a solution for affordable and emergency housing. Government-backed innovation programs and public-private partnerships are key drivers of adoption in this region. The rapid pace of urbanization provides a fertile market for automated construction methods.
Middle East and Africa
In the Middle East, countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in futuristic urban development and sustainable infrastructure. Dubai’s government, for example, has promoted the use of 3D printing in public buildings, aiming for a significant percentage of new construction to be printed by the 2030s. In Africa, partnerships between European printer manufacturers and local construction firms are creating opportunities to address housing shortages with cost-effective printed solutions.
Policy and Regulatory Environment
Across regions, several policy themes are shaping the market:
- Building Codes and Standards: Regulators are working to integrate 3D printing into existing construction codes, focusing on safety, strength, and long-term performance.
- Funding and Incentives: Governments provide grants and subsidies for pilot projects to accelerate proof-of-concept developments.
- Public Procurement: Some municipal governments are including 3D-printed projects in their infrastructure plans.
- Sustainability Mandates: As nations target net-zero emissions, 3D printing’s efficiency and reduced waste make it an attractive alternative.
These policies are critical for transforming the industry from experimental to mainstream.
Final Insights
The 3D printing construction market stands at a pivotal moment where technological innovation meets urgent global demand for sustainable and affordable housing. Although the market is still relatively young, its trajectory mirrors other disruptive technologies—rapid experimentation, fast iteration, and increasing institutional support. The combination of government initiatives, technological progress, and corporate investment ensures that 3D-printed construction will play an expanding role in how the world builds in the coming decades.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us
Read Report: Quantum Computing in Healthcare Market Growth Drivers, Trends, Key Players and Regional Insights by 2034